|
|
|
| Application of shallow drilling geochemical survey to shallow overburden area at the peripheral of Nanjinshan gold mine in Beishan, Gansu Province |
WEI Zhen-Hong1( ), ZHAO Ji-Chang2( ), ZHAO Ji-Chang2( ), QU Zheng-Gang3, FAN Xin-Xiang2, LI Sheng-Ye2, CHEN Hai-Yun2, LIU Yong-Biao2, YANG Zhen-Xi2 ), QU Zheng-Gang3, FAN Xin-Xiang2, LI Sheng-Ye2, CHEN Hai-Yun2, LIU Yong-Biao2, YANG Zhen-Xi2 |
1. Natural Resources Department of Gansu Province, Lanzhou, 730000, China
2. Fourth Institute of Geological and Mineral Exploraton of Gansu Provinical Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resourses,Jiuquan 735000, China
3. Geological Survey of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Nanjinshan gold deposit is a typical epithermal deposit in Beishan metallogenic belt, which extends in a N-E direction to the peripheral shallow cover zone. In order to further achieve the breakthrough of prospecting in the peripheral shallow overburden area, the pilot work of motorized shallow drilling geochemical survey carried out. Based on the nature and thickness of the overburden, 126 motorized shallow drilling geochemical exploration samples are taken in the shallow overburden area using the vehicle mounted air positive circulation and three wing alloy scraper drilling or pneumatic DTH hammer drilling technology, with a sampling density of 16.8 points per square kilometer. The shallow drilling geochemical exploration methods and technologies in the shallow overburden area are further discussed, including the selection of drilling technology, sampling network, sampling materials, sample collection, etc. Soil survey was carried out in sporadic bedrock areas, and 278 samples were collected, and the sampling density was 48.77 points per square kilometer. Fifteen elements including Au, Ag, as, Sb, Hg, Cu, Pb, Zn, W, Sn, Mo, Bi, Cr, Co and Ni were analyzed. Through the above work, seven comprehensive geochemical anomalies were delineated. After anomaly investigation, six gold deposit bodies and one silver deposit body were found in the new circle in the bedrock area, and two concealed gold deposits and one silver deposit body were found in the shallow overburden area. The results show that shallow drilling geochemical survey is effective and feasible in the shallow overburden area of arid Gobi landscape in Beishan.
|
|
Received: 15 April 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
22])
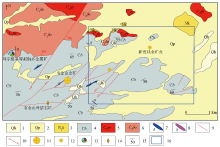
1—Quaternary Holocene alluvium; 2—Quaternary Pleistocene alluvial diluvium; 3—Neogene Kuquan formation; 4—Carboniferous Baishan formation; 5—middle Carboniferous monzogranite; 6—middle Carboniferous quartz diorite; 7—diorite vein; 8—quartz vein; 9—fault of unknown nature; 10—strike-slip fault; 11—location of medium-sized gold deposit; 12—location of gold mine; 13—location of copper polymetallic deposit; 14—location of pyrophyllite deposit; 15—stratum occurrence; 16—study area
">
|
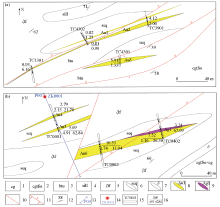
Geological and mineral map of the periphery of Nanjinshan gold mine (revised according to 1:50,000 Yemadaquan map[22])
1—Quaternary Holocene alluvium; 2—Quaternary Pleistocene alluvial diluvium; 3—Neogene Kuquan formation; 4—Carboniferous Baishan formation; 5—middle Carboniferous monzogranite; 6—middle Carboniferous quartz diorite; 7—diorite vein; 8—quartz vein; 9—fault of unknown nature; 10—strike-slip fault; 11—location of medium-sized gold deposit; 12—location of gold mine; 13—location of copper polymetallic deposit; 14—location of pyrophyllite deposit; 15—stratum occurrence; 16—study area
|
|
Comprehensive histogram of overburden structure unit layer (a), contour map of overburden thickness(b) and schematic diagram of overburden deposition (c) in the study area
|

|
Photos of landform and landscape of shallow overburden area in the study area (a) and on-site construction photos of motorized shallow drilling (b)
|

| 参数 | Cr | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Mo | W | Pb | Bi | As | Sb | Sn | Ag | Hg | Au | | 算术平均值 | | 72.0 | 8.3 | 26.6 | 31.1 | 96.7 | 2.42 | 3.15 | 22.8 | 0.27 | 70.8 | 4.37 | 1.1 | 66.528 | 35 | 5.5 | | | 62.8 | 6.9 | 24.4 | 20.4 | 69.2 | 1.91 | 2.48 | 23.4 | 0.28 | 62.5 | 5.37 | 1.4 | 71.539 | 55 | 5 | | 校正系数 | k1 | 0.87 | 0.83 | 0.92 | 0.66 | 0.72 | 0.79 | 0.79 | 1.03 | 1.04 | 0.88 | 1.23 | 1.27 | 1.08 | 1.57 | 0.91 | | k2 | 1.15 | 1.20 | 1.09 | 1.52 | 1.40 | 1.27 | 1.27 | 0.97 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 0.81 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.64 | 1.10 |
|
Arithmetic mean value and correction coefficient after iterative elimination
|

| 元素 | 地球化学场(n=384) | 地球化学背景场 | D | 北山地区
背景值[31] | | | S | Cv | Kk | | S0 | Cv0 | Kk0 | | Cr | 73.40 | 87.70 | 1.19 | 1.63 | 66.00 | 22.30 | 0.50 | 1.47 | 4.37 | 44.94 | | Co | 8.30 | 9.80 | 1.18 | 0.88 | 7.40 | 3.30 | 0.35 | 0.78 | 3.33 | 9.43 | | Ni | 29.10 | 30.90 | 1.06 | 1.24 | 25.30 | 12.10 | 0.52 | 1.08 | 2.94 | 23.38 | | Cu | 29.20 | 42.50 | 1.46 | 1.72 | 24.40 | 13.40 | 0.79 | 1.44 | 3.80 | 17.00 | | Zn | 93.30 | 79.40 | 0.85 | 2.21 | 78.50 | 34.10 | 0.81 | 1.86 | 2.77 | 42.30 | | Mo | 2.76 | 2.98 | 1.08 | 3.58 | 1.86 | 1.13 | 1.47 | 2.42 | 3.91 | 0.77 | | W | 4.29 | 6.85 | 1.60 | 4.77 | 2.61 | 1.16 | 1.29 | 2.90 | 9.71 | 0.90 | | Pb | 34.90 | 87.60 | 2.51 | 2.53 | 23.50 | 10.50 | 0.76 | 1.70 | 12.39 | 13.80 | | Bi | 0.43 | 0.72 | 1.67 | 0.62 | 0.27 | 0.12 | 0.17 | 0.39 | 9.56 | 0.69 | | As | 122.10 | 185.60 | 1.52 | 33.73 | 66.20 | 69.10 | 19.09 | 18.29 | 4.95 | 3.62 | | Sb | 8.02 | 9.98 | 1.24 | 19.56 | 5.03 | 4.50 | 10.98 | 12.27 | 3.54 | 0.41 | | Sn | 1.40 | 0.70 | 0.50 | 0.76 | 1.30 | 0.30 | 0.16 | 0.70 | 2.51 | 1.85 | | Ag | 286.91 | 764.48 | 2.66 | 5.58 | 69.69 | 21.32 | 0.41 | 1.36 | 147.62 | 51.40 | | Hg | 52.00 | 35.00 | 0.67 | 3.05 | 49.00 | 29.00 | 1.70 | 2.88 | 1.28 | 17.03 | | Au | 22.90 | 88.20 | 3.85 | 18.62 | 4.90 | 3.80 | 3.09 | 3.98 | 108.47 | 1.23 |
|
Statistical table of geochemical parameters in the study area
|
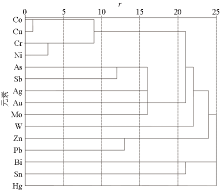
|
Element cluster analysis pedigree chart
|

| 元素 | 成分 | | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | | Cr | -0.039 | 0.041 | 0.952 | -0.002 | 0.043 | 0.08 | | Co | 0.099 | 0.896 | 0.295 | 0.063 | 0.017 | 0.016 | | Ni | 0.123 | 0.458 | 0.835 | 0.02 | 0.088 | 0.023 | | Cu | 0.199 | 0.912 | 0.039 | 0.108 | 0.038 | 0.003 | | Zn | 0.151 | 0.183 | 0.17 | 0.019 | 0.863 | 0.012 | | Mo | 0.603 | 0.299 | -0.037 | 0.003 | 0.252 | 0.014 | | W | -0.187 | 0.075 | -0.044 | 0.787 | 0.198 | 0.056 | | Pb | 0.029 | -0.092 | -0.045 | 0.002 | 0.852 | 0.099 | | Bi | -0.066 | 0.081 | -0.138 | -0.035 | 0.165 | 0.857 | | As | 0.699 | 0.36 | 0.086 | -0.018 | 0.033 | -0.156 | | Sb | 0.842 | 0.093 | 0.069 | 0.194 | 0.133 | -0.061 | | Sn | 0.039 | -0.072 | 0.356 | 0.06 | -0.036 | 0.752 | | Ag | 0.494 | -0.017 | 0.123 | 0.642 | -0.091 | -0.038 | | Hg | 0.541 | -0.253 | -0.083 | 0.063 | -0.147 | 0.275 | | Au | 0.223 | 0.085 | -0.004 | 0.786 | -0.111 | -0.008 |
|
Component matrix after factor rotation
|
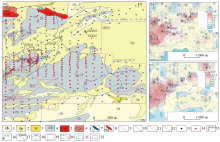
|
Geological sketch map (a), Au geochemical anomaly distribution (b) and Ag geochemical anomaly distribution (c) of the study area
1—Holocene; 2—Pleistocene; 3—Neogene; 4—Carboniferous Baishan formation; 5—middle Carboniferous monzogranite; 6—middle Carboniferous quartz diorite; 7—middle Carboniferous diorite; 8—secondary quartzite; 9—fault of unknown nature; 10—strike-slip fault;11—normal fault; 12—reverse fault; 13—motor-driven shallow drilling position; 14—soil survey points; 15—drilling of ore in construction; 16—high value point of element; 17—position of shallow drilling section; 18—comprehensive abnormality and number; 19—geochemical survey range; 20—concentrator location; 21—gold mineralization zone; 22—gold-silver mineralized zone
|
|
Sampling plan of Au1~Au3 orebody (a) and Au4~Au6 orebody (b) in bedrock area
1—tuffaceous conglomerate; 2—pebbly tuffaceous sandstone; 3—sedimentary tuff; 4—siliceous limestone; 5—dacite tuff; 6—secondary quartz vein; 7—diorite vein; 8—Au ore body and number; 9—Ag ore body and number; 10—measured fault with unknown nature; 11—measured reverse fault; 12—stratum occurrence; 13—location and number of exploration line; 14—location and number of borehole in the mine; 15—completed exploratory trench and its number; 16—thickness of ore body (m) / average grade of gold (g/t) average grade of silver (g/t)
|
|
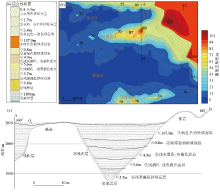
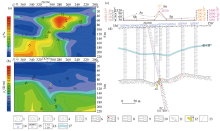
Section diagram of apparent polarizability (a), section diagram of apparent resistivity (b), element curve (c) and geological section (d) of 96 exploration line in the study area
1—Quaternary alluvial sand gravel; 2—conglomerate; 3—silty mudstone; 4—pebbly silty mudstone; 5—breccia bearing dacite tuff; 6—tuffaceous slate; 7—limonitized breccia bearing tuffaceous slate; 8—sericite mother slate; 9—carbonaceous sericite mother slate; 10—pyritized carbonaceous sericite mother rock; 11—secondary quartzite; 12—gold orebody; 13—inferred fault boundary; 14—position and number of completed motorized shallow drilling; 15—location and number of completed boreholes; 16—thickness of ore body (m) / average grade of gold (g/t); 17—water table
|
33]
Au—natural gold;Py—pyrite;Cpy—chalcopyrite;Qz—quartz
">
|
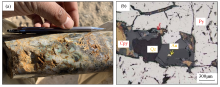
Photo of ore in ZK9601 borehole at the periphery of Nanjinshan (a) and photo of Nanjinshan gold ore under microscope (b)[33]
Au—natural gold;Py—pyrite;Cpy—chalcopyrite;Qz—quartz
|
| [1] |
卜建军, 吴俊, 史冀忠, 等. 北山—巴丹吉林地区石炭纪—二叠纪构造古地理及其演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):113-120.
|
| [1] |
Bu J J, Wu J, Shi J Z, et al. Carboniferous-permian tcetonic paleogeography of Beishan-Badanjilin region and lisevolution[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6):113-120.
|
| [2] |
段海龙, 陈耀, 张青, 等. 北山成矿带月牙山—老硐沟地区铜多金属矿床成矿预测[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5):188-197.
|
| [2] |
Duan H L, Chen Y, Zhang Q, et al. Metallogenic prediction of copper polymetallic deposit in the Yucyashan-Laodonggou area,Beishan ore belt[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5):188-197.
|
| [3] |
王钏屹, 王琦崧, 疏孙平, 等. 北山成矿带金窝子金矿床成矿流体时空演化与成矿机制[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(9):3126-3140.
|
| [3] |
Wang C Y, Wang Q S, Shu S P, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of ore-forming fluid and metallogenic belt[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(9):3126-3140.
|
| [4] |
田争亮, 吴锡丹. 北山成矿带金矿床(点)分布规律及找矿方向[J]. 新疆地质, 2001, 19(2):127-129,141.
|
| [4] |
Tian Z L, Wu X D. Methods for predlcting reservoir of gravity-flow sandbody in deep water and results analysis[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2001, 19(2):127-129,141.
|
| [5] |
曾长华, 吴大江, 夏文彬, 等. 北山成矿带金矿成矿规律与远景[J]. 新疆地质, 2002, 20(3):219-223.
|
| [5] |
Zeng C H, Wu D J, Xia W B, et al. Metallogenic regularity and prospect of gold depostits of Beishan minerallzation belt[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2002, 20(3):219-223.
|
| [6] |
王玉往, 王京彬. 北山地区与火山活动有关铜多金属成矿条件及找矿前景浅析[J]. 地质与勘探, 2005, 41(6):37-40.
|
| [6] |
Wang Y W, Wang J B. Metallogenic factors and potential for Cu-polymetallic deposits related to volcanic activilf in the Beishan area[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2005, 41(6):37-40.
|
| [7] |
聂凤军, 胡朋, 江思宏, 等. 北山北部古生代两类花岗岩及有关矿床的钕同位素特征[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(S1):139-142.
|
| [7] |
Nie F J, Hu P, Jiang S H, et al. Nd isotope features of two types of granitoids and related ore deposits in the northern part of Beishan area,Northwest China[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(S1):139-142.
|
| [8] |
李厚民, 丁建华, 李立兴, 等. 东天山雅满苏铁矿床矽卡岩成因及矿床成因类型[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12):2477-2489.
|
| [8] |
Li H M, Ding J H, Li L X, et al. The genesis of the skarn and the genetic type of the Yamansu iron deposit,Eastern Tianshan,Xingjiang[J]. Atca Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(12):2477-2489.
|
| [9] |
丁建华, 邢树文, 肖克炎, 等. 东天山—北山Cu-Ni-Au-Pb-Zn成矿带主要成矿地质特征及潜力分析[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90(7):1392-1412.
|
| [9] |
Ding J H, Xing S W, Xiao K Y, et al. Geological characteristics and resource potential analysis of the Dongtianshan-Beishan Cu-Ni-Au-Pb-Zn metallogenic belts[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90(7):1392-1412.
|
| [10] |
疏孙平, 张静, 陈衍景, 等. 北山成矿带霍勒扎德盖金矿床碲化物的发现及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(6):1859-1871.
|
| [10] |
Shu S P, Zhang J, Chen Y J, et al. Discovery and geological significance of tellurides in the Herzhedegai gold deposit,Beishan metallogenic belt[J]. Actor Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(6):1859-1871.
|
| [11] |
李小东, 王明卫, 写熹, 等. 安徽凤阳地区浅钻地球化学方法的找矿应用研究[J]. 地质调查与研究, 2018, 41(3):217-223.
|
| [11] |
Li X D, Wang M W, Xie X, et al. Application of shallow drilling geochemical method in Fengyang area Anhui Province[J]. Geological Survey and Research, 2018, 41(3):217-223.
|
| [12] |
孟贵祥, 吕庆田, 严加永, 等. “穿透性”探测技术在覆盖区地质矿产调查中的应用研究[J]. 地球学报, 2019, 40(5):637-650.
|
| [12] |
Meng G X, Lyu Q T, Yan J Y, et al. The research and application of explorational technology of “penetrating” to geology and mineral investigation in overburden area[J]. Acte Geoscientica Sinica, 2019, 40(5):637-650.
|
| [13] |
段星星, 黑欢, 梁楠, 等. 新疆东天山玉海铜矿外围浅覆盖区1:5万化探方法技术及应用[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(3):143-150.
|
| [13] |
Duan X X, Hei H, Liang N, et al. 1:50000 geochemical prospecting techniques and their applications in shallow covered area outside the yuhai copper deposit in east Tianshan mountains,Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(3):143-150.
|
| [14] |
段星星, 刘拓, 董会, 等. 东天山玉海浅覆盖区机动浅钻化探方法技术研究[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(3):192-199.
|
| [14] |
Duan X X, Liu T, Dong H, et al. Research and application of motorized shallow drilling geochemical exploration in Yuhai shallow overburden area,east Tianshan[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(3):192-199.
|
| [15] |
张小胖, 王帅, 赖柏生, 等. 浅覆盖区1:5万浅钻地球化学测量采样密度探讨——以安徽凤阳大王府—江山铅锌金矿为例[J]. 华东地质, 2021, 42(1):116-123.
|
| [15] |
Zhang X P, Wang S, Lai B S, et al. Discussion on sampling density of 1:50 000 short-hole drilling geochemical survey in shallow covered region:A case study of Dawangfu-Jiangshan Pb-Zn-Au deposit in Fengyang,Anhui Province[J]. East China Geology, 2021, 42(1):116-123.
|
| [16] |
Wang X Q, Zhang B B, Lin X, et al. Geochemical challenges of diverse regolithcovered terrains for mineral exploration in China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 73:417-431.

|
| [17] |
Anand Ravi R. Regolith-landform processes and geochemical exploration for base metal deposits in regolith-dominated terrains of the Mt Isa region,Northwest Queensland,Australia[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 73:451-474.

|
| [18] |
杨帆, 孔牧, 刘华忠, 等. 北山干旱荒漠戈壁残山景观1:5万地球化学勘查方法技术的选择[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 35(3):308-312,332.
|
| [18] |
Yang F, Kong M, Liu H Z, et al. The technological application of teand tmmode to the prospelting for structural flssure water[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 35(3):308-312,332.
|
| [19] |
曹亮, 许荣科, 段其发, 等. 甘肃北山南金山金矿床地质特征及深部成矿预测[J]. 地质与勘探, 2010, 46(3):377-384.
|
| [19] |
Cao L, Xu R K, Duan Q F, et al. Geolgical features of Nanjinshan gold deposit and prediction to minera lization at depth in the Beishan area,Gansu Province[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2010, 35(3):377-384.
|
| [20] |
潘桂棠, 肖庆辉, 陆松年, 等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质, 2009, 36(1):1-28.
|
| [20] |
Pan G T, Xiao Q H, Lu S N, et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(1):1-28.
|
| [21] |
张新虎, 刘建宏, 赵彦庆. 甘肃省成矿区(带)研究[J]. 甘肃地质, 2008, 17(2):1-8,49.
|
| [21] |
Zhang X H, Liu J H, Zhao Y Q. Study on metallogenic provinces(Zones)in Gansu Province[J]. Gansu Geology, 2008, 17(2):1-8,49.
|
| [22] |
甘肃省地质矿产局酒泉地质矿产调查队. 甘肃省肃北蒙古族自治县南金山金矿区详查地质报告[R]. 1992:16-18.
|
| [22] |
Jiuquan Geological and Mineral Survey Team of Gansu Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources. Detailed geological survey report of Nanjinshan gold mine area,Subei Mongolian Autonomous County,Gansu Province[R]. 1992:16-18.
|
| [23] |
沈远超, 申萍, 曾庆栋, 等. 甘肃北山地区南金山金矿床隐爆角砾岩体的发现及成矿规律研究[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(5):572-581.
|
| [23] |
Shen Y C, Shen P, Zeng Q D, et al. Discovery of cryptoexplosive breccia in Nanjinshan fold deposit of Beishan area,Gansu Province and study of metallogenic regularity[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(5):572-581.
|
| [24] |
熊文勃, 赵龙兴. 甘肃南金山金矿地质特征及金富集规律分析[J]. 矿产勘查, 2020, 11(1):40-46.
|
| [24] |
Xiong W B, Zhao L X. Analysis on geological characteristics and gold enrichment law of Nanjinshan gold deposit in Gansu Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2020, 11(1):40-46.
|
| [25] |
冯治汉, 刘元平, 叶得金, 等. 甘肃省景观地球化学特征初探[J]. 地质地球化学, 2002, 30(3):68-72.
|
| [25] |
Feng Z H, Liu Y P, Ye D J, et al. Preliminary study of landscape geochemical features in Gansu[J]. Geology-Geochemistry, 2002, 30(3):68-72.
|
| [26] |
徐仁廷. 甘肃北山干旱荒漠景观化探方法技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2006.
|
| [26] |
Xu R T. The study of geochemical technology for mineral exploration in the arid Gobi Desert terrain,Beishan Mountains area,Gansu[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2006.
|
| [27] |
赵吉昌, 范应, 雷一兰, 等. 构造地球化学岩屑测量在甘肃党河南山地区找金中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(4):923-932.
|
| [27] |
Zhao J C, Fan Y, Lei Y L, et al. The application of tectonogeochemical cuttings survey to gold prospecting in Nanshan area of Danghe,Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4):923-932.
|
| [28] |
喻劲松, 刘华忠, 宋殿兰, 等. 应用机动浅钻的地球化学勘查方法技术研究成果报告[R]. 2012.
|
| [28] |
Yu J S, Liu H Z, Song D L, et al. Report on research results of geochemical exploration method and technology using motorized shallow drilling[R]. 2012.
|
| [29] |
成秋明, 张生元, 左仁广, 等. 多重分形滤波方法和地球化学信息提取技术研究与进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2):185-198.
|
| [29] |
Cheng Q M, Zhang S Y, Zuo R G, et al. Progress of multifractal filtering techniques and their applications in geochemical information extraction[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(2):185-198.
|
| [30] |
高艳芳, 柳青青, 王学求, 等. 地球化学勘查数据一体化处理系统(Geochem Studio 3.6)用户指南[R]. 2019.
|
| [30] |
Gao Y F, Liu Q Q, Wang X Q, et al. User guide of geochemical exploration data integrated processing system (Geochem Studio 3.6)[R]. 2019.
|
| [31] |
樊新祥, 李省晔, 赵吉昌, 等. 甘肃北山双井子地区1:25000水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿预测[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2022, 22(36):15938-15951.
|
| [31] |
Fan X X, Li S Y, Zhao J C, et al. Geochemical characteristics and prospecting prediction of 1:25000 stream sediments in Shuangjingzi area,Beishan,Gansu Province[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2022, 22(36):15938-15951.
|
| [32] |
吴锡生. 化探数据处理方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1993:38-39.
|
| [32] |
Wu X S. Geochemical data processing method[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1993:38-39.
|
| [33] |
赵鹏大. 定量地质学理论与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2004:178-180.
|
| [33] |
Zhao P D. Theory and method of quantitative geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2004:178-180.
|
| [34] |
向东进. 实用多元统计分析[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2005:157-171.
|
| [34] |
Xiang D J. Practical multivariate statistical analysis[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2005:157-171.
|
| [35] |
薛薇. SPSS计分析方法及应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2004:9-12.
|
| [35] |
Xue W. SPSS analysis method and application[M]. Beijing: Electronic Industry Press, 2004:9-12.
|
| [36] |
王磊, 杨建国, 王小红, 等. 甘肃北山拾金坡—南金滩地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(2):585-593.
|
| [36] |
Wang L, Yang J G, Wang X H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in the Shijinpo-Nanjintan area of Beishan,Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(2):585-593.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Ji-Chang, FAN Ying, LEI Yi-Lan, YAO Bin-Bin. The application of tectonogeochemical cuttings survey to gold prospecting in Nanshan area of Danghe, Gansu Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(4): 923-932. |
| [2] |
Jia-Yi WANG, Li-Bo HAO, Xin-Yun ZHAO, Cheng-You MA, Ji-Long LU, Yu-Yan ZHAO, Qiao-Qiao WEI. The identification of bedrock types based on soil chemical composition[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(6): 1180-1185. |
|
|
|
|

