|
|
|
| Exploring the standards of Se-rich soil in Qinghai Province |
MA Qiang( ), ZHANG Ya-Feng, HUANG Qiang, JI Bing-Yan, Miao Guo-Wen, MA Feng-Juan, MA Ying ), ZHANG Ya-Feng, HUANG Qiang, JI Bing-Yan, Miao Guo-Wen, MA Feng-Juan, MA Ying |
| The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, Xining 810099,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The acid-base properties and Se background values of the soil in Qinghai Province were obtained by analyzing the pH and Se content of the soil based on the data derived from the geochemical survey of land quality conducted in Qinghai Province. The Se enrichment models of root soil and crops such as wheat, rapeseed, pea, garlic, and forage were established accordingly. The recommended values of Se-rich soil in Qinghai were calculated by combining the recommended in take of Se in the population with the standard value of Se content in Se-rich agricultural and livestock products in Qinghai Province. It is recommended that the lower limit of Se-rich soil for alkaline soil and neutral and acidic soil in Qinghai Province should be 0.23×10-6 and 0.25×10-6, respectively. This study is greatly significant for the formulation of the local standards for Se-rich soil in Qinghai Province and for guiding the development of the selenium industry.
|
|
Received: 16 May 2021
Published: 21 June 2022
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 地区或单位 | 标准或文献 | 条件 | 硒含量值/10-6 | | 中国地质调查局 | 天然富硒土地划定与标识(试行)
DD2019—10 | pH≤7.5
pH>7.5 | ≥0.40
≥0.30 | | 黑龙江省 | 富硒土壤评价要求
DB23/T 2071—2018 | pH<6.5
6.5≤pH≤7.5
pH>7.5 | 0.4~3.0
0.35~3.0
0.325 | | 河北省 | 天然富硒土地判定要求 | pH≤7.5
pH>7.5 | ≥0.40
≥0.30 | | 河南省 | 富硒土壤硒含量要求
DB41/T 1871—2019 | pH<6.5
6.5≤pH≤7.5
pH>7.5 | ≥0.35
≥0.32
≥0.3 | | 宁夏回族自治区 | 宁夏富硒土壤标准
DB64/T 1220—2016 | 无 | ≥0.222 | | 甘肃省 | 甘肃省富硒土壤标准研究与探讨 | pH>7.5 | ≥0.28 | | 广西壮族自治区 | 土壤中全硒含量的分级要求 | 水田
旱地
园地 | 0.45~3.0
0.49~3.0
0.55~3.0 |
|
Summary of different regions of standards for selenium-rich soils
|
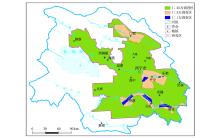
|
Spatial diagram of different scale workspaces in eastern Qinghai
|

| 参数 | 酸性
pH<6.5 | 中性
6.5≤pH≤7.5 | 碱性
7.5<pH≤8.5 | 强碱性
pH>8.5 | | 中位值 | 6.37 | 7.1 | 8.15 | 8.65 | | 样品数 | 92 | 1175 | 5835 | 1171 | | 占比 | 1% | 14% | 71% | 14% |
|
pH distribution and statistics of the proportion of samples of soil
|
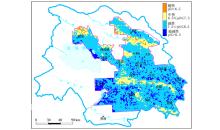
|
The distribution of pH in soil
|

| 类型 | 样品数 | 最小值/10-6 | 最大值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 中位数/10-6 | 累频75%值/10-6 | 变异系数 | 背景值/10-6 | | 特征值 | 8273 | 0.02 | 2.31 | 0.20 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.50 | 0.20 |
|
Statistical table of characteristic values of soil Se content
|
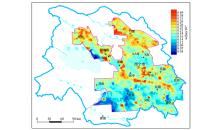
|
The distribution of Se in soil
|
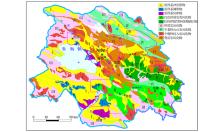
|
The distribution of mother-to-earth in eastern Qinghai
|

| 指标 | 区间/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 百分比/% | | 水溶态Se | 0.001~0.038 | 0.012 | 3.3 | | 离子交换态Se | 0.001~0.036 | 0.011 | 3.1 | | 碳酸盐态Se | 0.002~0.033 | 0.011 | 3.1 | | 加和1) | 0.004~0.107 | 0.034 | 9.5 | | 腐殖酸态Se | 0.011~0.159 | 0.052 | 14.3 | | 强有机态Se | 0.012~0.775 | 0.143 | 31.8 | | 残渣态Se | 0.055~0.627 | 0.172 | 43.0 | | 加和2) | 0.078~1.561 | 0.367 | 89.1 | | 铁锰氧化态Se | 0.001~0.016 | 0.005 | 1.5 | | 全Se | 0.113~1.846 | 0.443 | 100 | | pH | 7.99~9.06 | 8.56 | — |
|
Statistical table of morphological eigenvalues of selenium species(n=50)
|
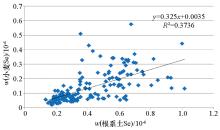
|
Linear model of Se in wheat and root soil(n=161)
|
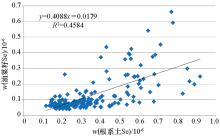
|
Linear model of Se in rapeseed and root soil(n=173)
|
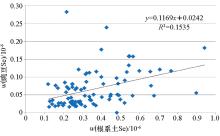
|
Linear model of Se in pea and root soil(n=88)
|
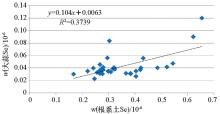
|
Linear model of Se in garlic and root soil(n=35)
|

| pH | 样本数 | 酸碱性 | pH | | 富集系数/% | | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | | pH≤7.5 | 7 | 中酸性 | 7.37 | 6.47 | 6.96 | | 73.3 | 25.4 | 53.6 | | pH>7.5 | 16 | 碱性 | 8.85 | 7.78 | 8.24 | | 89.5 | 40.7 | 57.2 |
|
Statistical table of Se in forage grass and root soil
|
| [1] |
齐玉薇, 史长义. 硒的生态环境与人体健康[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2005, 22(2):63-66.
|
| [1] |
Qi Y W, Shi C Y. Se ecological environment and human boby health[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2005, 22(2): 63-66.
|
| [2] |
李家熙, 张光弟, 葛晓立, 等. 人体硒缺乏与过剩的地球化学环境特征及其预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2000.
|
| [2] |
Li J X, Zhang G D, Ge X L, et al. Prediction and geochemical environmental chatacter of human selenium imbalances[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2000.
|
| [3] |
陈亮, 李桃. 元素硒与人体健康[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2004, 21(3):58-59.
|
| [3] |
Chen L, Li T. Selenium and human boby health[J]. Studies of Trace Elements and Health, 2004, 21(3): 58-59.
|
| [4] |
尹红星, 张殊佳, 邓学仿, 等. 硒的抗肿瘤作用研究综述[J]. 大连大学学报, 2008, 29(6):18-25.
|
| [4] |
Yin H X, Zhang S J, Deng X F, et al. A review of the antitumoreffect of selenium[J]. Journal of Dalian University, 2008, 29(6): 18-25.
|
| [5] |
张丽珊, 朱岩, 可夫, 等. 东北大骨节病区主要土壤腐殖酸硒与大骨节病关系的研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 1990, 1(4):333-337.
|
| [5] |
Zhang L S, Zhu Y, Ke F, et al. Study on relations between Kaschin-back disease and content of selenium bounded byhumic acids in Northest China[J]. Journal of Applied Ecology, 1990, 1(4): 333-337.
|
| [6] |
赵少华, 宇万太, 张璐, 等. 环境中硒的生物地球化学循环和营养调控及分异成因[J]. 生态学杂志, 2005, 24(10):1197-1203.
|
| [6] |
Zhao S H, Yu W T, Zhang L, et al. Biogeochemical cycling of selenium nutrition adjustment and differentiation canuse in environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2005, 24(10): 1197-1203.
|
| [7] |
崔剑波. 生态环境中的生命元素硒与健康的研究[J]. 生态学进展, 1989, 6(4):243-251.
|
| [7] |
Cui J B. Study on selenium of life elements and health in ecological environment[J]. Development on Ecology, 1989, 6(4): 243-251.
|
| [8] |
国土资源部中国地质调查局. 中国耕地地球化学调查报告(2015)[R]. 北北京:国土资源部中国地质调查局, 2015.
|
| [8] |
Ministry of Land and Resources China Geological Survey. Survey report on geochemistry of cultivated land in China(2015)[R]. Beijing: Ministry of Land and Resources China Geological Survey, 2015.
|
| [9] |
彭祚全, 张欣, 牟敏, 等. 富硒食品含硒量范围标准的研究[J]. 微量元素与健康研究, 2013, 30(1):41-43.
|
| [9] |
Peng Z Q, Zhang X, Mu M, et al. Study on the standand of selenium content range of selenium-enriched Food J[J]. The Micronutrient, 2013, 30(1): 41-43.
|
| [10] |
中国富硒农业产业技术创新联盟. 中国富硒农业发展蓝皮书[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2016.
|
| [10] |
China Selenium-rich Agricultural Industry Technology Innovation Alliance. China’s selenium-rich agricultural development blue book[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2016.
|
| [11] |
自然资源部中国地质调查局. DD2019-10 天然富硒土地划定与标识(试行)[S]. 2019.
|
| [11] |
China Geological Survey, Ministry of Natural Resources. DD2019-10 Delimitation and the logo for natural selenium-enriched land[S]. 2016.
|
| [12] |
黑龙江省质量技术监督局. DB23/T 2071—2018 富硒土壤评价要求[S]. 2018.
|
| [12] |
The Quality and Technology Supervision Bureauc of Heilongjiang Province. DB23/T 2071—2018 Assessment requirements for selenium enriched soil[S]. 2018.
|
| [13] |
河南省市场监督管理局. DB41/T 1871—2019富硒土壤硒含量要求[S]. 2019.
|
| [13] |
The Quality and Technology Supervision Bureauc of Henan Province. DB41/T 1871—2019 Selenium content requirements in selenium-rich soils[S]. 2019.
|
| [14] |
宁夏回族自治区质量技术监督局. DB64/T 1220—2016 宁夏富硒土壤标准[S]. 2016.
|
| [14] |
The Quality and Technology Supervision Bureauc of Ningxia Province. DB64/T 1220—2016 Seleium-enriched soil standards of Ningxia[S]. 2016.
|
| [15] |
河北省市场监督管理局. DB13/T 5318—2020天然富硒土地判定要求[S]. 2020.
|
| [15] |
The Quality and Technology Supervision Bureauc of Hebei Province. DB13/T 5318—2020 The determination requirements for natural selenium-enriched land[S]. 2020.
|
| [16] |
李春亮, 李洚, 杨菁, 等. 甘肃省富硒土壤标准研究与探讨[J]. 西北地质, 2021, 54(1):242-246.
|
| [16] |
Li C L, Li J, Yang J, et al. Study and discussion on standard of selenium-rich in Gansu Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2021, 54(1): 242-246.
|
| [17] |
广西壮族自治区质量技术监督局. DB45/T 1442—2016 土壤中全硒含量的分级要求[S]. 2016.
|
| [17] |
The Quality and Technology Supervision Bureauc of Guangxi Province. DB45/T 1442—2016 Grading requirements for total selenium content soil[S]. 2016.
|
| [18] |
DZ/T 0295—2016 土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 2016.
|
| [18] |
DZ/T 0295— DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification of land quality geochemical assessment[S]. 2016.
|
| [19] |
DZ/T 0258—2014 多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1:250000)[S]. 2014.
|
| [19] |
DZ/T 0258—2014 Specification of multi-purpose regional geochemical survey (1:250000)[S]. 2014.
|
| [20] |
张亚峰, 苗国文, 马强, 等. 青海东部碱性土壤中硒的形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5):1138-1144.
|
| [20] |
Zhang Y F, Miao G W, Ma Q, et al. Distribution characteristics of Se speciation of alkaline soil in eastern Qinghai[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5): 1138-1144.
|
| [21] |
郎春燕, 黄秀丽, 李小娇. 成都东郊稻田土壤中硒的形态的分布特征[J]. 西南农业学报, 2013, 26(2):642-646.
|
| [21] |
Lang C Y, Huang X L, Li X J. Distribution of selenium species in rice paddy soils of east suburb in Chengdu[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 26(2): 642-646.
|
| [22] |
郦逸根, 徐静, 李琰, 等. 浙江富硒土壤中硒赋存形态特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2007, 31(2):95-109.
|
| [22] |
Li Y G, Xu J, Li Y, et al. The modes of occurrence of selenium in selenium-rich soil of Zhejiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 31(2): 95-109.
|
| [23] |
青海省标准化协会. T/QAS 011—2020青海省农产品硒含量分类标准[S]. 2019.
|
| [23] |
Qinghai Provincial Standardization Association. T/QAS 011—2020 The classification standard of selenium content of agricultural products in Qinghai Province[S]. 2019.
|
| [24] |
成晓梦, 马荣荣, 彭敏, 等. 中国大宗作物及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤标准建议[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1367-1372.
|
| [24] |
Cheng X M, Ma R R, Peng M, et al. Characteristics of selenium in crops and roots in China and recommendations for selenium-enriched soil standards[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1367-1372.
|
| [25] |
时章亮, 金立新, 廖超, 等. 四川雷波县重点耕地区土壤硒含量特征及其成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(5):1253-1260.
|
| [25] |
Shi Z L, Jin L X, Liao C, et al. Content characteristics and genesis of soil selenium in important cultivated areas of Leibo County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(5): 1253-1260.
|
| [26] |
李永华, 王五一, 杨林生, 等. 陕西土壤中水溶态硒、氟的含量及其在生态环境的表征[J]. 环境化学, 2005, 24(3):279-283.
|
| [26] |
Li Y H, Wang W Y, Yang L S, et al. Concentration and environmental significance of water soluble-Se and water soluble-F in soils of south Shanxi province[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2005, 24(3): 279-283.
|
| [27] |
马强, 姬丙艳, 张亚峰, 等. 青海东部土壤及生物体中硒的地球化学特征[J]. 地球科学进展, 2012, 27(10):1148-1152.
|
| [27] |
Ma Q, Ji B Y, Zhang Y F, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium in soils and organisms in the east of Qinghai Province[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2012, 27(10): 1148-1152.
|
| [28] |
中国营养学会. 中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量(2013版)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.
|
| [28] |
Chinese Academy of Nutrition. Reference intake of dietary nutrients for Chinese residents(2013)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014.
|
| [29] |
王惠艳, 曾道明, 郭志娟, 等. 天然富硒土地划定的富硒阈值[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(1):333-342.
|
| [29] |
Wang H Y, Zeng D M, Guo Z J, et al. Selenium threshold for the delimitation of natural selenium-enriched land[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(1): 333-342.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Ya-Feng, JI Bing-Yan, SHEN Xiao, YAO Zhen, MA Qiang, WANG Shuai, HE Lian-Zhen, HAN Wei-Ming. Formation mechanisms and significance of saline-lacustrine Se-rich soils in the Xining Basin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 470-476. |
| [2] |
WANG Zhi-Qiang, YANG Jian-Feng, SHI Tian-Chi. A preliminary study of Se-rich soil in the Shizuishan area, Ningxia and its potential for application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 228-237. |
|
|
|
|

