|
|
|
| 3D magnetic field forward modeling by finite-infinite element coupling method |
GUO Chu-Feng( ), ZHANG Shi-Hui( ), ZHANG Shi-Hui( ), LIU Tian-You ), LIU Tian-You |
| Institute of Geophysics and Geomatics, China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), Wuhan 430074,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Due to the influence of the artificial boundary condition, when the conventional finite element method is used to carry out the forward simulation of the three-dimensional geophysical field in a limited space, local abnormal distortion may occur, which affects the accuracy of the numerical simulation. This problem is usually solved by expanding the edge, but this requires a larger range, which greatly increases the computational cost and affects the efficiency of forward simulation. In this paper, on the basis of COMSOL Multiphysics software, infinite elements are set on the external boundary to replace the traditional boundary conditions so as to reduce the calculation area. Compared with the traditional finite element method, the finite element infinite element coupling method, by setting the isolated sphere and the combined body model and considering the conditions of demagnetization, remanence and surface undulation, can effectively overcome the boundary effect, improve the calculation accuracy and reduce the amount of calculation, thus improving the forward numerical simulation efficiency of the finite element method.
|
|
Received: 01 December 2020
Published: 27 July 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
ZHANG Shi-Hui
E-mail: gcf2013@cug.edu.cn;zsh2008@cug.edu.cn
|
|
|
|
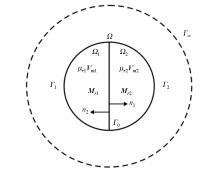
|
Distribution of inhomogeneous medium (modified from Xu Shizhe,1994)
|
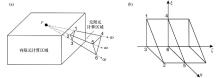
|
3-D infinite element mapping(modified from Tang et al.,2010)
|
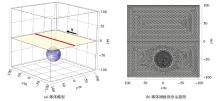
|
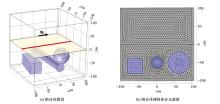
Diagram of the Sphere model and mesh generation(the blue region is the sphere, the red line is observation line, the yellow plane is the range of observation plane)
|
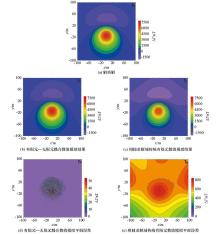
|
The plane total-field anomaly of the sphere using different methods
|
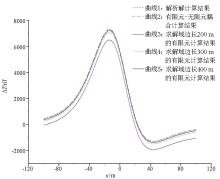
|
The total-field anomaly curve of the sphere using different methods
|
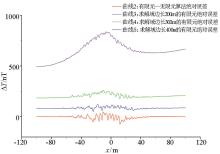
|
The absolute error distribution curve
|

| 方法 | 有限元求
解域边长
/m | 网格节
点数 | 平均网
格间距
/m | 占用内存
/GB | 计算时间
/s | 最大绝
对误差
/nT | 均方根
误差
/nT | 平均相
对误差
/% | | 有限元—无限元 | 200 | 453751 | 1.5 | 4.85 | 70 | 73.83 | 17.49 | 0.78 | | 传统有限元 | 200 | 383250 | 1.5 | 4.33 | 34 | 837.88 | 656.69 | 63.90 | | 传统有限元 | 300 | 1255245 | 1.5 | 12.06 | 120 | 261.82 | 205.02 | 20.27 | | 传统有限元 | 400 | 2951989 | 1.5 | 23.91 | 240 | 120.91 | 86.13 | 8.41 |
|
Comparison about efficiency and relative error of different model
|
|
Diagram of combined model and mesh generation(the red line is observation line, the yellow plane is the range of observation plane)
|
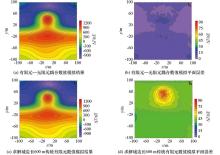
|
The map of the Finite element numerical simulation results and plane error distribution
|

| 方法 | 有限元求解
域边长/m | 网格节
点数 | 平均网格
间距/m | 占用内存
/GB | 计算时间
/s | 最大绝对
误差/nT | 均方根误
差/nT | 平均相对
误差/% | | 有限元—无限元 | 200 | 134853 | 5 | 3.67 | 109 | 35.22 | 12.53 | 1.68 | | 传统有限元 | 200 | 114193 | 5 | 3.46 | 27 | 704.77 | 504.73 | 262.94 | | 传统有限元 | 400 | 880751 | 5 | 10.98 | 60 | 159.25 | 114.61 | 18.02 | | 传统有限元 | 600 | 2951638 | 5 | 28.46 | 262 | 98.21 | 50.32 | 7.62 |
|
Comparison about efficiency and relative error of different model
|
|
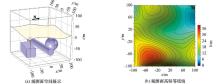
Diagram of rugged surface model (The yellow plane is the range of observation plane)
|
|
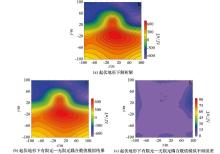
The map of the Finite element numerical simulation results and plane error distribution in rugged surface
|
| [1] |
徐世浙. 地球物理中的有限单元法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1994.
|
| [1] |
Xu S Z. The finite element method in geophysics [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1994.
|
| [2] |
Coggon J H. Electromagnetic and electrical modeling by the finite element method[J]. Geophysics, 1971, 36(1):132-132.

|
| [3] |
赵宁, 王绪本, 余刚, 等. 面向目标自适应海洋可控源电磁三维矢量有限元正演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(2):779-788.
|
| [3] |
Zhao N, Wang X B, Yu G, et al. 3D MCSEM parallel goal-oriented adaptive vector finite element modeling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(2):779-788.
|
| [4] |
Kordy M, Wannamaker P, Maris V, et al. 3-D magnetotelluric inversion including topography using deformed hexahedral edge finite elements and direct solvers parallelized on SMP computers - Part I: forward problem and parameter Jacobians[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2016, 204(1):74-93.

|
| [5] |
Ren Z, Kalscheuer T, Greenhalgh S, et al. A goal-oriented adaptive finite-element approach for plane wave 3-D electromagnetic modelling[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2013, 194(2):700-718.

|
| [6] |
曹晓月, 殷长春, 张博, 等. 面向目标自适应有限元法的带地形三维大地电磁各向异性正演模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(6):2618-2628.
|
| [6] |
Cao X Y, Yin C C, Zhang B, et al. A goal-oriented adaptive finite-element method for 3D MT anisotropic modeling with topography[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(6):2618-2628.
|
| [7] |
刘云鹤, 殷长春, 蔡晶, 等. 电磁勘探中各向异性研究现状和展望[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(8):3468-3487.
|
| [7] |
Liu Y H, Yin C C, Cai J, et al. Review on research of electrical anisotropy in electromagnetic prospecting[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(8):3468-3487.
|
| [8] |
李勇, 吴小平, 林品荣, 等. 电导率任意各向异性海洋可控源电磁三维矢量有限元数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(5):1955-1978.
|
| [8] |
Li Y, Wu X P, Ling P R, et al. Three-dimensional modeling of marine controlled-source electromagnetism using the vector finite element method for arbitrary anisotropic media[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(5):1955-1978.
|
| [9] |
蒋甫玉, 谢磊磊, 常文凯, 等. 三度体重力矢量的有限单元法正演计算[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2015, 45(4):1217-1226.
|
| [9] |
Jiang F Y, Xie L L, Chang W K, et al. Forward calculation of three dimensional gravity vector using finite element method[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2015, 45(4):1217-1226.
|
| [10] |
May D A, Knepley M G. Optimal, scalable forward models for computing gravity anomalies[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2011, 187(1):161-177.

|
| [11] |
Cai Y, Wang C. Fast finite-element calculation of gravity anomaly in complex geological regions[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 2005, 162(3):696-708.

|
| [12] |
朱自强, 曾思红, 鲁光银, 等. 二度体的重力张量有限元正演模拟[J]. 物探与化探, 2010, 34(5):668-671.
|
| [12] |
Zhu Z Q, Zeng S H, Lu G Y, et al. Finite element forward simulation of the two-dimensional gravity gradient tensor[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2010, 34(5):668-671.
|
| [13] |
朱自强, 邢泽峰, 鲁光银. 有限元重力任意复杂地形校正方法研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2019, 41(6):768-773.
|
| [13] |
Zhu Z Q, Xing Z F, Lu G Y. Research on the gravity arbitrarily complex terrain correction method based on FEM[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 41(6):768-773.
|
| [14] |
王书惠. 磁各向异性条件下的磁法勘探正问题及其解法[J]. 地球物理学报, 1983, 26(1):58-69.
|
| [14] |
Wang S H. The direct problem of magnetic prospecting under anisotropic condition and the solution to solve it[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1983, 26(1):58-69.
|
| [15] |
刘双, 刘天佑, 高文利, 等. 基于FlexPDE考虑退磁作用的有限元法磁场正演[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2013, 35(2):134-141.
|
| [15] |
Liu S, Liu T Y, Gao W L, et al. Magnetic forward modeling considering demagnetization effect using finite element method based on FlexPDE[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 35(2):134-141.
|
| [16] |
刘双, 刘天佑, 高文利, 等. 退磁作用对磁测资料解释的影响[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(4):602-606.
|
| [16] |
Liu S, Liu T Y, Gao W L, et al. The Influence of demagnetization on magnetic data interpretation[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(4):602-606.
|
| [17] |
张林成, 汤井田, 任政勇, 等. 基于二次场的可控源电磁法三维有限元—无限元数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2017, 60(9):3655-3666.
|
| [17] |
Zhang L C, Tang J T, Ren Z Y, et al. Forward modeling of 3D CSEM with the coupled finite-infinite element method based on the second field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2017, 60(9):3655-3666.
|
| [18] |
Ungless R F. An infinite finite element[D]. Prince George:University of British Columbia, 1973.
|
| [19] |
Bettess P, Zienkiewicz O C. Diffraction and refraction of surface waves using finite and infinite elements[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1977, 11(8):1271-1290.

|
| [20] |
Astley R J, Bettess P, Clark P J. Mapped infinite elements for exterior wave problems[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering, 1991, 32(1):207-209.

|
| [21] |
Astley R J, Macaulay G J. Mapped wave envelope elements for acoustical radiation and scattering[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 1994, 170(1):207-209.
|
| [22] |
Astley R J, Macaulay G J, Coyette J, et al. Three-dimensional wave-envelope elements of variable order for acoustic radiation and scattering. Part I. Formulation in the frequency domain[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 103(1):49-63.

|
| [23] |
Burnett D S. A three‐dimensional acoustic infinite element based on a prolate spheroidal multipole expansion[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1994, 96(5):2798-2816.

|
| [24] |
Burnett D S, Holford R L. Prolate and oblate spheroidal acoustic infinite elements[J]. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 1998, 158(1):117-141.

|
| [25] |
史贵才. 脆塑性岩石破坏后区力学特性的面向对象有限元与无界元耦合模拟研究[D]. 武汉:中国科学院研究生院(武汉岩土力学研究所), 2005.
|
| [25] |
Shi G C. Research on post-failure mechanical properties of Brittle-plastic rocks by OOFEM coupled with IEM[D]. Wuhan:Wuhan Institute of Rock and Soil Mechanics, The Chinese Academy of Sciences,P.R. China, 2005.
|
| [26] |
李录贤, 国松直, 王爱琴. 无限元方法及其应用[J]. 力学进展, 2007, 37(2):161-174.
|
| [26] |
Li L X, Guo S Z, Wang A Q. The infinite element method and its application[J]. Advances in Mechanics, 2007, 37(2):161-174.
|
| [27] |
Wu S, Xiang Y, Yao J, et al. An element-free galerkin coupled with improved infinite element method for exterior acoustic problem[J]. Journal of Theoretical and Computational Acoustics, 2019, 27(2):411-454.
|
| [28] |
Fu L Y, Wu R S. Infinite boundary element absorbing boundary for wave propagation simulations[J]. Geophysics, 2000, 65(2):596-602.

|
| [29] |
朱军, 唐章宏, 顿月芹, 等. 无限元法在三维电测井计算中的应用[J]. 天然气工业, 2008, 28(11):59-61.
|
| [29] |
Zhu J, Tang Z H, Dun Y Q, et al. Application of infinite element method in 3D electric logging calculation[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2008, 28(11):59-61.
|
| [30] |
汤井田, 公劲喆. 三维直流电阻率有限元—无限元耦合数值模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2010, 53(3):717-728.
|
| [30] |
Tang J T, Gong J Z. 3D DC resistivity forward modeling by finite-infinite element coupling method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2010, 53(3):717-728.
|
| [31] |
欧洋, 冯杰, 赵勇, 等. 同时考虑退磁和剩磁的有限体积法正演模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(11):4635-4646.
|
| [31] |
Ou Y, Feng J, Zhao Y, et al. Forward modeling of magnetic data using finite volume method with a simultaneous consideration of demagnetization and remanence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61(11):4635-4646.
|
| [32] |
刘鹏飞. 岩石磁性特征及考虑退磁影响的正反演研究[D]. 武汉:中国地质大学(武汉), 2019.
|
| [32] |
Liu P F. Magnetic behavior of rocks and forward and inverse models incorporating demagnetization[D]. Wuhan:China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2019.
|
| [1] |
HE Shuai, YANG Bing-Nan, RUAN Shuai, LI Yong-Gang, HAN Yao-Fei, ZHU Da-Wei. Fine Interpretation of the exploration results of diamond-bearing rock masses in Maping area, Guizhou using the 3D AMT forward modeling and inversion technologies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 618-627. |
| [2] |
ZHAO You-Chao, ZHANG Jun, FAN Tao, YAO Wei-Hua, YANG Yang, SUN Huai-Feng. Analysis of 3D ground-borehole TEM response characteristics and rapid positioning method for anomalous bodies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2): 383-391. |
|
|
|
|

