|
|
|
| Application of the high-density resistivity method in detailed exploration of superficial paleochannels in Xiong'an New Area |
SU Yong-Jun1,2,3( ), CAO Zhan-Ning1,3( ), CAO Zhan-Ning1,3( ), ZHAO Geng-Xin1,3, HU Xiang-Yun2, FAN Jian4, ZHANG Jing1,3, FAN Cui-Song1,3, HUANG Zhong-Feng1,3 ), ZHAO Geng-Xin1,3, HU Xiang-Yun2, FAN Jian4, ZHANG Jing1,3, FAN Cui-Song1,3, HUANG Zhong-Feng1,3 |
1. Tianjin Center,China Geological Survey,Tianjin 300170,China
2. School of Geophysics and Geomatics,China University of Geosciences,Wuhan 430074,China
3. Geological Science & Technology Innovation Center of North China,Tianjin 300170,China
4. Tianjin North China Geological Exploration Bureau,Tianjin 300170,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To explore in detail superficial paleochannels in Xiong'an New Area,this study investigated two profiles in the study area using the high-density resistivity method based on previous remote sensing.The interpretation results were verified through drilling.The distribution range of the paleochannels that was delineated using the high-density resistivity method was more accurate than that obtained from remote sensing.This study determined that the superficial paleochannels in the study area exhibit curved,tortuous,and braided planar distribution,achieving excellent application performance in the detailed exploration of superficial paleochannels.This study provided a new idea for future exploration and study of superficial paleochannels and can be used as a reference for the selection of methods used to investigate paleochannels in similar geological conditions.
|
|
Received: 01 June 2022
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
CAO Zhan-Ning
E-mail: syj95123@163.com;guffawn@foxmail.com
|
|
|
|

| 岩 性 | 常见电阻率值/(Ω·m) | | 黏土、粉质黏土 | 5~25 | | 砂质黏土 | 30~55 | | 细砂、粉砂 | 35~90 | | 中细砂 | 75~140 |
|
Statistics of physical parameters of rock(soil)layer in the study area
|
9])
">
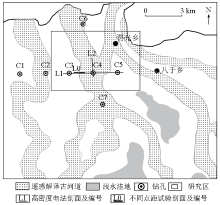
|
The survey line map of the study area(revised from reference[9])
|
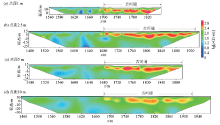
|
Comparison of test inversion results of high-density resistivity method with different point spacings of L0 line
|

| 点距 | 指标/m | x/m | 均值/m | | 1690 | 1710 | 1730 | 1750 | 1770 | 1790 | 1810 | 1830 | 1850 | 1870 | 1890 | 1910 | 1930 | | 1 m | 上顶板标高 | 11.83 | 8.88 | 8.44 | 9.62 | 8.00 | 9.18 | | | | | | | | 9.33 | | 下底板标高 | 1.80 | 2.39 | 5.05 | 0.92 | 0.92 | 0.18 | | | | | | | | 1.88 | | 砂层厚度 | 10.03 | 6.49 | 3.39 | 8.70 | 7.08 | 9.00 | | | | | | | | 7.45 | | 2.5 m | 上顶板标高 | 11.25 | 8.10 | 8.29 | 9.68 | 8.49 | 8.89 | 6.91 | 8.69 | 9.28 | 8.49 | 11.45 | 11.25 | 10.27 | 9.31 | | 下底板标高 | 4.74 | 2.17 | 6.71 | 2.37 | -1.18 | -1.58 | -5.92 | 0.40 | 3.56 | -2.37 | 4.15 | 3.75 | 7.50 | 1.87 | | 砂层厚度 | 6.51 | 5.92 | 1.58 | 7.30 | 9.67 | 10.46 | 12.83 | 8.29 | 5.72 | 10.86 | 7.30 | 7.50 | 2.76 | 7.44 | | 5 m | 上顶板标高 | 10.43 | 7.28 | 5.51 | 9.64 | 6.49 | 4.52 | 7.87 | 8.66 | 7.67 | | | | | 7.56 | | 下底板标高 | 4.13 | 2.15 | 1.17 | -2.38 | -1.59 | -3.36 | -6.12 | -3.56 | 1.37 | | | | | -0.91 | | 砂层厚度 | 6.31 | 5.12 | 4.34 | 12.02 | 8.08 | 7.88 | 13.99 | 12.22 | 6.31 | | | | | 8.47 | | 10 m | 上顶板标高 | 9.05 | 3.84 | 9.67 | 7.38 | 6.55 | 5.51 | 2.80 | 6.34 | 4.46 | 4.67 | 6.34 | | | 6.06 | | 下底板标高 | 1.97 | 1.97 | -1.57 | -4.07 | -4.07 | -6.78 | 0.72 | -3.03 | -1.57 | -3.45 | -0.95 | | | -1.90 | | 砂层厚度 | 7.08 | 1.87 | 11.24 | 11.45 | 10.62 | 12.29 | 2.08 | 9.37 | 6.04 | 8.12 | 7.29 | | | 7.95 |
|
Statistics of sand thickness of paleochannels,upper roof and lower floor by inversion interpretation of high-density resistivity method with different point spacings
|
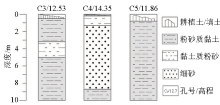
|
The geological column of boreholes
|
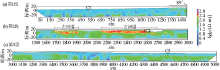
|
Inversion result and interpretation of L1 high density resistivity method
|
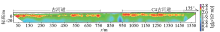
|
Inversion result and interpretation of L2 high density resistivity method
|
|
Distribution range of shallow paleochannels by remote sensing interpretation and the high density resistivity method interpretation
a—distribution range of paleochannels by remote sensing interpretation;b—distribution range of shallow paleochannels by geophysical interpretation
|
| [1] |
郝爱兵, 吴爱民, 马震, 等. 雄安新区地上地下工程建设适宜性一体化评价[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(5):513-522.
|
| [1] |
Hao A B, Wu A M, Ma Z, et al. A study of engineering construction suitability integrated evaluation of surface-underground space in Xiong’an New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(5):513-522.
|
| [2] |
吴忱, 王子惠, 许清海. 河北平原的浅埋古河道[J]. 地理学报 1986, 41(4):332-340
|
| [2] |
Wu C, Wang Z H, Xu H Q. The shallow buried paleochannels in Hebei plain[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1986, 41(4):332-340.
|
| [3] |
吴忱, 朱宣清, 何乃华, 等. 华北平原古河道的形成研究[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 1991(2):188-197.
|
| [3] |
Wu C, Zhu X Q, He N H, et al. Study on the formation of paleochannels in North China Plain[J]. Science China (B), 1991(2):188-197.
|
| [4] |
秦磊, 詹华明, 宋小军, 等. 基于遥感技术的静海县浅埋古河道分析[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2008, 31(4):321-327.
|
| [4] |
Qin L, Zhan H M, Song X J, et al. Research on the distribution and characteristic of the shallow buried ancient channel in Jinghai county[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2008, 31(4):321-327.
|
| [5] |
赵艳霞, 徐全洪, 刘芳圆, 等. 近20年来中国古河道研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展, 2013, 32(1):3-19.
|
| [5] |
Zhao Y X, Xu Q H, Liu F Y, et al. Progresses of palaeochannel studies in China in the past 20 years[J]. Progress in Geography, 2013, 32(1):3-19.
|
| [6] |
谢小国, 魏良帅, 王绪本, 等. 半航空顺变电磁法在古河道结构探测中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2021, 36(4):1734-1742.
|
| [6] |
Xie X G, Wei L S, Wang X B, et al. Application of semi-airborne TEM to structure exploration in the old channels[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2021, 36(4):1734-1742.
|
| [7] |
籍增贤. 物探及遥感资料在腾格尔坳陷古河谷(道)研究中的应用[J]. 铀矿地质, 2007, 23(2):96-100.
|
| [7] |
Ji Z X. Application of geophysical and remote sensing data in the study of pa;eovalley in the Tengeer depression[J]. Uranium Geology, 2007, 23(2):96-100.
|
| [8] |
张艳国, 周永贵. 综合物探方法在浅埋古河道调查中的应用研究[J], 工程地球物理学报, 2021, 18(3):386-390.
|
| [8] |
Zhang Y G, Zhou Y G. Study on the application of integrated geophysical method in the investigation of shallow-buried ancient channel[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2021, 18(3):386-390.
|
| [9] |
张竞, 马震, 吴爱民, 等. 基于岩性光谱特征的雄安新区地面古河道识别研究[J]. 地球学报, 2018, 39(5):542-548.
|
| [9] |
Zhang J, Ma Z, Wu A M, et al. A study of Paleochannels interpretation by the spectrum of lithology in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2018, 39(5):542-548.
|
| [10] |
胡镜荣, 石凤英. 华北平原古河道发育的环境条件及其沉积特征[J]. 地理研究, 1983, 2(4):48-59.
|
| [10] |
Hu J R, Shi F Y. The environmental conditions of the development of paleoghannels in the Hua Bei (North China) plain and their sedimental characteristics[J]. Geographical Research, 1983, 2(4):48-59.
|
| [11] |
邹承杰. 河北省容城县中更新世以来的钻孔沉积物地球化学特征及古气候演化[D]. 石家庄: 河北地质大学, 2008.
|
| [11] |
Zou C J. Geochemical characteristics of borehole sediments and paleoclimatic evolution since the middle pleistocene in Rongcheng county,Hebei,China[D]. Shijiazhuang: Heibei Dizhi University, 2008.
|
| [12] |
马岩, 李洪强, 张杰, 等. 雄安新区城市地下空间探测技术研究[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(4):535-542
|
| [12] |
Ma Y, Li H Q, Zhang J, et al. Geophysical technology for underground space exploration in Xiong'an New Area[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(4):535-542.
|
| [13] |
吴曲波, 陈聪, 杨龙泉. 二连盆地中部古河道砂岩型铀矿综合地球物理响应特征研究[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(8):2521 -2536.
|
| [13] |
Wu Q B, Chen C, Yang L Q. Study of integrated geophysical characteristics of paleo-valley sandstone-type uranium deposits in the middle of the Erenhot basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(8):2521-2536.
|
| [14] |
苏永军, 王绪本, 罗建群. 高密度电阻率法在三星堆壕沟考古勘探中应用研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2007, 22(1):268-272.
|
| [14] |
Su Y J, Wang X B, Luo J Q. The archaeological application of high-density resistivity method to ditch exploration on Sanxingdui Site[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2007, 22(1):268-272.
|
| [15] |
王俊, 李家存, 张迪. 基于多源遥感数据的古河道识别方法——以磴口地区古黄河河道为例[J]. 首都师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 40(1):70-77.
|
| [15] |
Wang J, Li J C, Zhang D. Identification of ancient river channels based on multi-source remote sensing data:Take the ancient Yellow River channel in Dengkou area as an example[J]. Journal of Capital Normal University:Natural Science Edition, 2019, 40(1):70-77.
|
| [16] |
郭龙凤, 黄少文, 李亮亮, 等. 综合物探方法在古河道型地下水库工程建设中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2018, 33(3):1205-1212.
|
| [16] |
Guo L F, Huang S W, Li L L, et al. Application and research of integrated geophysical method in construction of paleochannel groundwater reservoir[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 33(3):1205-1212.
|
| [17] |
姜国庆, 黄敬军, 张大莲, 等. 徐州地区全新世古河道地电特征研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(2):422-428.
|
| [17] |
Jiang G Q, Huang J J, Zhang D L, et al. Research on geoelectric characteristics of Holocene ancient channels in Xuzhou area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(2):422-428.
|
| [18] |
苏永军, 范翠松, 赵更新, 等. 综合电法在探测海水入侵界面中的研究与应用——以莱州湾地区为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(3):704-708.
|
| [18] |
Su Y J, Fan C S, Zhao G X, et al. Research and application of comprehensive electrical method in detecting saltwater intrusion interface:A case study of Laizhou Bay area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3):704-708.
|
| [19] |
李富, 欧阳渊, 刘洪, 等. 高密度电阻率法与地质雷达法在土壤厚度调查中应用效果——以西昌市土壤厚度调查为例[J]. 华北地质, 2021, 44(1): 27-32.
|
| [19] |
Li F, Ouyang Y, Liu H, et al. Application of high density resistivity and geological radar in soil thickness survey:a case study of the soil thickness survey in Xichang[J]. North China Geology, 2021, 44(1):27-32.
|
| [20] |
郭高轩, 刘文臣, 辛宝东, 等. 利用电测深法探测泃河与错河古河道[J]. 工程勘察, 2010, 38(4):87-90.
|
| [20] |
Guo G X, Liu W C, Xin B D et al. Old course detection of Juhe and Cuohe river by electric sounding method[J]. Geotechnical Investigation&Surveying, 2010, 38(4):87-90.
|
| [21] |
王文杰, 郝一, 薄海军, 等. 包头市固阳县矿集区高密度电阻率法找水定井实例分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):869-881.
|
| [21] |
Wang W J, Hao Y, Bao H J, et al. A case analysis of multielectrode resistivity method for determining a well location in groundwater prospecting in the ore concentration area of Guyang County’Baotou city[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):869-881.
|
| [22] |
陈学群, 李成光, 田婵娟, 等. 高密度电阻率法在咸水入侵监测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1347-1353.
|
| [22] |
Chen X Q, Li C G, Tian C J, et al. The application of high density electrical resistivity method to monitoring saltwater intrusion[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1347-1353.
|
| [23] |
李忠平. 基于高密度电法温纳装置的三维电阻率反演应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2020, 35(3):970-975.
|
| [23] |
Li Z P. Application of 3-D resistivity inversion based on Winner device of high density electricity method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2020, 35(3):970-975.
|
| [24] |
范剑, 马为, 夏训银, 等. 高密度电阻率法在天津市七里海牡蛎礁博物馆选址中的应用[J]. 地球物理进展, 2018, 32(2):790-796.
|
| [24] |
Fan J, Ma W, Xia X Y, et al. Application of high density resistivity method on site-selection for the oyster reefs museum in Qilihai,Tianjin[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2018, 32(2):790-796.
|
| [25] |
杜成亮, 甘伏平, 张远海, 等. 地球物理方法探索隐伏岩溶古河道——以湖南郴州万华岩为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2018, 37(4):624-631.
|
| [25] |
Du C P, Gan F P, Zhang Y H, et al. Exploratory research on buried karst paleochannels comprehensive geophysical methods:A case study of Wanhua cave system,Chenzhou,Hunan Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2018, 37(4):624-631.
|
| [26] |
罗延钟. 高密度电阻率法的2.5维反演软件[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2006, 28(3):187-193.
|
| [26] |
Luo Y Z. 2.5-diversion software for high density resistivity[J]. Computing Techniques for Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 28(3):187-193.
|
| [1] |
ZHOU Jian-Bing, LUO Rui-Heng, HE Chang-Kun, PAN Xiao-Dong, ZHANG Shao-Min, PENG Cong. New geophysical evidence for karst water-bearing seepage pathways in the Xiaohewei reservoir,Wenshan City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 707-717. |
| [2] |
LIU Si-Xin, SHI Wei, SONG Zi-Hao, CHEN Chun-Lin, DAI Zheng. Identification of footwalls and roofs of coal seams in underground coal mines using borehole radar[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 365-371. |
|
|
|
|

