|
|
|
| Geochemical anomaly characteristics of Cuonadong Dome,southern Tibet |
Jian-Cuo Luo-Sang1, Cheng-Shi QING2, Guang-Ming LI2( ), Lin-Kui ZHANG2, Sui-Liang DONG2, Jian-Gang FU2, Hua-Wen CAO2, Wen-Xing FAN1 ), Lin-Kui ZHANG2, Sui-Liang DONG2, Jian-Gang FU2, Hua-Wen CAO2, Wen-Xing FAN1 |
1. School of Earth Sciences,Chengdu University of Technology,Chengdu 610059,China
2. Chengdu Center of China Geological Survey,Chengdu 610081,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Cuonadong Dome is located in the eastern part of the Tethyan Himalaya, within which a Be-W-Sn deposit, accompanied by a variety of rare elements, has been found. On the basis of field investigation and whole-rock geochemical characteristics, the authors discuss the elemental enrichment rules of Au, Ag, Cu, Pb, Zn, W, Sn, Li, Be, As, Sb and U in the dome, by means of geochemical clustering analysis, factor analysis and other methods, combined with the structural characteristics of the dome. Analytical results show that the dome system itself provides sufficient material sources for the enrichment of Sn, As, Be, Li, Pb and W. The dome controls the enrichment of various elements differently. The core mainly controls W, Sn ,Be and Pb. The slip system mainly controls W, Sn and Be. The capping layer mainly controls Pb, Cu, Zn, Ag and Pb elements, and the dome presents the distribution rule of high temperature (W-Sn-Se) -medium temperature (Cu-Pb-Zn) -medium low temperature (Sb-Ag) from the inner part outwards on the whole. The W-Sn-Be elements are highly enriched and large in scale, and are found to be related to pale granite and pegmatite, skarn marble as well as failure of the decollement tectonic-shear caprock.
|
|
Received: 28 December 2018
Published: 03 March 2020
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
Guang-Ming LI
E-mail: 13982257109@163.com
|
|
|
|
20]
">
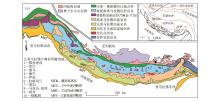
|
Sketch geological map of the Lhasa terrane(a) and regional geological map of Himalayan orogenic belt(b)[20]
|
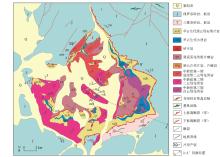
|
Geological map of the Cuonadong dome and comprehensive profile position
|
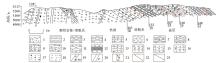
|
The measured geological profile A-A' of Cuonadong dome
1—Quaternary alluvial diluvial;2—thin siltstone intercalates fine sandstone; 3—andalusite-slate intercalated with carbonaceous slate;4—fine sandy slate argillaceous slate;5—cordierite phyllite; 6—garnet cordierite schist;7—silty slate intercalated with garnet mica schist;8—staurolite garnet mica schist intercalated with fine sandy slate;9—staurolite garnet dicmica schist;10—mica quartz schist;11—kyanite schist;12—bands of marble intercalate skarn;13—augen granitic gneiss;14—garnet muscovite directional granite;15—allochroite dimicaceous granite;16—banded granite;17—tourmalinite dimicaceous granite;18—dimicaceous granite;19—beryl pegmatite vein;20—pegmatite vein;21—fault fracture zone;22—upper detachment fault;23—underneath detachment fault
|

|
The measured geological profile B-B' of Cuonadong dome
1—garnet dicmica granite; 2—garnet muscovite granite; 3—augen granitic gneiss; 4—tourmaline, garnet muscovite granite; 5—kyanite,garnet mica schist; 6—garnet mica schist; 7—marble; 8—contains tourmaline, staurolite, garnet, mica schist; 9—skarn; 10—foliated marble; 11—metamorphic quartz fine sandstone; 12—grenatite,garnet two mica schists; 13—metamorphic fine sandstone; 14—crushed zone; 15—pegmatite vein; 16—upper detachment fault;17—underneath detachment fault
|

| 剖面编号 | 比例尺 | 长度/km | 测制方向/(°) | 采集样品数 | | A-A' | 1∶10000 | 15.93 | 134 | 375 | | B-B' | 1∶10000 | 7.13 | 76 | 111 |
|
The measured geological profile information of Cuonadong dome
|

| 元素 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 背景值
(平均值) | 异常
下限 | 藏南壳体
丰度[25] | 中国大陆
岩石圈丰度[26] | 富集系数
q1 | 富集系数
q2 | | Au | 0.00028 | 0.0059 | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.0017 | 0.0018 | 0.20 | 0.19 | | Ag | 0.0120 | 59.5200 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 1.10 | 1.30 | | Sn | 0.7900 | 340.35 | 11.81 | 43.71 | 3.08 | 2.77 | 3.83 | 4.26 | | As | 0.7900 | 1284.26 | 4.44 | 38.26 | 1.59 | 1.20 | 2.79 | 3.70 | | Sb | 0.0652 | 358.180 | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 1.09 | | Be | 0.4722 | 92.7800 | 3.93 | 17.56 | 1.60 | 1.96 | 2.46 | 2.01 | | Cu | 1.0000 | 358.180 | 10.56 | 47.86 | 44.00 | 38.80 | 0.24 | 0.27 | | Li | 30.7864 | 482.737 | 153.81 | 407.13 | 26.00 | 17.60 | 5.92 | 8.74 | | Pb | 3.2926 | 6178.00 | 33.88 | 122.23 | 6.50 | 6.15 | 5.21 | 5.51 | | U | 0.2904 | 23.8208 | 2.47 | 9.77 | 2.40 | 2.43 | 1.03 | 1.02 | | W | 0.4183 | 2200.84 | 2.01 | 6.38 | 0.92 | 1.18 | 2.19 | 1.71 | | Zn | 6.7370 | 1746.00 | 68 | 200 | 66 | 72 | 1.03 | 0.94 |
|
The background value and abnormal lower limit of the content of surrounding rock elements in the Cuonadong dome
|
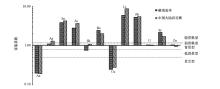
|
Element enrichment coefficient in rock profile samples of Cuonadong dome
|

| 元素 | 背景值 | 外带异常 | 中带异常 | 内带异常 | | Au | 0.0003 | 0.0005 | 0.0009 | 0.0019 | | Ag | 0.06 | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.54 | | Sn | 11.81 | 43.71 | 87.42 | 174.84 | | As | 4.44 | 38.26 | 76.51 | 153.03 | | Sb | 0.12 | 0.45 | 0.89 | 1.79 | | Be | 3.93 | 17.56 | 35.13 | 70.26 | | Cu | 10.56 | 47.86 | 95.71 | 191.42 | | Li | 153.81 | 407.13 | 814.26 | 1628.53 | | Pb | 33.88 | 122.23 | 244.46 | 488.92 | | U | 2.47 | 9.77 | 19.54 | 39.08 | | W | 2.01 | 6.38 | 12.77 | 25.53 | | Zn | 68.16 | 200.23 | 400.46 | 800.92 |
|
Abnormal grading of element contents in the rock profile samples of Cuonadong dome
|
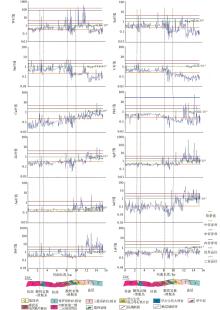
|
variation curves of elements contrast in the rock profile samples of Cuonadong dome
|

| 元素 | Au | Ag | Sn | As | Sb | Be | Cu | Li | Pb | U | W | Zn | | Au | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | | Ag | 0.028 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | | Sn | 0.233 | 0.116 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | As | 0.689 | 0.145 | 0.207 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | Sb | 0.051 | 0.840 | 0.091 | 0.284 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | Be | 0.009 | -0.028 | 0.296 | 0.000 | -0.042 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | Cu | 0.044 | 0.345 | -0.015 | 0.161 | 0.298 | -0.123 | 1.000 | | | | | | | Li | 0.073 | 0.056 | 0.060 | 0.035 | 0.042 | -0.052 | 0.132 | 1.000 | | | | | | Pb | 0.017 | 0.490 | 0.077 | 0.108 | 0.360 | -0.018 | 0.750 | 0.018 | 1.000 | | | | | U | -0.012 | -0.034 | 0.275 | 0.011 | -0.060 | 0.358 | -0.141 | -0.011 | -0.013 | 1.000 | | | | W | -0.004 | 0.000 | 0.257 | -0.005 | -0.011 | 0.039 | 0.081 | -0.011 | -0.011 | -0.028 | 1.000 | | | Zn | 0.000 | 0.421 | 0.044 | 0.293 | 0.475 | -0.073 | 0.667 | 0.069 | 0.670 | -0.102 | 0.009 | 1.000 |
|
Element correlation coefficient of rock profile sample in chutna cave dome
|
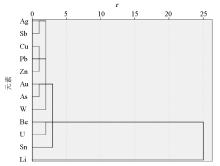
|
The R-type clustering pedigree of rock profile sample elements in the cunadong dome
|

| 成分 | 初始特征值 | 提取载荷平方和 | 旋转载荷平方和 | | 总计 | 方差/% | 累积/% | 总计 | 方差/% | 累积/% | 总计 | 方差/% | 累积/% | | 1 | 3.281 | 27.345 | 27.345 | 3.281 | 27.345 | 27.345 | 2.372 | 19.769 | 19.769 | | 2 | 1.859 | 15.491 | 42.837 | 1.859 | 15.491 | 42.837 | 1.948 | 16.23 | 35.999 | | 3 | 1.489 | 12.407 | 55.244 | 1.489 | 12.407 | 55.244 | 1.766 | 14.714 | 50.713 | | 4 | 1.151 | 9.594 | 64.838 | 1.151 | 9.594 | 64.838 | 1.577 | 13.143 | 63.856 | | 5 | 1.053 | 8.772 | 73.61 | 1.053 | 8.772 | 73.61 | 1.17 | 9.753 | 73.61 | | 6 | 0.994 | 8.282 | 81.892 | | | | | | | | 7 | 0.637 | 5.306 | 87.198 | | | | | | | | 8 | 0.56 | 4.664 | 91.862 | | | | | | | | 9 | 0.451 | 3.758 | 95.62 | | | | | | | | 10 | 0.226 | 1.882 | 97.503 | | | | | | | | 11 | 0.188 | 1.565 | 99.068 | | | | | | | | 12 | 0.112 | 0.932 | 100 | | | | | | |
|
Accumulation of variance of element factor analysis of rock profile samples in Cunadong dome
|

| 元素 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | | Au | -0.008 | -0.03 | 0.919 | 0.011 | 0.024 | | Ag | 0.256 | 0.91 | 0.008 | 0.006 | 0.022 | | Sn | 0.017 | 0.117 | 0.292 | 0.54 | 0.526 | | As | 0.135 | 0.168 | 0.888 | 0.017 | -0.016 | | Sb | 0.189 | 0.933 | 0.11 | -0.042 | -0.001 | | Be | -0.054 | -0.013 | -0.03 | 0.781 | 0.053 | | Cu | 0.909 | 0.108 | 0.034 | -0.118 | 0.052 | | Li | 0.21 | -0.116 | 0.147 | -0.052 | 0.061 | | Pb | 0.862 | 0.269 | -0.032 | 0.079 | -0.035 | | U | -0.052 | -0.04 | -0.021 | 0.804 | -0.092 | | W | 0.034 | -0.027 | -0.053 | -0.053 | 0.934 | | Zn | 0.795 | 0.326 | 0.088 | -0.047 | -0.021 |
|
Element factor analysis of rock profile sample rotation component matrixin of Cuonadong dome
|

|
Metamorphic quartz sandstone intercalated in a phyllite
|
| [1] |
Fu J, Li G, Wang G , et al. First field identification of the Cuonadong dome in southern Tibet:implications for EW extension of the North Himalayan gneissdome[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2017,106:1581-1596.
|
| [2] |
李光明, 张林奎, 焦彦杰 , 等. 西藏喜马拉雅成矿带错那洞超大型铍锡钨多金属矿床的发现及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2017,36(4):1003-1008.
|
| [2] |
Li G M, Zhang L K, Jiao Y J , et al. First discovery and implications of Cuonadong superlarge Be-W-Sn polymetallic deposit in Himalayan metallogenic belt,southern Tibet[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2017,36(4):1003-1008.
|
| [3] |
张志, 张林奎, 李光明 , 等. 北喜马拉雅错那洞穹窿:片麻岩穹窿新成员与穹窿控矿新命题[J]. 地球学报, 2017,38(5):754-766.
|
| [3] |
Zhang Z, Zhang L K, Li G M , et al. The Cuonadong gneiss dome of north himalaya: A new member of gneiss dome and a new proposition for the ore-controlling role of north himalaya gneiss domes[J]. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2017,38(5):754-766.
|
| [4] |
林彬, 唐菊兴, 郑文宝 , 等. 西藏错那洞淡色花岗岩地球化学特征、成岩时代及岩石成因[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2016,35(3):391-406.
|
| [4] |
Lin B, Tang J X, Zheng W B , et al. Geochemical characteristics,age and genesis of Cuonadong leucogranite,Tibet[J]. ACTA Petrologica ET Mineralogica, 2016,35(3):391-406.
|
| [5] |
付建刚, 李光明, 王根厚 , 等. 北喜马拉雅双穹窿构造的建立:来自藏南错那洞穹窿的厘定[J]. 中国地质, 2018,45(4):783-802.
|
| [5] |
Fu J G, Li G M, Wang G H , et al. Establishment of the North Himalayan double gneiss domes: evidence from field identification of the Cuonadong dome, south Tibet[J]. Geology in China, 2018,45(4):783-802.
|
| [6] |
Pan G T, Wang L Q, Li R S , et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012,53:3-14.
|
| [7] |
Xu Z Q, Dilek Y, Cao H , et al. Paleo-tethyan evolution of Tibet as recorded in the east Cimmerides and west Cathaysides[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015,105:320-337.
|
| [8] |
Yin A, Dubey C S, Kelty T K , et al. Geologic correlation of the Himalayan orogen and Indian craton: Part 2. Structural geology, geochronology, and tectonic evolution of the Eastern Himalaya[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2010,122(3-4):360-395.
|
| [9] |
Ding H X, Zhang Z M, Dong X , et al. Early Eocene (c. 50 Ma) collision of the Indian and Asian continents: Constraints from the North Himalayan metamorphic rocks, southeastern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2016a,435:64-73.
|
| [10] |
郭磊, 张进江, 张波 . 北喜马拉雅然巴穹窿的构造、运动学特征、年代学及演化[J]. 自然科学进展, 2008(6):640-650.
|
| [10] |
Guo L, Zhang J J, Zhang B . Tectonic,kinematic,characteristics, geochronology and evolution of the Ranba Dome in the Northern Himalayas[J]. Progress in Natural Science, 2008(6):640-650.
|
| [11] |
Wang X X, Zhang J J, Santosh M , et al. Andean-type orogeny in the Himalayas of south Tibet: Implications for early Paleozoic tectonics along the Indian margin of Gondwana[J]. Lithos, 2012,154:248-262.
|
| [12] |
King J, Harris N, Argles T , et al. Contribution of crustal anatexis to the tectonic evolution of Indian crust beneath southern Tibet[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 2011,123(1):218-239.
|
| [13] |
辜平阳, 何世平, 李荣社 , 等. 藏南拉轨岗日变质核杂岩核部花岗质片麻岩的地球化学特征及构造意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013,29(3):756-768.
|
| [13] |
Gu P Y, He S P, Li R S , et al. Geochemical features and tectonic significance of granitic gneiss of Laguigangri metamorphic core complexes in southern Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013,29(3) 756-768.
|
| [14] |
Liu Z C, Wu F Y, Ding L , et al. Highly fractionated Late Eocene (~ 35 Ma) leucogranite in the Xiaru Dome, Tethyan Himalaya, South Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2016, 240-243:337-354.
|
| [15] |
Diedesch T F, Jessup M J, Cottle J M , et al. Tectonic evolution of the middle crust in southern Tibet from structural and kinematic studies in the Lhagoi Kangri gneiss dome[J]. Lithosphere, 2016,8(5):480-504.
|
| [16] |
Gao L E, Zeng L S, Gao J H , et al. Oligocene crustal anatexis in the Tethyan Himalaya, southern Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2016,264:201-209.
|
| [17] |
Xu Z Q, Wang Q, Pêcher A , et al. Orogen-parallel ductile extension and extrusion of the Greater Himalaya in the late Oligocene and Miocene[J]. Tectonics, 2013,32(2):191-215.
|
| [18] |
曾令森, 刘静, 高利娥 , 等. 藏南也拉香波穹窿早渐新世地壳深熔作用及其地质意义[J]. 科学通报, 2009,54(3):373-381.
|
| [18] |
Zeng L S, Liu J, Gao L E , et al. Early Oligocene anatexis in the Yardoi gneiss dome, southern Tibet and geological implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2009,54(1):104-112.
|
| [19] |
张进江 . 北喜马拉雅及藏南伸展构造综述[J]. 地质通报, 2007,26(6):639-649.
|
| [19] |
Zhang J J . Structure and kinematics of the Yalashangbo dome in the northern Himalaya dome belt, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 2007,26(6):639-649.
|
| [20] |
Guillot S, Machheo G, de Sigoyer J , et al. Tethyan and Indian subduction viewed from the himaiayan high-to ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks[J]. Tectono-physics, 2008,451(1-4):225-241.
|
| [21] |
许志琴, 马绪宣 . 中国大陆显生宙俯冲型、碰撞型和复合型片麻岩穹窿(群)[J]. 岩石学报, 2015,31(12):3509-3523.
|
| [21] |
Xu Z Q, Ma X X . The Chinese Phanerozoic gneiss domes: Subduction-related type,collision-related type and combination type of subduction-collision[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015,31(12):3509-3523.
|
| [22] |
Tukey J W . Exploratory data analysis[M]. New York:Pearson Education Group, 1977.
|
| [23] |
史长义 . 勘查数据分析(EDA)技术的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 1993(11):52-58.
|
| [23] |
Shi C Y . Application of the exploratory date analysis technique[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1993(11):52-58.
|
| [24] |
罗先熔, 文美兰, 欧阳菲 , 等. 勘查地球化学[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2007: 218.
|
| [24] |
Luo X R, Wen M L, Ou Y F , et al. Exploration geochemistry[M]. BeiJing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2007: 218.
|
| [25] |
黎彤, 袁怀雨, 吴胜昔 , 等. 中国大陆壳体的区域元素丰度[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 1999(2):2-8.
|
| [25] |
Li T, Yuan H Y, Wu S X , et al. Regional element abundances of continental crustobodies in China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 1999(2):2-8.
|
| [26] |
黎彤, 倪守斌 . 中国大陆岩石圈的化学元素丰度[J]. 地质与勘探, 1997(1):31-37.
|
| [26] |
Li T, Ni S B . Element abundances of the continental lithosphere in China[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 1997(1):31-37.
|
| [27] |
邵跃, 傅学信 . 热液矿床岩石测量(原生晕法) 找矿[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1997.
|
| [27] |
Shao Y, Fu X X . Hydrothermal deposit rock survey (primary halo method) prospecting[M]. Beijing: Geology Publishing House, 1997.
|
| [28] |
蒋敬业, 程建萍, 祁士华 , 等. 应用地球化学[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2006: 145-179.
|
| [28] |
Jiang J Y, Cheng J P, Qi S H , et al. Applied geochemistry [M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2006: 145-179.
|
| [29] |
谢佳佳 . 藏南错那地区淡色花岗岩年代学及地球化学研究[D]. 广州:中国科学院大学, 2018.
|
| [29] |
Xie J J . Geochronology and geochemistry of the Cuonadong and Cuora leucogranites in Cuona area,SouthTibet.[D]. Guangzhou:University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018.
|
| [30] |
梁维, 张林奎, 夏祥标 , 等. 藏南地区错那洞钨锡多金属矿床地质特征及成因[J]. 地球科学, 2018,43(8):2742-2754.
|
| [30] |
Liang W, Zhang L K, Xia X B , et al. Geology and preliminary mineral genesis of the Cuonadong W-Sn polymetallic deposie, southern, Tibet, China[J]. Earth Science, 2018,43(8):2742-2754.
|
| [1] |
FANG Yong-Kun, Cao Cheng-Gang, DONG Jun-Lin, LI Ling-Gui. Geochronology and geochemistry of the granodiorite intrusion in Yangkang area of Qinghai Province and its geological significance[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1367-1377. |
| [2] |
YANG Dan, LI Wei, WEI Yong-Liang, SONG Bin. Application of dual-tree complex wavelet transform in advanced geological prediction of the tunnel section in Lalin of Sichuan-Tibet Railway[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(6): 1504-1511. |
|
|
|
|

