|
|
|
| Geochemical exploration and resource potential evaluation of biogenic gas in Dongting Lake Basin |
Chun-Yan SUN1( ), Hao ZHAO1,2( ), Hao ZHAO1,2( ), Hui-Ce HE1,3, Jian-Hua LI4, Ming-Guo XIAO5, Shi-Qiang ZHANG1, Dong-Lin WANG1, Yao TANG1 ), Hui-Ce HE1,3, Jian-Hua LI4, Ming-Guo XIAO5, Shi-Qiang ZHANG1, Dong-Lin WANG1, Yao TANG1 |
1.School of Engineering and Technology,China University of Geosciences(Beijing),Beijing 100083, China
2.No.4 Gold Geological Party of CAPF,Liaoyang 111000,China
3.Guangzhou Marine Geological Survey,Guangzhou 510075,China
4.Hunan Geo-sun High Technology Limited Company,Changsha 410208,China
5.HunanHuasheng Energy Resource and Investment Development Co. Ltd.,Changsha 410004,China |
|
|
|
|
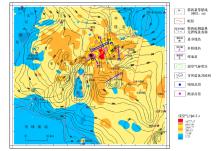
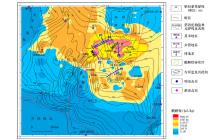
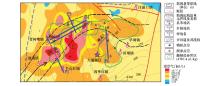
Abstract Dongting Lake Basin has the conditions for forming biogenic gas reservoirs of certain scales. For the exploration of biogenic gas resources, the authors carried out a comprehensive exploration work mainly based on geochemical methods during the period of 2013~2016, and conducted fairly systematic surface sediments survey. Geochemical exploration covered an area of 2060 km2, and collected 1498 samples. All the samples were tested by in situ headspace gas (free hydrocarbon), indoor acidolysis hydrocarbon and a small quantity of methane isotope indexes. The results are as follows: 1. The geochemical anomaly of methane in the Dongting Lake basin is composed of free hydrocarbon (headspace gas) and adsorbed hydrocarbon (acid hydrolysis hydrocarbon). The free hydrocarbon is a dynamic reflection of the existing underground biogenic gas, and the hydrocarbon accumulation of the acidolysis hydrocarbon is related to the distribution of the paleo-channel. 2. The Dongting Lake basin is the area of a high background and high anomaly of methane, and the distribution of the abnormal area is basically consistent with the distribution of the Quaternary fault basin, especially in Yuanjiang sag. 3. Acidolysis hydrocarbon anomaly of the Heba Town, bead-like anomaly in NE direction and southeastern secondary local anomalies form a ring anomaly zone surrounding the Yuanjiang sag, which means that the sag may be the potential supply area of biogenic gas in Dongting Lake basin. 4. The area of Qingshuzuie-Heba Town north of Yuanjiang sag is the abnormal high value area of the hydrocarbon methane in Dongting Lake Basin, and this is the direct reflection of natural gas seepage in shallow surface. The high value of acidolysis hydrocarbon methane surrounds the anomaly area of free hydrocarbon methane in Qingshuzui, which constitutes the best combinational hydrocarbon reservoir model. The area of Qingshui-Haba Town is the 'chimney' of the biogenic gas underlying the Dongting Lake Basin and hence the most hopeful breakthrough area for biogas survey in the Dongting Lake Basin.
|
|
Received: 08 May 2017
Published: 20 February 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 特征 | 生物气类型 | | 细菌成因气与菌解气 | 低成熟气 | | 重烃含量 | <0.5%,典型干气 | | | 干燥系数(C1/C1-C5) | ≥99% | 70%~99% | | 湿度系数(K=C1/(C2+C3)) | ≥1 000 | 100~1 000 | | 甲烷碳同位素δ13Cl | <-55‰ | -60‰~-46‰(腐殖型)
-55‰~-48‰(腐泥型) | | 甲烷氢同位素δD | -250‰~-175‰
陆相环境δD<-190‰
海相环境δD>- 190 ‰ | -271‰~-215‰ | | 有机质成熟度Ro | <0.3% | 0.3%~0.6% |
|
|
|

| 位置 | 气藏时代 | 深度/m | δ13Cl/‰PDB | 储量/1012 m3 | | 美国 | 阿拉斯加库克湾 | 古近纪、新近纪 | 910~1 650 | -63~-56 | 0.21 | | 墨西哥湾 | 更新世 | 460~2 800 | -69~-55 | 0.34 | | 落基山盆地群 | 白垩纪—古近纪、新近纪 | 120~840 | -72~-55 | | | 伊利诺伊 | 更新世 | 40 | -84~-72 | | | 日本 | 新潟 | 古近纪、新近纪 | 100~1 000 | -75~-65 | 0.13 | | 意大利 | 波河、前亚平宁 | 古近纪、新近纪 | 400~1 830 | -71~-55 | | | 德国 | | 古近纪、新近纪 | 900~1 800 | -72~-64 | | | 加拿大 | 南阿尔伯塔 | 白垩纪 | 300~1 000 | -68~-60 | 5.6 | | 前苏联 | 北威海 | 古近纪、新近纪 | 320~350 | -72~-64 | | | 西伯利亚 | 白垩纪 | 700~1 300 | -68~-58 | | | 斯特拉瓦波尔 | 白垩纪—古近纪、新近纪 | 200~1 200 | -75~-37 | | | 北普里阿拉尔 | 古近纪、新近纪 | 300~500 | -72~-63 | | | 特立尼达 | | 古近纪、新近纪 | 890~3 350 | -71~-64 | | | 波兰 | 喀尔巴阡 | 白垩纪—古近纪、新近纪 | | | |
|
|
|

|
|
|

| 时期 | 洞庭盆地 | 安乡凹陷 | 沅江凹陷 | 安乡县城
顶空气安乡异常带
酸解烃安乡异常带
酸解烃三仙湖异常带 | 酉港镇以西 | 南县县城
顶空气青树嘴
异常带,酸解烃
河坝镇异常带 | 草尾镇—杨罗洲—
南大膳,顶空气
草尾镇—茶盘洲—
四季红异常带 | 茈湖口—白马寺 | | 地球化学异常显示分布 | 酸解烃强
顶空气强 | 无 | 酸解烃强
顶空气强 | 顶空气强
酸解烃弱 | 无 | | 沉积期 | Q2早期
(洞庭湖组) | 断陷至第四纪最大
规模,整体接收沉积 | 50~80 m | 50~100 m | 70~80 m | 40~100 m | 70~80 m | Q1晚期
(汨罗组) | 盆地统一断陷,局部
沉降强度不同 | 20~60 m | 20~80 m,
北厚南薄 | 20~60 m,
西厚南薄 | 20~100 m,
西薄东厚 | 20~60 m,
南薄北厚 | Q1早期
(华田组) | 盆地局部发生断陷,
沉积范围扩大 | 50~140 m | 10~50 m,
中间薄边缘厚 | 50~140 m | 30~60 m
厚度较均匀 | 10~50 m | | E3—N | 隆起剥蚀,沉积间断 | | 沉积期 | E2
(新河口组) | 持续接受沉积,
沉积中心转移
至沅江凹陷 | 沉积 | 沉积 | 沉积 | 阳罗-河心洲以东
最厚400 m | 没有沉积 | | E2
(汉寿组) | 沉积 | 沉积 | 沉积 | 冯家湾一带
厚达1 000 m | 南塘-马劲山达
1 000 m | E2
(沅江组) | 沉积 | 沉积 | 沉积 | 黄土包-河心洲-冯家湾
湘深17井厚474 m | 南塘一带,湘深
27井535.5 m | E1
(桃源组) | 沉积 | 沉积 | 沉积 | 湘深30井445 m
5井390 m | 湘深27井153 m,
32井311.5 m | | K2 | 整体断陷,接受沉积,
沉积中心位于
安乡凹陷 | 沉积中心,沉积厚度最大 | 沉积 | 沉积 | 沉积 | | 钻井资料 | | ZK148(Q1-Q2)
ZK149(Q1缺失
华田组) | ZK138 | ZK151、ZK153、ZK155、
ZK157Z、K158、ZK160、
ZK161、ZK165(Q1-Q2) | |
|
|
|
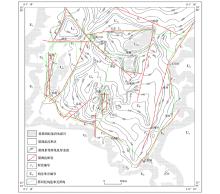
|
|
|
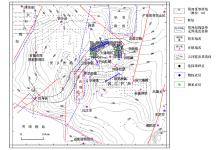
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
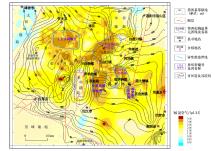
|
|
|

|
|
|
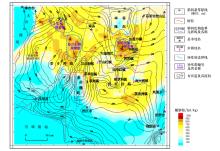
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| [1] |
湖南省地质矿产局.湖南省区域地质志[M].北京:地质出版社,1988.
|
| [2] |
周国祺,成铁生,赵守勤.洞庭湖盆的由来和演变[J].湖南地质,1984,3(1):54-65.
|
| [3] |
柏道远,李长安.洞庭盆地第四纪地质研究现状[J].地质科技情报,2010,29(5):1-8.
|
| [4] |
黄泽新,罗小平.洞庭盆地第四系生物气地质特征及远景分析[J].石油天然气地质,1996,17(1):62-67.
|
| [5] |
Martini A M,Walter L M,Budai J M,et al. Genetic and temporal relations between formation waters and biogenicmethane: upper devonian antrim shale,michigan basin,USA[J].Geochimica Et CosmochimicaActa,1998,62(10): 1699-1720.
|
| [6] |
关德师,戚厚发,钱贻伯,等.生物气的生成演化模式[J].石油学报,1997,18(3):31-36.
|
| [7] |
郑华平. 洞庭盆地沅江凹陷的发育特征和含油气性研究[D].成都:西南石油大学,2006.
|
| [8] |
Rice D D,Claypool G E. Generation,accumulation,and resource potential of biogenic gas [J]. AAPG Bulletin,1981,65(1):5-25.
|
| [9] |
Shurr G W,Ridgley J L.Unconventional shallow biogenic gas systems[J]. AAPG Bulletin,2002,86(11): 1939-1969.
|
| [10] |
贾承造,赵文智,魏国齐,等.国外天然气勘探与研究最新进展及发展趋势[J].天然气工业,2002,22(4):5-9.
|
| [11] |
Robinson E,Pack M R,Farwell S O,et al. Biogenic sulfur gas emissions from soils in eastern and southeastern United States[J].Journal of the Air & Waste Management Association,1981,31(10):1083-1089.
|
| [12] |
Schulz H M,Biermann S,et al. From shale oil to biogenic shale gas: Retracing organic-inorganic interactions in the Alum Shale (Furongian-Lower Ordovician) in southern Sweden[J].AAPG Bulletin,2015,99(5):927-956.
|
| [13] |
Quillinan S A,Frost C D.Carbon isotope characterization of powder river basin coal bed waters: Key to minimizing unnecessary water production and implications for exploration and production of biogenic gas[J].International Journal of Coal Geology,2014,126:106-119.
|
| [14] |
张祥,纪宗兰,杨银山,等.关于生物气源岩评价标准的讨论——以柴达木盆地第四系生物气为例[J].天然气地球科学,2004,15(5):465-470.
|
| [15] |
戚厚发,关德师,钱贻伯,等.中国生物气成藏条件[M].北京:石油工业出版社,1997.
|
| [16] |
Rice D D.Generation. Accumlation and resource petential of biogenic gas[J].AAPG Bull,1981,65(1):5-25.
|
| [17] |
陈安定,刘桂霞,莲莉文,等.生物甲烷形成实验与生物气聚集的有利地质条件探讨[J].石油学报,1991,12(3):7-16.
|
| [18] |
关德师.控制生物气富集成藏的基本地质因素[J].天然气工业,1997,17(5):8-12.
|
| [19] |
何家雄,卢振权,苏丕波,等.南海北部天然气水合物气源系统与成藏模式[J].西南石油大学学报:自然科学版,2016,38(6):8-24.
|
| [20] |
何家雄,张伟,卢振权,等.南海北部大陆边缘主要盆地含油气系统及油气有利勘探方向[J].天然气地球科学,2016(6):943-959.
|
| [21] |
张伟,何家雄,卢振权,等.琼东南盆地疑似泥底辟与天然气水合物成矿成藏关系初探[J].天然气地球科学,2015(11):2185-2197.
|
| [22] |
林春明,李艳丽,漆滨汶.生物气研究现状与勘探前景[J].古地理学报,2006,8(3):317-330.
|
| [23] |
谢秋元.我国生物气资源的开发前景[J].中国地质,1991,(1):23-25.
|
| [24] |
王民,卢双舫,胡慧婷,等.有机质生成生物气的生化动力学模型及其应用[J].石油学报,2008,29(1):75-78.
|
| [25] |
王民. 生物气生成量、生成期评价方法探讨及其在松辽盆地的应用[D]. 大庆:东北石油大学,2007.
|
| [26] |
Zhang S C,Shuai Y H,Chen Z H.Geochemistry and distribution of biogenic gas in China[J].Bulletin of Canadian Petroleum Geology,2015,63(1):53-65.
|
| [27] |
Cokar M,Ford B,Kallos M S,et al. New gas material balance to quantify biogenic gas generation rates from shallow organic-matter-rich shales[J].FUEL,2013,104:443-451.
|
| [28] |
陈渡平,李长安,柏道远,等.洞庭盆地第四纪地层格架初拟[J].地质科技情报,2014,33(1):67-73.
|
| [29] |
陈立德,邵长生.江汉—洞庭盆地下更新统地层划分与对比:"白沙井砾石层"再研究[J].地层学杂志,2014,38(2):208-219.
|
| [30] |
戴传瑞,张廷山,郑华平,等.沅江凹陷古近纪层序地层、沉积相特征及演化[J].天然气工业,2006,26(11):40-43.
|
| [31] |
赵举兴,李长安,张玉芬,等.洞庭盆地S3-7孔第四纪年代地层[J].地球科学,2016,41(4):633-643.
|
| [32] |
柏道远,王先辉,李长安,等.洞庭盆地第四纪构造演化特征[J].地质论评,2011,57(2):261-276.
|
| [33] |
柏道远,李长安,王先辉,等.第四纪洞庭盆地构造性质及动力机制探讨[J].大地构造及成矿学,2010,34(3):317-330.
|
| [34] |
柏道远,吴能杰,李长安,等.华容隆起及周缘第四纪构造-沉积特征与演化[J].中国地质,2010,37(7):1243-1256.
|
| [35] |
姚秋昌,楼基胜.洞庭盆地沅江凹陷油气成藏条件分析[J].天然气工业,2008,28(9):37-40.
|
| [36] |
朱伟, 曹子剑, 王红云,等.洞庭盆地浅层生物气成藏条件及潜力圈闭评价[J].特种油气藏,2014,21(4):17-21.
|
| [37] |
汤玉平,丁相玉,吴向华,等.中国主要含油气盆地区域地球化学场参数特征及其成因研究[J].石油勘探与开发,2001,28(3):1-4.
|
| [1] |
YANG Zhi-Bin, ZHANG Fu-Gui, WANG Hui-Yan. Characteristics and indicative significance of hydrocarbon composition in shallow soil of polar permafrost region[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(6): 1190-1194. |
| [2] |
SUN Chun-Yan, SONG Teng, HE Hui-Ce, ZHANG Zhi-Bing, LI Pan-Feng, ZHAO Hao, LI Ji-Peng. The intelligent-control geochemical sample pretreatment system and its application to marine gas hydrate exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 39(5): 954-961. |
|
|
|
|

