|
|
|
| The high-precision magnetic anomaly characteristics and prospecting forecast in Xunhua region of Qinghai |
Mei-Ding WANG1, Jian-Qing MA2( ) ) |
1. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration Corporation, Bureau of Geological Exploration for Nonferrous Metals in Northwest China, Xi'an 710068,China
2. School of Geological Engineering and Surveying, Chang'an University, Xi'an 710054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Xunhua region of Qinghai is located in the joints of the Qilian orogenic belt and the west Qinling orogenic belt. In order to reveal the structural feature, and determine the key metallogenic prospect areas, the 150 000 high precision magnetic survey was carried out in the selected area. The azimuth of survey lines is north east to 30°, 391 pieces rock (mineral) magnetic specimens were cellected. through the analysis of the magnetic parameters, characteristics analysis and interpretation of magnetic anomaly, the ZongWuLong-tianshui thrust fault F1 towards NW50°. The key metallogenic prospect areas are mainly distributed in the northeast of the surveyed area, by caledonian period intrusive mass of JiShiShan ultrabasic diorite and LeiJiShan basite granite, and have high mineral content. This work shows that the high-precision magnetic survey is one of the important basic methods in regional geological survey and mineral survey, provides geophysical basis for the next step of mineral survey in the investigated area.
|
|
Received: 12 May 2017
Published: 04 June 2018
|
|
|
|
|
|
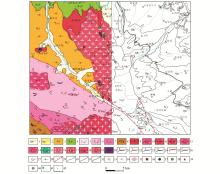
|
|
|

| 岩矿石名称 | 测定块数 | κ/(4π×10-5SI) | Mr/(10-3A/m) | | 变化范围 | 平均值 | 变化范围 | 平均值 | | 变粒岩 | 9 | 48.85~2655.12 | 987.94 | 5.94~473.15 | 138.13 | | 变玄武岩 | 7 | 79.58~1440.55 | 576.49 | 17.18~149.72 | 56.4 | | 变英安岩 | 5 | 105.78~525.08 | 228.04 | 23.58~289.51 | 89.81 | | 玢岩 | 2 | 17.07~109.92 | 63.5 | 35.44~44.32 | 39.88 | | 大理岩 | 2 | 34.86~49.82 | 42.34 | 9.14~40.08 | 24.61 | | 二长花岗岩 | 12 | 21.14~320.11 | 90.69 | 21.07~330.89 | 56.7 | | 粉砂质板岩 | 12 | 22.64~212.18 | 97.45 | 9.03~91.54 | 37.09 | | 灰岩 | 18 | 29.04~230.75 | 81.26 | 7.77~201.87 | 40.89 | | 花岗闪长岩 | 48 | 7.59~1230.3 | 187.73 | 2.99~505.93 | 88.66 | | 辉绿岩 | 7 | 92.55~7450.87 | 1863.41 | 48.26~540.67 | 160.85 | | 辉石岩 | 13 | 22.54~7028.25 | 1597.27 | 7.22~1110.1 | 285.27 | | 辉长闪长岩 | 14 | 72.6~5184.95 | 1721.69 | 12.22~7905.13 | 1528.57 | | 辉长岩 | 17 | 41.0~3506.9 | 856.95 | 16.12~4183.18 | 387.94 | | 钾长花岗岩 | 10 | 19.94~178.21 | 81.27 | 5.87~89.88 | 28.05 | | 砾岩 | 4 | 27.38~44.7 | 51.3 | 9.04~18.29 | 14.11 | | 砂岩 | 91 | 10.12~4417.4 | 136.17 | 1.68~265.9 | 33.64 | | 闪长岩 | 51 | 6.34~3214.76 | 684.03 | 10.07~7965.5 | 346.34 | | 石英砂岩 | 8 | 21.38~166.9 | 55.79 | 10.39~325.45 | 58.47 | | 石英闪长岩 | 12 | 77.53~1839.16 | 487.16 | 35.5~663.64 | 235.46 | | 似斑状二长花岗岩 | 8 | 27.37~99.76 | 58.24 | 9.24~20.9 | 17 | | 斜长角闪岩 | 36 | 20.37~1531.5 | 199.62 | 7~1871.96 | 92.4 | | 长石石英砂岩 | 3 | 36.33~101.03 | 61.75 | 8.3~35.62 | 21.06 |
|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|
|
|
| [1] |
裴先治, 丁仨平, 李佐臣 , 等. 西秦岭北缘早古生代天水—武山构造带及其构造演化[J]. 地质学报, 2009,83(11):1547-1564.
|
| [2] |
徐学义, 李婷, 陈隽璐 , 等. 西秦岭西段花岗岩浆作用与成矿[J]. 西北地质, 2012,45(4):76-83.

|
| [3] |
邓中林, 侯元才, 古凤宝 . 青海东北部第三纪西宁—贵德—化隆盆地充填特征、孢粉组合方式与古气候演变[J]. 青海地质, 2000,9(1):43-53.

|
| [4] |
谷祖纲, 白生海, 张显庭 , 等. 青海省贵德、化隆两盆地新第三系的划分与对比[J]. 地层学杂志, 1992,16(2):96-104.

|
| [5] |
刘梦儒 . 西宁—民和盆地上第三系层序及所含化石[J]. 青海地质, 1992,1(2):1-18.
|
| [6] |
刘少峰, 张国伟 . 循化—贵德地区新生代盆地发育及其对高原增生的指示[J]. 中国科学:D辑, 2007,37(1):235-248.
|
| [7] |
骆满生, 吕欣蕾, 张克信 , 等. 青海循化盆地中新世中期—上新世早期介形类组合及其地质意义[J]. 微体古生物学报, 2010,27(2):125-134.

|
| [8] |
陈靖, 王万银, 李增涛 , 等. 高精度磁测技术在甘肃西成铅锌矿勘探中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2014,50(5):976-983.

|
| [9] |
屈栓柱, 胡华伟, 潘德仁 . 高精度磁测在尼勒克县穹库尔铁矿中的应用分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2016,40(5):910-915.
|
| [10] |
赖月荣, 韩磊, 杨树生 . 高精度磁测在阿勒泰冰碛物覆盖区地质填图中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2014,38(6):1181-1185.
|
| [11] |
柳建新, 郭振威, 童孝忠 , 等. 地面高精度磁法在新疆哈密地区磁铁矿勘查中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011,47(3):432-438.
|
| [12] |
齐文秀 . 地面高精度磁测在金矿勘查中的应用效果[J]. 中南工业大学学报, 1995,26(2):153-156.
|
| [13] |
王建新, 夏训银, 王身龙 , 等. 高精度磁测在山西孤山隐伏铁矿勘查中的应用[J]. 矿产与地质, 2014,28(3):361-364.

|
| [14] |
武斌, 曹俊兴, 唐玉强 , 等. 红格地区钒钛磁铁矿地质特征及地球物理找矿的探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012,48(1):140-147.
|
| [15] |
许东青, 白大明, 李荣光 . 大比例尺高精度磁测在卡休他他铁(金、钴)矿生产中的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2006,42(3):76-80.

|
| [16] |
朱朝吉, 周肇武, 刘天佑 , 等. 高精度磁测找矿效果:以青海尕林格矿区为例[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011,47(2):277-283.

|
| [17] |
许生武 . 青海循化地区区域地质特征及成矿地质背景研究[D]. 西安:长安大学, 2015.
|
| [18] |
张雪亭, 杨生德 . 青海省板块构造研究1∶100万青海省大地构造图说明书[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [19] |
张楗钰, 张克信, 季军良 , 等. 青藏高原东北缘循化盆地渐新世—上新世沉积相分析与沉积演化[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010,35(5):774-788.
|
| [20] |
张远泽, 王国灿, 王岸 , 等. 循化—化隆盆地晚白垩世以来盆山耦合过程:来自物源与磷灰石裂变径迹年代学分析的证据[J]. 地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2013,38(4):725-744.

|
| [1] |
YOU Jun, ZHANG Xiao-Ming, LOU Qian-Zhou, SHI Zhao-Yang, YANG Yun-Jun, CHEN Jian-Xiang, YUAN Pan. The inferential basis and significance of the deep fault to the west of the Baiquesi complex in Lueyan[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3): 645-652. |
| [2] |
YANG Yu-Qin, ZHANG Xiang, SHI Lian-Cheng, DENG De-Wei. A study of the method of extracting aeromagnetic weak anomalies from sandstone-type uranium deposits[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(1): 29-36. |
|
|
|
|

