|
|
|
| Research and application of brittleness logging evaluation method to tight sandstone reservoirs:Exemplified by Weibei oilfield in Ordos Basin |
ZHU Yan( ), HAN Xiang-Yi( ), HAN Xiang-Yi( ), YUE Xin-Xin, YANG Chun-Feng, CHANG Wen-Xin, XING Li-Juan, LIAO Jing ), YUE Xin-Xin, YANG Chun-Feng, CHANG Wen-Xin, XING Li-Juan, LIAO Jing |
| Exploration and Development Research Institute of Henan Oilfield Company,Sinopec,Zhengzhou 450018,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Tight sandstone reservoirs have the characteristics of strong heterogeneity,poor physical properties,and difficulty in exploration and development.In order to find the high-brittleness section of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Weibei oilfield and fracture this kind of reservoirs,this paper proposes a method based on ANN (artificial neural network) model for shear wave prediction under the condition of lacking suitable brittleness prediction methods for tight sandstone reservoirs in the Weibei oilfield at present.The predicted value is highly consistent with the measured value,and the brittleness index of each well in the study area is calculated by the elastic parameter method further.For the purpose of improving the accuracy of the brittleness index predicted by this method,X-ray diffraction full-rock analysis of fewer wells in the study area is utilized,and it is concluded that quartz and carbonate rocks are the main brittle minerals of the Yanchang formation in the study area."(quartz+carbonate) content/ total minerals " are adopted to calculate the rock brittleness index and then improve the brittleness index predicted by the elastic parameter method.This technique which takes advantage of the balance between the mineral composition method and the elastic parameter method not only improves the prediction accuracy but also makes up for the lack of array acoustic logging and whole rock analysis data.This method was used to predict the brittleness of tight sandstone reservoirs in the WB2 well area of the Yanchang formation in the Weibei oilfield, and high-brittleness sections of WB52 and WB49 were further chosen to be fractured.It is shown that the production stimulation effect was obvious after fracturing,which is of great significance for guiding hydraulic fracturing.The method and process proposed in this paper have strong application and promotion value.
|
|
Received: 29 September 2020
Published: 15 December 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
HAN Xiang-Yi
E-mail: zhu007yan@163.com;610220744@qq.com
|
|
|
|
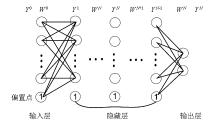
|
Structure diagram of artificial neural network
|
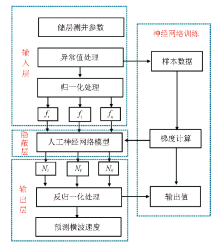
|
Flow chart of ANN shear wave velocity prediction method
|
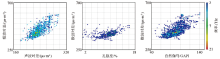
|
Intersection of well logging curves and shear wave velocity in the study area
|
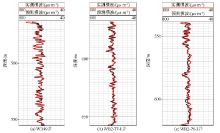
|
Comparison of predicted values of S-wave velocity and actual measured values with different wells
|
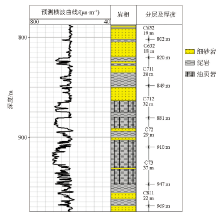
|
Analysis results of shear wave velocity in the target interval of WB48 well
|

| 深度/m | 层位 | 黏土类
矿物/% | 石英/% | 长石(钾
长石+钠长
石)/% | 碳酸盐类矿物
(方解石+
白云石)/% | 498.02
499.65
501.01
502.42
503.35
522.91
524.86
526.16
528.08
530.38
533.66
538.8
807.28
809.05
810.5
811.66
812.74
813.7
815.45
817.17
827.28
828.73
830.76
831.9
833.44 | C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C3
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
C6
C7
C7
C7
C7
C7 | 11
9
6
9
10
12
12
11
8
8
7
9
16
17
13
15
10
10
17
14
15
22
13
13
17 | 49
52
33
46
55
52
47
49
44
50
44
40
47
43
49
44
40
48
44
49
44
37
44
26
40 | 30
30
42
41
30
29
30
33
40
32
44
48
26
30
32
32
28
31
29
26
32
28
34
36
32 | 10
9
19
4
5
7
11
7
8
10
5
3
11
10
6
9
22
11
10
11
9
13
9
25
11 |
|
X-ray diffraction data of the whole rock in the Yanchang Formation of WB48 well
|
|
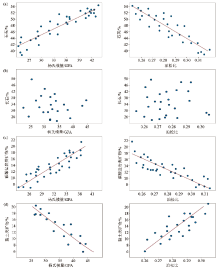
Intersection analysis of quartz,feldspar,carbonate and clay minerals with Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio
a—intersection analysis of quartz with Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio;b—intersection analysis of feldspar with Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio;c—intersection analysis of carbonate with Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio;d—intersection analysis of clay minerals with Young's modulus and Poisson's ratio
|
|
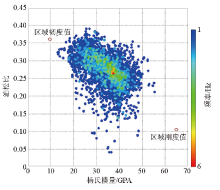
Intersection diagram of Young’s modulus and Poisson’s ratio
|
|
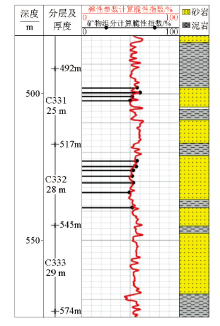
Prediction of brittleness index of tight oil wells in Weibei area
|
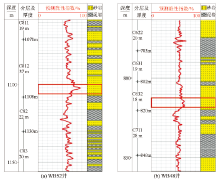
|
Brittleness prediction results of tight oil wells in Weibei area
|
| [1] |
邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望——以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2):173-187.
|
| [1] |
Zou C N, Zhu R K, Wu S T, et al. Types,haracteristics,genesis and prospects of conventional andunconventional hy drocarbon accumulations:Taking tight oil and tight gas in China an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2):173-187.
|
| [2] |
田建涛, 赵超峰, 张伟, 等. 水力压裂井中监测方法不对称压裂裂缝分析[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(4):563-571.
|
| [2] |
Tian J T, Zhao C F, Zhang W, et al. Analysis of asymmetric hydraulic fracture for borehole microseismic monitoring[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(4):563-571.
|
| [3] |
刘勇, 方伍宝, 李振春, 等. 基于叠前地震的脆性预测方法及应用研究[J]. 石油物探, 2016, 55(3):425-432.
|
| [3] |
Liu Y, Fang W B, Li Z C, et al. Brittleness prediction and application based on pre-stack seismic inversion[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2016, 55(3):425-432.
|
| [4] |
张晓语, 杜启振, 马中高, 等. 各向异性页岩储层脆性特征分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(3):541-549.
|
| [4] |
Zhang X Y, Du Q Z, Ma Z G, et al. Brittleness characteristics of anisotropic shale reservoirs[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(3):541-549.
|
| [5] |
马妮, 林正良, 胡华锋, 等. 页岩地层的破裂压力地震预测方法[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(6):926-934.
|
| [5] |
Ma N, Lin Z L, Hu H F, et al. A seismic-based prediction method for fracture pressure in a shale formation[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(6):926-934.
|
| [6] |
Obert L, Duvall W I. Rock mechanics and the design of structures in rock[M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 1967.
|
| [7] |
黄军平, 张智盛, 杨占龙, 等. 致密岩石矿物组分含量及脆性指数多元回归定量预测[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2016, 37(3):346-351.
|
| [7] |
Huang J P, Zhang Z S, Yang Z L, et al. Quantitative prediction of mineral component content and brittleness index in tight rocks based on multivariate regression analysis[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2016, 37(3):346-351.
|
| [8] |
任岩, 曹宏, 姚逢昌, 等. 吉木萨尔致密油储层脆性及可压裂性预测[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2018, 53(3):511-519.
|
| [8] |
Ren Y, Cao H, Yao F C, et al. Brittleness and fracability prediction for tight oil reservoir in Jimsar Sag,Junggar Basin[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2018, 53(3):511-519.
|
| [9] |
张平, 夏晓敏, 崔涵, 等. 基于岩石物理实验的致密油储集层脆性指数预测——以柴达木盆地跃灰101井区为例[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2019, 40(5):615-623.
|
| [9] |
Zhang P, Xia X M, Cui H, et al. Tight oil reservoir brittleness index prediction based on petrophysical experiments:A case from Yuehui 101 area of Qaidam Basin[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2019, 40(5):615-623.
|
| [10] |
孙赞东, 贾承造, 李相方, 等. 非常规油气勘探与开发[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2011:407-593.
|
| [10] |
Sun Z D, Jia C Z, Li X F, et al. Unconventional oil & gas exploration and development [M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2011:407-593.
|
| [11] |
石道涵, 张兵, 何举涛, 等. 鄂尔多斯长7致密砂岩储层体积压裂可行性评价[J]. 西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 29(1):53-55.
|
| [11] |
Shi D H, Zhang B, He J T, et al. Feasibility evaluation of volume fracturing of Chang 7 tight sandstone reservoir in Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University:Natural Science Edition, 2014, 29(1):53-55.
|
| [12] |
许孝凯, 翟勇, 刘美杰, 等. 复杂储层岩石脆性分析及应用研究[J]. 测井技术, 2015, 39(4):486-490.
|
| [12] |
Xu X K, Zhai Y, Liu M J, et al. Brittleness analysis of rock and its application to complex reservoirs[J]. Logging Technology, 2015, 39(4):486-490.
|
| [13] |
许杰, 刘坤岩, 武清钊, 等. 焦石坝页岩脆性评价与预测[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(3):453-460.
|
| [13] |
Xu J, Liu K Y, Wu Q Z. Evaluation and prediction of shale brittleness in the Jiaoshiba area[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(3):453-460.
|
| [14] |
刘雅杰, 李生杰, 王永刚, 等. 横波预测技术在苏里格气田储层预测中的应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(1):165-172.
|
| [14] |
Liu Y J, Li S J, Wang Y G, et al. Reservoir prediction based on shear wave in Sulige Gas Field[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2016, 51(1):165-172.
|
| [15] |
Castagna J P, Batzle M L, Eastwood R L. Relationships between compressional-wave and shear-wave velocities in clastic silicate rocks[J]. Geophysics, 1985, 50(4):571-581.

|
| [16] |
Xu S Y, White R E. A physical model for shear-wave velocity prediction[J]. Geophysical Prospecting, 1996, 44(4):687-717.

|
| [17] |
LEE M W. A simple method of predicting S-wave velocity[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(6):F161-F164.

|
| [18] |
刘财, 乔汉青, 郭智奇, 等. 基于粒子群算法的页岩孔隙结构反演及横波速度预测[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2017, 32(2):689-695.
|
| [18] |
Liu C, Qiao H Q, Guo Z Q, et al. Shale pore structure inversion and shear wave velocity prediction based on particle swarm optimization(pso) algorithm[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2017, 32(2):689-695.
|
| [19] |
刘倩, 印兴耀, 李超. 含不连通孔隙的致密砂岩储层岩石弹性模量预测方法[J]. 石油物探, 2015, 54(6):635-642.
|
| [19] |
Liu Q, Yin X Y, Li C. Rock elastic modulus estimation for tight sandstone reservoirs with disconnected pores[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2015, 54(6):635-642.
|
| [20] |
张秉铭, 刘致水, 刘俊州, 等. 富有机质泥页岩岩石物理横波速度预测方法研究[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(5):658-667.
|
| [20] |
Zhang B M, Liu Z S, Liu J Z, et al. A new S-wave velocity estimation method for organic-enriched shale[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(5):658-667.
|
| [21] |
Dutta S, Gupta J P. PVT correlations for Indian crude using artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2010, 72(1):93-109.

|
| [22] |
Cheng C S. A multi-yaler neural network model for detecting changes in the process mean[J]. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 1995, 28(1):51-61.

|
| [23] |
史忠科. 神经网络控制理论[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 1997.
|
| [23] |
Shi Z K. Neural network control theory [M]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, 1997.
|
| [24] |
李文成, 彭嫦姿, 杨鸿飞. 横波预测技术在 YB 地区的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2014, 29(4):1695-1700.
|
| [24] |
Li W C, Peng C Z, Yang H F. The application of S-wave prediction technology in YB area[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2014, 29(4):1695-1700.
|
| [25] |
周雪晴, 张占松, 张超谟, 等. 基于矿物组分和成岩作用的致密砂岩储层脆性评价方法——以鄂尔多斯盆地东北部某区块为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2017, 24(5):10-16.
|
| [25] |
Zhou X Q, Zhang Z S, Zhang C M, et al. A new brittleness evaluation method for tight sandstonereservoir based on mineral compositions and diagenesis:A case study of a certain block in the northeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2017, 24(5):10-16.
|
| [26] |
徐蕾, 师永民, 徐常胜, 等. 长石族矿物对致密油储渗条件的影响——以鄂尔多斯盆地长6油层组为例[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(4):448-454.
|
| [26] |
Xu L, Shi Y M, Xu C S, et al. Influences of feldspars on the storage and permeability conditions in tight oil reservoirs:A case study of Chang-6 Oil Layer Group,Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(4):448-454.
|
| [27] |
Rickman R, Mullen M J, Petre J E, et al. Apractical use of shale petrophysics for stimulation designoptimization:All shale plays are not clones of the Barnett Shale[C]// SPE Technical Conference and Exhibition,Society of Petroleum Engineers, 2008, 48(3):536-567.
|
|
|
|

