|
|
|
| Key techniques for seismic data processing of deep metal deposits:A case study of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield in Inner Mongolia |
YUE Hang-Yu1,2,3,4( ), WANG Xiao-Jiang2,3( ), WANG Xiao-Jiang2,3( ), WANG Lei5, CHEN Xiao-Qiang1, JIANG Chun-Xiang2,3, LI Pei2,3, ZHANG Bao-Wei1,2,3 ), WANG Lei5, CHEN Xiao-Qiang1, JIANG Chun-Xiang2,3, LI Pei2,3, ZHANG Bao-Wei1,2,3 |
1. Center for Geophysical Survey,China Geological Survey,Langfang 065000,China
2. Institute of Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration,Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,Langfang 065000,China
3. National Center for Geological Exploration Technology,Langfang 065000,China
4. School of Geophysics and Information Technology,China University of Geosciences (Beijing),Beijing 100083,China
5. Liaoning Institute of Geology and Mineral Resources Co., Ltd.,Shenyang 110032,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Deep metal deposits tend to be associated with heterogeneous geological bodies on different scales.Moreover,their orefields mostly lie in areas with complex geological structures,developed faults,and intense lithological changes and have complex surface conditions and structures.As a result,the seismic data of metal deposits frequently originate from complex and variable seismic wave fields suffering the mutual inference of multiple types of waves.Therefore,the seismic data have extremely low signal-to-noise ratios,which severely restricts the seismic interpretation of metal deposits and the prediction of concealed orebodies. With the 2D seismic data of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield in Inner Mongolia as a case study,this study explored the key techniques for the seismic data processing of deep metal deposits.Specifically,this study analyzed the characteristic of seismic data of the Chaganhua molybdenum deposit and summarized the difficulties with seismic data processing of the metal deposit.Based on these,this study developed a set of processes for the data processing of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield.The actual processing results agree well with the known orebody distribution in the geological borehole section.To be specific,zones with thick ore bodies generated strong reflected energy,while thinner ore bodies exhibited low-amplitude reflected waves.The results of this study can provide strong support for inferring geological structures and delineating concealed orebodies in the study area.
|
|
Received: 27 August 2021
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
WANG Xiao-Jiang
E-mail: yhangyu_cgs@163.com;wxiaojiang@mail.cgs.gov.cn
|
|
|
|
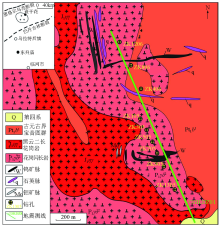
|
The location of 2D seismic line in Chaganhua molybdenum deposit
|
|
The original records of different position on the survey line in Chaganhua molybdenum mining area
|
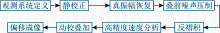
|
Seismic data processing flow of Chaganhua molybdenum ore area
|
|
Comparison of single-shot record before (a) and after (b) statics of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
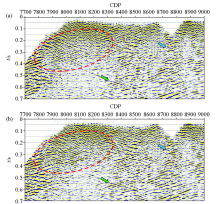
|
Comparison of stack section before (a) and after (b) statics of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
Comparison of single-shot record before (a) and after (b) true-amplitude recovery of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
Comparison of stack section before (a) and after (b) true-amplitude recovery of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
Comparison of single-shot record before (a) and after (b) noise attenuation of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
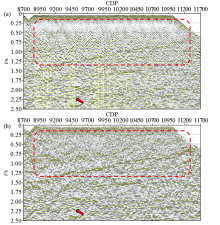
Comparison of stack section before (a) and after (b) noise attenuation of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
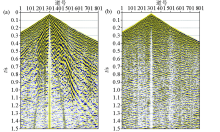
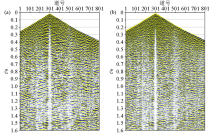
Comparison of single-shot record before (a) and after (b) deconvolution of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
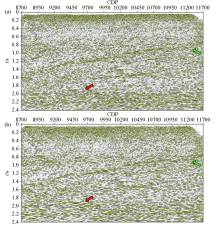
Comparison of stack section before (a) and after (b) deconvolution of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
|
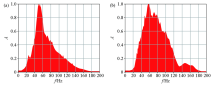
Spectrum comparison before (a) and after (b) deconvolution of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
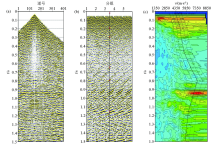
|
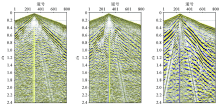
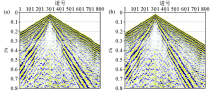
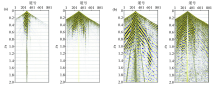
Seismic high-precision velocity analysis of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
a—controlled gathers;b—stack interval;c—velocity spectrum
|
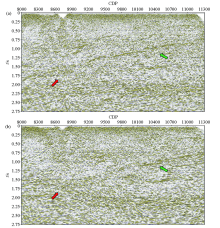
|
Section comparison before (a) and after (b) migration imaging of the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
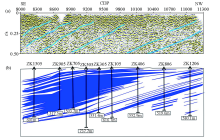
|
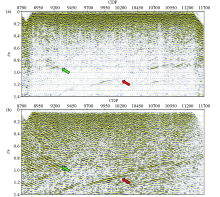
Magnified display of seismic section of metallic ore(a) and geological section of known ore body(b) in the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
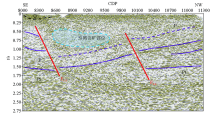
|
The result section of seismic data processing in the Chaganhua molybdenum orefield
|
| [1] |
Green A G, Mair J A. Subhorizontal fractures in a granitic pluton:Their detection and implications for radioactive waste disposal[J]. Geophysics, 1983, 48(11):1428-1449.

|
| [2] |
巩向博. 金属矿地震高精度成像与数据处理方法研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2011.
|
| [2] |
Gong X B. High precision imaging and applied research of data processing for mineral seismic exploration[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2011.
|
| [3] |
姜春香. 金属矿地震资料降矂处理技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2015.
|
| [3] |
Jiang C X. The serial denoising technology research in metal seismic data processing[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2015.
|
| [4] |
勾丽敏, 刘学伟, 雷鹏, 等. 金属矿地震勘探技术方法研究综述——金属矿地震勘探技术及其现状[J]. 勘探地球物理进展, 2007, 30(1):16-24.
|
| [4] |
Gou L M, Liu X W, Lei P, et al. Review of seismic survey in mining exploration:Theory and reflection seismic method[J]. Progress in Exploration Geophysics, 2007, 30(1):16-24.
|
| [5] |
Eaton D W, Milkereit B, Salisbury M. Seismic methods for deep mineral exploration: Mature technologies adapted to new targets[J]. The Leading Edge, 2003, 22(6):580-585.

|
| [6] |
Malehmir A, Durrheim R, Bellefleur G, et al. Seismic methods in mineral exploration and mine planning: A general overview of past and present case histories and a look into the future[J]. Geophysics, 2012, 77(5):WC173-WC190.

|
| [7] |
Malehmir A, Maries G, Bäckström E, et al. Developing cost-effective seismic mineral exploration methods using a landstreamer and a drophammer[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):10325.
|
| [8] |
徐明才, 高景华, 荣立新, 等. 从金属矿地震方法的试验效果探讨其应用前景[J]. 中国地质, 2004, 31(1):108-112.
|
| [8] |
Xu M C, Gao J H, Rong L X, et al. Application prospects of the seismic method as discussed from the experimental effects of the method for metal exploration[J]. Geology in China, 2004, 31(1):108-112.
|
| [9] |
徐明才, 高景华, 荣立新, 等. 散射波地震方法在蔡家营多金属矿区的试验研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2003, 27(1):49-54.

|
| [9] |
Xu M C, Gao J H, Rong L X, et al. An experimental study of seismic scattering event method in the Caijiaying polymetallic ore district[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 27(1):49-54.

|
| [10] |
徐明才, 高景华, 荣立新, 等. 地面地震层析成像和高分辨率地震联合勘探技术[J]. 地质与勘探, 2005, 41(4):83-87.
|
| [10] |
Xu M C, Gao J H, Rong L X, et al. Combining exploration technique of the ground seismic tomography and the high resolution seismic method[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2005, 41(4):83-87.
|
| [11] |
徐明才, 荣立新, 刘建勋, 等. 地震方法在拜仁达坝银铅锌多金属矿区的应用试验研究[J]. 地质与勘探, 2007, 43(4):61-64.
|
| [11] |
Xu M C, Rong L X, Liu J X, et al. Application of seismic method at Bairendaba Ag-Pb-Zn polymetallic deposit in Inner Mongolia[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2007, 43(4):61-64.
|
| [12] |
徐明才, 姜春香, 柴铭涛, 等. 内蒙古准苏吉花铜钼矿区三分量地震试验研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2016, 31(3):1229-1236.
|
| [12] |
Xu M C, Jiang C X, Chai M T, et al. Three-component seismic experimental study of the Zhunsujihua Cu-Mo mine in Inner Mongolia[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2016, 31(3):1229-1236.
|
| [13] |
徐明才, 周建勇, 柴铭涛, 等. 内蒙古准苏吉花斑岩型钼矿及外围反射地震探测[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(4):639-647.

|
| [13] |
Xu M C, Zhou J Y, Chai M T, et al. Seismic reflection detection in the Zhunsujihua porphyry molybdenum ore district and its periphery, Inner Mongolia[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4):639-647.

|
| [14] |
吕庆田, 侯增谦, 史大年, 等. 铜陵狮子山金属矿地震反射结果及对区域找矿的意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2004, 23(3):390-398.
|
| [14] |
Lyu Q T, Hou Z Q, Shi D N, et al. Tentative seismic reflection study of Shizishan Orefield in Tongling and its significance in regional exploration[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2004, 23(3):390-398.
|
| [15] |
吕庆田, 史大年, 赵金花, 等. 深部矿产勘查的地震学方法:问题与前景——铜陵矿集区的应用实例[J]. 地质通报, 2005, 24(3):211-218.
|
| [15] |
Lyu Q T, Shi D N, Zhao J H, et al. Seismic method for deeper mineral exploration:Problems and prospects——A case study of the Tongling ore district[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2005, 24(3):211-218.
|
| [16] |
吕庆田, 韩立国, 严加永, 等. 庐枞矿集区火山气液型铁、硫矿床及控矿构造的反射地震成像[J]. 岩石学报, 2010, 26(9):2598-2612.
|
| [16] |
Lyu Q T, Han L G, Yan J Y, et al. Seismic imaging of volcanic hydrothermal iron sulfur deposits and its hosting structure in Luzong ore district[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2010, 26(9):2598-2612.
|
| [17] |
王俊秋, 林君, 姜弢, 等. 可控震源地震方法在金昌铜镍矿区的应用实验[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2011, 41(5):1617-1622.
|
| [17] |
Wang J Q, Lin J, Jiang T, et al. Experiment and application of controlled vibrator seismic method at Jinchang Copper-Nickel metal deposit[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2011, 41(5):1617-1622.
|
| [18] |
刘建勋, 周建勇, 徐明才, 等. 地震勘查技术在喀拉通克矿区的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(3):437-444.

|
| [18] |
Liu J X, Zhou J Y, Xu M C, et al. The application of seismic exploration technology in the Kalatongke orefield[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(3):437-444.

|
| [19] |
周建勇, 徐明才, 刘建勋, 等. 反射地震成像技术在新疆喀拉通克铜镍矿区的应用[J]. 地质与勘探, 2016, 52(5):910-917.
|
| [19] |
Zhou J Y, Xu M C, Liu J X, et al. Application of seismic reflection imaging in the Karatungk Cu-Ni deposit of Xinjiang[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2016, 52(5):910-917.
|
| [20] |
李光辉, 李月. 金属矿山地地区地震勘探随机噪声的波动方程模拟[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(12):4576-4593.
|
| [20] |
Li G H, Li Y. Wave equation modeling of random noise in seismic exploration for metal deposits in mountainous areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(12):4576-4593.
|
| [21] |
张保卫, 王小江, 张凯. 新疆喀拉通克铜镍矿地震资料噪声分析与压制[J]. 物探与化探, 2016, 40(4):771-777.

|
| [21] |
Zhang B W, Wang X J, Zhang K. Analysis and suppression of seismic data noise in the Kalatongke copper-nickel deposit,northern Xinjiang[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 40(4):771-777.

|
| [22] |
郑升, 马海涛, 李月. 基于自适应阈值RCSST变换的金属矿山地地区地震信号随机噪声消减[J]. 地球物理学报, 2019, 62(10):4020-4027.
|
| [22] |
Zheng S, Ma H T, Li Y. Reduction of seismic random noise in mountainous metallic mines based on adaptive threshold RCSST[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2019, 62(10):4020-4027.
|
| [1] |
ZHU Jian-Bing, GAO Zhao-Qi, TIAN Ya-Jun, LIANG Xing-Cheng. Globally optimized seismic impedance inversion with lateral constraints and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6): 1477-1484. |
| [2] |
Rui-Qing HU, Yan-Chun WANG, Zhan-Wei YUE, Qi WANG. Feature extraction in wavelet domain and its application to shallow seismic data surface-wave suppression[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(6): 1228-1236. |
|
|
|
|

