|
|
|
| Application of the integrated engineering geophysical exploration technology in the predrilling stage of shale gas well platforms in southern Sichuan Province |
YU Chang-Heng1( ), ZHENG Jian2, ZHANG Xu-Lin1, ZHOU Hao2, WANG An-Ping1, LIU Lei1, LI Yi1 ), ZHENG Jian2, ZHANG Xu-Lin1, ZHOU Hao2, WANG An-Ping1, LIU Lei1, LI Yi1 |
1. Sichuan Zhongcheng Coalfield Geophysical Engineering Institute Co., Ltd., Chengdu 610072,China
2. Sichuan Changning Gas Development Co., Ltd., Chengdu 610056,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Southern Sichuan Province has widely developed karsts and densely distributed coal mine goafs, which cannot be accurately detected and identified using a single existent exploration method. Consequently, large-scale and industrial drilling for shale gas is prone to induce failures and complex events. In light of the complex topographic and geological conditions in southern Sichuan, this study conducted tests and comparative analysis using multiple engineering geophysical exploration methods including electrical resistivity imaging, shallow seismic method, transient electromagnetic method, audio-magnetotelluric method, and microtremor survey method. As a result, an integrated engineering geophysical exploration technology for shale gas well platforms in southern Sichuan was formed and applied to the construction of shale gas well platforms. As indicated by drilling results, the integrated technology can effectively identify unfavorable geological bodies (e.g., shallow karsts, coal mine goafs, and overburdens) at a depth of less than 1000 m and provide technical support for siting shale gas well platforms, optimizing casing programs, predicting drilling risks, shortening drilling cycles, and protecting ecological environment, with remarkable economic, social, and ecological benefits having been achieved. Moreover, this integrated technology provides a technical guarantee for the construction of both the Changning-Weiyuan national shale gas demonstration zone and the southern Sichuan shale gas exploration and development pilot zone and accelerates the shale gas development in southern Sichuan.
|
|
Received: 20 April 2020
Published: 24 February 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
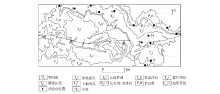
|
Distribution map of geological structure and test site in the study area
|

| 地层 | 主要岩性 | 标本数/块 | 电阻率/(Ω·m) | | 最小值~最大值 | 常见值 | | 第四系 | 全新统 | | 黏土、泥岩 | 65 | 10~135 | 80 | | 侏罗系 | 下统 | 自流井组 | 泥岩 | 50 | 46~107 | 77 | | 三叠系 | 上统 | 须家河组 | 泥岩
砂岩 | 80
110 | 44~290 | 130 | | 81~583 | 309 | | 中统 | 雷口坡组 | 灰岩
泥质灰岩 | 70
50 | 170~1529 | 1281 | | 501~1258 | 813 | | 下统 | 嘉陵江组
飞仙关组 | 灰岩
泥岩 | 85
60 | 395~11523 | 2445 | | 47~285 | 179 | | 二叠系 | 上统 | 长兴组
龙潭组 | 泥质灰岩
页岩 | 55
60 | 33~1324 | 38 | | 13~159 | 106 | | 中统 | 茅口组 | 灰岩 | 85 | 1023~11195 | 5231 | | 岩溶/断层/裂缝/采空区(充水) | 45 | 2~50 | 10 | | 岩溶/断层/裂缝/采空区(未充水) | 50 | 12000~120000 | 30000 |
|
Statistics of measured rock resistivity
|
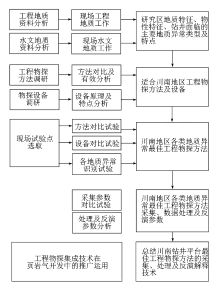
|
Research road
|

| 编号 | 方法 | 特点 | 勘查深度 | 解决问题 | | 1 | 工程地质+水文地
质相结合综合勘查 | 调查内容为:地层及其厚度、岩性特征、接触关系、构造位置、构造特征、地貌特征、面临的工程地质问题以及地表水、地下水类型、地下水分布规律、地下水补给、径流及排泄条件 | 以平台为中心,在600 m范围内进行调查,视情况扩大调查范围 | 地层界限及其厚度、岩性特征、接触关系、构造位置、构造特征、地貌特征、地表水系分布、地下水类型、地下水分布规律、地下水补给、径流及排泄条件 | | 2 | 浅层地震 | 1)探测精度高
2)构造破碎带、岩层界面识别能力强 | 100 m以浅 | 覆盖层基覆界面、构造破碎带的探测识别 | | 3 | 高密度电法 | 1)分布式设计,大电流、连续剖面测量
2)多种电极排列方式,能获取丰富的地电断面信息
3)具有电阻率剖面和电阻率测深双重性质 | 100 m以浅 | 覆盖层基覆界面、采空区、浅层岩溶以及构造破碎带的探测识别 | | 4 | 瞬变电磁法 | 1)断电后观测纯二次场,不受一次场干扰
2)对低阻层的分辨率高,能清晰、直观地显示探测目标埋藏的相对位置
3)受地形影响小
4)工作装置形式灵活多样,工作效率高 | 400 m以浅 | 采空区、中深部岩溶以及构造破碎带的探测识别 | | 5 | 微动 | 1)智能勘探,实时获得表征地质分层的面波速度曲线
2)适应环境能力强,不受电磁干扰影响
3)无需人工震源、安全、快捷、环保 | 1 000 m以浅 | 覆盖层基覆界面、采空区、深部岩溶以及构造破碎带的探测识别 | | 6 | 音频大地
电磁法 | 1)不受高阻层(如碳酸盐岩地区)影响
2)穿透深度大
3)装备轻便、适应于地形条件较差的地区 | 1 000 m以浅 | 区域性宏观构造破碎带控制、深部岩溶探测 |
|
Summary table of geophysical prospecting methods for pre-drilling engineering of shale gas platform in south Sichuan
|

| 序号 | 方法 | 试验点 | 地质异常类型 | 仪器型号 | 实验时间 | | 1 | 浅层地震法(反射波法、层析成像法) | 12 | 覆盖层 | 428lite数字地震仪 | 2020.07 | | 2 | 高密度电阻率法 | 1、5、12 | 构造破碎带、嘉陵江组岩溶、覆盖层 | N2电法测量系统 | 2020.07、2021.07 | | 3 | 音频大地电磁法 | 12、13 | 雷口坡组及嘉陵江组岩溶、龙潭组煤矿采空区 | Aether | 2020.07、2021.07 | | 4 | 微动 | 2 | 龙潭组煤矿采空区 | 高精度一体化宽频带地震仪 | 2020.08 | | 5 | 可控源高频大地
电磁法 | 6 | 嘉陵江组岩溶 | UltraEM Z4多功能电法工作站 | 2020.09 | | 6 | 瞬变电磁法 | 3、4、2、13 | 嘉陵江组岩溶、龙潭组煤矿采空区 | HPTEM-18等值反磁通瞬变电磁系统 | 2020.09、2021.07 | | 7 | 瞬变电磁法 | 7、9 | 嘉陵江组岩溶、茅口组岩溶 | FCTEM60-1高分辨瞬变电磁系统 | 2020.09 | | 8 | 瞬变电磁法 | 11 | 嘉陵江组岩溶 | CUGTEM-8瞬变电磁仪 | 2020.09 | | 9 | 瞬变电磁法 | 14 | 嘉陵江组岩溶 | emrs-3瞬变电磁仪 | 2020.10 | | 10 | 微动 | 7、10、12 | 嘉陵江组岩溶、龙潭组煤矿采空区、覆盖层 | Node X3 | 2021.03 | | 11 | 瞬态面波 | 8 | 覆盖层 | Node X3 | 2021.03 |
|
Geophysical prospecting methods for pre-drilling engineering of shale gas platform in south Sichuan and statistics of application test points
|
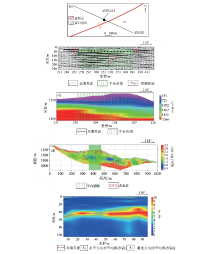
|
Engineering layout(a) of Survey Point 12 and its detection results of shallow seismic depth profile (b), shallow seismic velocity profile (c), high-density electrical method (d) and constant time fretting method(e)
|
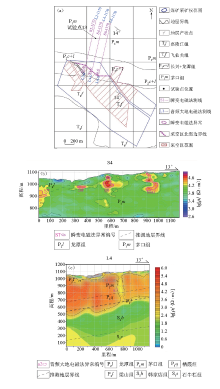
|
Engineering layout of measurement point 13 (a) and its detection results of transient electromagnetic method (b) and audio frequency magnetotelluric method (c)
|
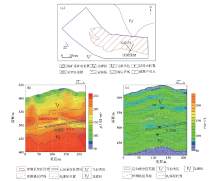
|
Engineering layout of measuring point 2 (a) and test results of transient electromagnetic method (b) and fretting method (c)
|
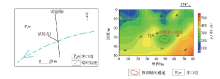
|
Engineering layout of measuring point 3 and test results of transient electromagnetic method
|
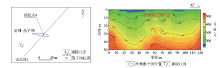
|
Engineering layout of measuring point 4 and test results of transient electromagnetic method
|
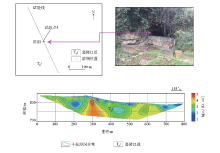
|
Engineering layout of measuring point 5 and its high-density electrical method test results
|
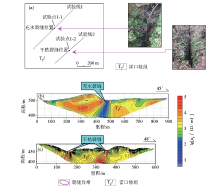
|
Engineering layout (a)of measuring point 1 and its high-density electrical method test results(b、c)
|

| 标类型 | 研究区
状况 | 0~100 m | 100~200 m | 200~1000 m | 备注 | 第一优
选组合 | 第二优
选组合 | 第一优
选组合 | 第二优
选组合 | 第一优
选组合 | 第二优
选组合 | | 覆盖层 | 干扰较强、
场地狭小 | ①+⑧ | ①+⑩ | ①+⑧ | ①+⑧ | ①工程地质及水文地质调查
②采空区调查
③高密度电法
④瞬变电磁法(大定源)
⑤等值反磁通瞬变电磁法
⑥音频大地电磁法
⑦可控源音频大地电磁法
⑧浅层地震反射波法/层析成像法
⑨微动
⑩常时微动
?瞬态面波 | 干扰较弱、
场地开阔 | ①+⑧ | | 岩溶 | 干扰较弱、
场地开阔 | ①+③ | ①+⑤ | ①+⑤ | ①+③ | ①+④+⑦ | ①+④+⑥ | 干扰较强、
场地狭小 | ①+③ | ①+⑤ | ①+⑤ | ①+③ | ①+④+⑦ | ①+④+⑥ | | 采空区 | 干扰较弱、
场地开阔 | ①+②+③ | ①+②+⑤ | ①+②+⑤ | ①+②+④ | ①+②+④ | ①+②+⑧ | 干扰较强、
场地狭小 | ①+②+③ | ①+②+⑤ | ①+②+⑤ | ①+②+④ | ①+②+④ | ①+②+⑧ |
|
Integrated geophysical exploration technology for shale gas well platform engineering in southern Sichuan
|
| [1] |
雍锐, 陈更生, 杨学锋, 等. 四川长宁—威远国家级页岩气示范区效益开发技术与启示[J]. 天然气工业, 2022, 42(8):136-147.
|
| [1] |
Yong R, Chen G S, Yang X F, et al. Profifitable development technology of the Changning-Weiyuan national shale gas demonstration area in the Sichuan basin and its enlightenment[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2022, 42(8):136-147.
|
| [2] |
赵瑞, 许模, 范辰辰, 等. 川南古叙地区岩溶发育特征及影响因素探讨[J]. 水土保持研究, 2015, 22(2):316-319,327.DOI:10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2015.02.059.
|
| [2] |
Zhao R, Xu M, Fan C C, et al. Discussion on the characteristics of Karst development and influence factors in Gulin-Xuyong area of Southern Sichuan[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015, 22(2):316-319,327.DOI:10.13869/j.cnki.rswc.2015.02.059.
|
| [3] |
Wang X M, Zhou X J, Yang X, et al. High-precision three-dimensional shale gas acquisition technology and its effectiveness in southern Sichuan rovince, Sichuan asin Province[C]// Proceedings of the 32nd National Natural Gas Academic Annual Conference (2020), 2020:538-547.DOI:10.26914/c.cnkihy.2020.064916.
|
| [4] |
余长恒, 周昊, 邹忠平, 等. 长宁地区页岩气钻井平台不同开孔层位不良地质体勘查[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2019, 16(1):61-69.
|
| [4] |
Yu C H, Zhou H, Zou Z P, et al. The Exploration of Unfavorable Geological Body ofShale Gas Drilling Platform at Different Openings in Changning Area[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2019, 16(1):61-69.
|
| [5] |
籍增贤, 张正阳, 孙永彬. 高密度电阻率法对泥石流松散堆积层探测效果的分析[J]. 勘察科学技术, 2020(4):61-64.
|
| [5] |
Ji Z X, Zhang Z Y, Sun Y B. Analysis of the effect of high density resistivity method on the detection of debris flow loose accumulation layer[J]. Investigation Science and Technology, 2020 (4): 61-64.
|
| [6] |
马董伟. 地震勘探方法在薄覆盖层区城市活断裂探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(5):1038-1045.
|
| [6] |
Ma D W. Application of seismic exploration method to urban active fault detection in thin overburden area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5):1038-1045.
|
| [7] |
孟凡松, 张刚, 陈梦君, 等. 高密度电阻率法二维勘探数据的三维反演及其在岩溶探测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 42(3):672-678.
|
| [7] |
Meng F S, Zhang G, Chen M J, et al. 3D inversion of 2D high density resistivity data and its application in Karst Exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 42(3):672-678.
|
| [8] |
吴俊林, 靳月文. 瞬变电磁法在采空区勘查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(S1):168-170.
|
| [8] |
Wu J L, Jin Y W. Application of transient electromagnetic method in goaf exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(S1):168-170.
|
| [9] |
余长恒, 张旭林, 王强, 等. 高密度电法在岩溶勘查中的参数试验——以四川南部宜宾市长宁页岩气开发区为例[J]. 矿产勘查, 2020, 11(9):1986-1992.
|
| [9] |
Yu C H, Zhang X L, Wang Q, et al. Parameter test of high density electrical method in Karst exploration:Take the changning shale gas development area in Yibin, southern Sichuan Province as an example[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2020, 11(9):1986-1992.
|
| [10] |
沈福斌, 刘江宾, 王星明. 岩溶裂隙探测技术及应用[J]. 煤矿隐蔽致灾因素及探查技术研究, 2015(5):332-337.
|
| [10] |
Shen F B, Liu J B, Wang X M. Karst fissure detection technology and its application[J]. Study on Hidden Disaster Causing Factors and Exploration Technology in Coal Mine, 2015 (5): 332-337.
|
| [1] |
ZHANG Fan, FENG Guo-Rui, QI Ting-Ye, YU Chuan-Tao, ZHANG Xin-Jun, WANG Chao-Yu, DU Sun-Wen, ZHAO De-Kang. Feasibility of the transient electromagnetic method in the exploration of double-layer waterlogged goafs with different layer spacings in coal mines[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1215-1225. |
| [2] |
ZHOU Jian-Bing, LUO Rui-Heng, HE Chang-Kun, PAN Xiao-Dong, ZHANG Shao-Min, PENG Cong. New geophysical evidence for karst water-bearing seepage pathways in the Xiaohewei reservoir,Wenshan City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 707-717. |
|
|
|
|

