|
|
|
| Karst cave prospecting using cross-hole ultra-high density resistivity method |
SU Bao1( ), LIU Xiao-Li2,3, WEI Xiao-Bo4, GAO Ge5, WANG Yun-Peng5 ), LIU Xiao-Li2,3, WEI Xiao-Bo4, GAO Ge5, WANG Yun-Peng5 |
1. Guangdong Pearl River Delta Intercity Rail Transit Co., Ltd., Guangzhou 510335,China
2. School of Civil Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084,China
3. State Key Laboratory of Hydroscience and Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084,China
4. Guangzhou Metro Group Co. Ltd., Guangzhou 510330, China
5. Research Institute of Exploration and Development, Huabei Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Renqiu 062552,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The prospecting of shallowly concealed karst caves is studied using the cross-hole ultra-high density resistivity method. The results are as follows. It was feasible to prospect Karst caves using existing survey boreholes according to the cross-hole ultra-high density resistivity method. The transverse and longitudinal distribution ranges of karst caves can be directed reflected by the distribution characteristics of the cross-hole resistivity obtained through forward and inverse calculations. Meanwhile, it was difficult to distinguish the connectivity between karst caves, and the depth deviation was the distance between two adjacent electrodes. It is suggested that the depth of the boreholes used should be consistent, the ratio of the borehole depth to the borehole space should be higher than 1.5, and the electrode space should be 1~2 m in practice.
|
|
Received: 12 May 2021
Published: 15 December 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Electrode layout of ultra-density resistivity method
|
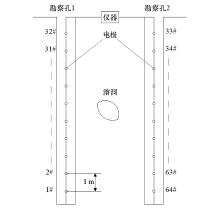
|
Electrode layout of cross-hole ultra-density resistivity method
|
|
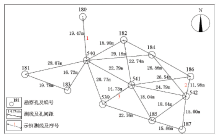
Layout of resistivity hole and survey line in Qingbu station of Guangzhou Metro
|

剖面
序号 | 对应勘察孔
(电缆I—电缆II) | 电缆I
孔深/m | 电缆II
孔深/m | 孔间距
/m | | 1 | 540—180 | 40.0 | 42.5 | 19.47 | | 2 | 542—186 | 45.0 | 39.0 | 11.98 | | 3 | 541—539 | 39.0 | 38.0 | 14.73 | | 电极间距: 1 m | 采样间隔:2 s |
|
Parameters of resistivity holes
|
|
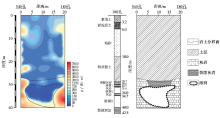
Inversion resistivity profile, stratigraphic histogram and geological inference profile between No.540 hole and No.180 hole
|
|
Inversion resistivity profile, stratigraphic histogram and geological inference profile between No.542 hole and No.186 hole
|
|
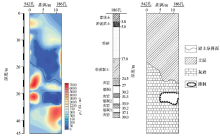
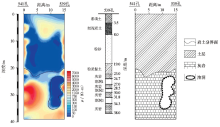
Inversion resistivity profile, stratigraphic histogram and geological inference profile between No.541 hole and No.539 hole
|
| [1] |
郭贵安, 魏柏林. 井间电磁波CT技术在溶洞探测中的应用[J]. 华南地震, 1999, 4(19):28-34.
|
| [1] |
Guo G A, Wei B L. Prospecting corroded cavities using cross-section electromagnetic tomographic technique between boreholes[J]. South China Journal of Seismology, 1999, 4(19):28-34.
|
| [2] |
严加永, 孟贵祥, 吕庆田, 等. 高密度电法的时展与展望[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(4):576-584.
|
| [2] |
Yan J Y, Meng G X, Lyu Q T, et al. The progress and prospect of the electrical resistivity imaging survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(4):576-584.
|
| [3] |
刘宏岳. 直流高密度电法在浅海工程勘察中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(4):756-760.
|
| [3] |
Liu H Y. The application of DC resistivity to shallow marine engineering exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(4):756-760.
|
| [4] |
蔡运胜. 高密度电法探测地下牡蛎礁(滩)的实验[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(6):635-637.
|
| [4] |
Cai Y S. The experimental application of the high density electric method to the detection of underground oyster bioherm[J]. Geophysical ang Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(6):635-637.
|
| [5] |
孟娟, 颜庭成, 陈晓飞, 等. 双线隧道盾构机侧穿时古石塔地基及塔身变形规律研究[J]. 河南科学, 2020, 38(4):626-631.
|
| [5] |
Meng J, Yan T C, Chen X F, et al. Deformation of the foundation and tower body of ancient tower when double-line shield tunneling beside the tower[J]. Henan Science, 2020, 38(4):626-631.
|
| [6] |
吕根根, 张晓平, 刘泉声, 等. TBM掘进速度预测模型研究[J]. 河南科学, 2019, 37(8):1289-1295.
|
| [6] |
Lyu G G, Zhang X P, Liu Q S, et al. Prediction models of the TBM penetration rate[J]. Henan Science, 2019, 37(8):1289-1295.
|
| [7] |
张兵. 基于改进信息熵值分析的TBM掘进参数研究[J]. 河南科学, 2019, 37(5):785-791.
|
| [7] |
Zhang B. TBM driving parameters based on improved information entropy analysis[J]. Henan Science, 2019, 37(5):785-791.
|
| [8] |
李俊杰, 何建设, 严家斌, 等. 超高密度电阻率在隐伏断层探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(3):624-628.
|
| [8] |
Li J J, He J S, Yan J B, et al. The application of ultra-density resistivity method to detection of buried fault[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(3):624-628.
|
| [9] |
李红立, 张华, 汪传斌. 跨孔超高密度电阻率法在花岗岩球状风化体勘探中的试验研究[J]. 工程勘察, 2010, 38(8):88-92.
|
| [9] |
Li H L, Zhang H, Wang C B. Experimental study on the cross-hole ultra-density resistivity method used in the exploration for the spheric lightly-weathered granite[J]. Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying, 2010, 38(8):88-92.
|
| [10] |
刘申芬, 李天成, 慕洪涛. 三维井地电阻率有限元数值模拟及反演[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(1):88-90.
|
| [10] |
Liu S F, Li T C, Mu H T. The numerical modeling and inversion of 3D borehole-surface resistivity finite element[J]. Geophysical & Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(1):88-90.
|
| [11] |
王志刚, 何展翔, 刘昱. 井地直流电法三维数值模拟及异常规律研究[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2006, 3(2):87-92.
|
| [11] |
Wang Z G, He Z X, Liu Y. Research of three-dimensional modeling and anomalous rule on borehole-ground DC method[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2006, 3(2):87-92.
|
| [12] |
余鹏洲, 张志勇, 黄临平, 等. 带井观测高密度电阻率法2.5维非结构化网格反演[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(4):1687-1693.
|
| [12] |
Yu P Z, Zhang Z Y, Huang L P, et al. 2.5D inversion of borehole and surface multi-electrode DC data using unstructured mesh[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(4):1687-1693.
|
| [1] |
HE Sheng, WANG Wan-Ping, DONG Gao-Feng, NAN Xiu-Jia, WEI Feng-Feng, BAI Yong-Yong. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in urban geological surveys[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1379-1386. |
| [2] |
WANG Liang, LONG Xia, WANG Ting-Ting, XI Zhen-Zhu, CHEN Xing-Pen, ZHONG Ming-Feng, DONG Zhi-Qiang. Application of the opposing-coils transient electromagnetic method in detection of urban shallow cavities[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1289-1295. |
|
|
|
|

