|
|
|
| Fluid inclusions and formation mechanisms of the Dongjianian silver deposit in Lingbao City, Henan Province, China |
LIU Chang1( ), ZHANG Can-Hui2, ZHANG Xin1, ZONG Rui2 ), ZHANG Can-Hui2, ZHANG Xin1, ZONG Rui2 |
1. Institute of Resources & Environment, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo 454000, China
2. No. 2 Institute of Geological and Mineral Survey, Henan Bureau of Geo-exploration & Mineral Development, Zhengzhou 450000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Dongjianian silver deposit, located on the southern margin of the Xiaoqinling Mountains, is controlled by the secondary structures of the Xiaohe fault and is the first large precious metal deposit discovered in the southern belt of the Xiaoqinling Mountains. This deposit has three hydrothermal metallogenic stages, namely the quartz-pyrite metallogenic stage (Ⅰ), the dominant quartz-polymetallic sulfide metallogenic stage (Ⅱ), and the quartz-carbonate metallogenic stage (Ⅲ). Three types of inclusions have primarily developed in the ore bodies, namely gas-liquid two-phase inclusions (W-type), CO2-bearing inclusions (C-type), and pure CO2 inclusions (PC-type). Stage I primarily witnessed the development of C- and W-type inclusions and a small quantity of PC-type inclusions, and stage II mainly saw the development of W-type inclusions and a small amount of C-type inclusions. The quartz fluid inclusions formed in stages I and II have homogenization temperature ranges of 151~270 ℃ and 126~240 ℃, respectively, which exhibits a downward trend. Their salinity varies slightly in the ranges of 3.8%~22.42% NaCleqv and 4.16%~20.48% NaCleqv, respectively, indicating a low-salinity environment. Their CO2 content transformed from enrichment into deficiency. The metallogenic pressure and depth were estimated to be 22.08~76.6 MPa and 3.77~7.13 km, respectively. Therefore, the Dongjianian silver deposit is a low-salinity medium- to low-temperature meso-epithermal silver deposit.
|
|
Received: 02 March 2022
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
23])
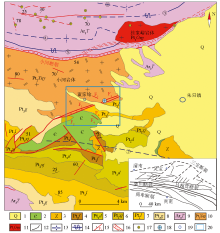
1—Quaternary system;2—Cambrian system;3—Sinian system;4—Fengjiawan formation;5—Duguan formation;6—Xunjiansi formation;7—Longjiayuan formation;8—Gaoshanhe formation;9—Neoarchean Taihua group gneiss;10—Xiaohe rock mass;11—Guijiayu rock mass;12—geological boundary;13—syncline structure;14—back structure;15—fault and occurrence;16—cataclastic rock zone;17—gold deposits;18—lead-silver deposit;19—towns;20—study area;①—Mengjiacun-Minwan syncline;②—Qishuping syncline;③—Laoyacha back shape;④—Miaogou syncline;⑤—Shangyangzhai back shape
">
|
Geological map of Dongjianian silver deposit(modified according to reference [23])
1—Quaternary system;2—Cambrian system;3—Sinian system;4—Fengjiawan formation;5—Duguan formation;6—Xunjiansi formation;7—Longjiayuan formation;8—Gaoshanhe formation;9—Neoarchean Taihua group gneiss;10—Xiaohe rock mass;11—Guijiayu rock mass;12—geological boundary;13—syncline structure;14—back structure;15—fault and occurrence;16—cataclastic rock zone;17—gold deposits;18—lead-silver deposit;19—towns;20—study area;①—Mengjiacun-Minwan syncline;②—Qishuping syncline;③—Laoyacha back shape;④—Miaogou syncline;⑤—Shangyangzhai back shape
|
|
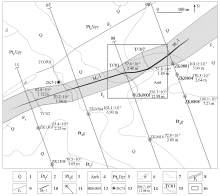
Sketch plan view of M1-Ⅰ major orebody of the Dongjianian silver deposit
1—Quaternary system;2—Longjiayuan formation of Guandaokou group;3—Gaoshanhe formation of Guandaokou group;4—Archaeozoic Taihua group;5—monzogranite of Xiaohe rock;6—diorite vein;7—geological boundary;8—measured or inferred tectonic altered belt;9—measured or inferred fault;10—silver orebody and its serial number;11—exploration line and its serial number;12—drill hole intersecting mineralization body;13—drill hole intersecting orebody;14—grade and thickness of major orebody controlled by exploratory trench or drill hole;15—exploratory trench and its serial number;16—sampling range
|
|
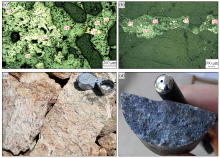
The main ore minerals of Dongjianian silver deposit
a—light sheet of TC01 trench,galena(Gn),sphalerite(Sp) and chalcopyrite(Ccp) are associated;b—light sheet of TC01 trench,fine grained pyrite(Py),spiral silver sulfide(Arn)and silver arsenic sulfide(Bgt) are associated;c—veinlet disseminated metallization in TC01 trench;d—pyritized and galena silver ore in ZK0001 borehole
|
|
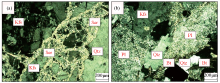
The gangue mineral characteristics of Dongjianian silver deposit
a—silver mineralization altered rock slice thin sections:rocks are mainly composed of potash feldspar(Kfs),quartz(Qtz),sericite(Ser),etc.;b—borehole silver ore thin sections:rocks are mainly composed of plagioclase(Pl),potassium feldspar(Kfs),quartz(Qtz),biotite(Bt),etc.
|
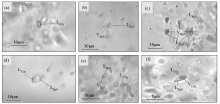
|
Photomicrograph of fluid inclusions of Dongjianian silver deposit
a—pure CO2 inclusions in stage Ⅰ;b—gas-liquid two-phase inclusions in stage Ⅲ;c—grouped distribution inclusions in stage Ⅲ;d—CO2-bearing two-phase inclusions in stage Ⅱ;e—gas-liquid two-phase and pure CO2 inclusions in stage Ⅱ;f—CO2-containing three-phase inclusions in stage Ⅱ
|

| 成矿阶段 | 包裹体类型 | /℃ | Tm,ice/℃ | /℃ | Tm,clath/℃ | Th,tot/℃ | | 石英—黄铁矿阶段(Ⅰ) | W型包裹体 | | -1.0~9.0 | | | 210~270 | | C型包裹体 | -56.9~-56.5 | | 12.1~29.6 | 7.2~10.8 | 151~268 | 石英—多金属
硫化物阶段(Ⅱ) | W型包裹体 | | -0.2~-3.5 | | | 126~240 | | C型包裹体 | -56.8~-56.6 | | 20.2~24.6 | 8~11.9 | 127~238 |
|
Temperature measurement results of fluid inclusions of Dongjianian silver ore deposit
|
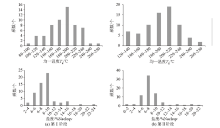
|
Histogram of uniform temperature and salinity of fluid inclusions in stage Ⅰ (a) and Ⅱ (b) metallogenic of Dongjianian silver deposit
|
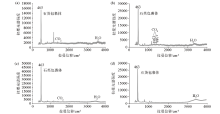
|
Laser Raman spectra of fluid inclusion
a、b—stage Ⅰ composition of quartz inclusions;c—stage Ⅱ composition of quartz inclusions;d—stage Ⅲ composition of quartz inclusions
|
19]
1—geological boundary;2—fault and occurrence;3—orebody and number;4—exploration line and number;5—drilling and number;6—alteration boundary;Q—Quaternary;Jxg—Gaoshanhe formation;Ar3T—Archaeozoic Taihua group;Pt2Xηγ—Xiaohe monzonitic granite;A—internal alteration zone;B—medium alteration zone;C—external alteration zone;D—normal surrounding rock
">
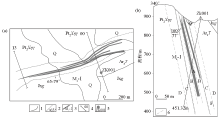
|
Silver orebody plane in mining area (a)、No.00 prospecting line profile map (b)[19]
1—geological boundary;2—fault and occurrence;3—orebody and number;4—exploration line and number;5—drilling and number;6—alteration boundary;Q—Quaternary;Jxg—Gaoshanhe formation;Ar3T—Archaeozoic Taihua group;Pt2Xηγ—Xiaohe monzonitic granite;A—internal alteration zone;B—medium alteration zone;C—external alteration zone;D—normal surrounding rock
|
| [22] |
Feng J Z. Structural ore-controlling law and ore-controlling model of the Xiaoqinling gold deposit,Henan Province[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2009, 23(4):302-307.
|
| [23] |
赵海香. 河南小秦岭金矿成矿作用地球化学研究[D]. 南京: 南京大学, 2011.
|
| [23] |
Zhao H X. Geochemical study of gold mineralization in Xiaoqinling, Henan Province[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University, 2011.
|
| [24] |
国家能源局. SY/T 6010—2011中华人民共和国石油天然气行业标准:沉积盆地流体包裹体显微测温方法[S]. 2011.
|
| [24] |
National Energy Administration. SY/T 6010—2011 Petroleum and natural gas industry standards of the People ’s Republic of China:Microscopic temperature measurement method for fluid inclusions in sedimentary basins[S]. 2011.
|
| [25] |
Hall D L, Sterner S M, Bodnar R J. Freezing point depression of NaCl-KCl-H2O solutions[J]. Econ Geol, 1988, 83(1):197-202.

|
| [26] |
刘斌, 段光贤. NaCl-H2O溶液包裹体的密度式和等容式及其应用[J]. 矿物学报, 1987, 7(4):345-352.
|
| [26] |
Liu B, Duan G X. The density and isochoric formulae for NaCl-H2O fluid inclusions(salinity≤25wt%)and their applications[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 1987, 7(4):345-352.
|
| [27] |
Collins P L F. Gas hydrates in CO2-bearing fluid inclusions and the use of freezing data for estimation of sal inity[J]. Econ Geol, 1979, 74: 1435-1444.

|
| [28] |
孙丰月, 金巍, 李碧乐, 等. 关于脉状热液金矿床成矿深度的思考[J]. 长春科技大学学报, 2000, 30(S):27-30.
|
| [28] |
Sun F Y, Jin W, Li B L, et al. Thoughts on the mineralization depth of the vein hydrothermal gold deposit[J]. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2000, 30(S):27-30.
|
| [29] |
李晶, 陈衍景, 李强之, 等. 甘肃阳山金矿流体包裹体地球化学和矿床成因类型[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(9):2144-2154.
|
| [29] |
Li J, Chen Y J, Li Q Z, et al. Geochemistry and genesis types of fluid inclusions of Yangshan gold deposit in Gansu[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(9):2144-2154.
|
| [30] |
陈衍景, 倪培, 范宏瑞, 等. 不同类型热液金矿系统的流体包裹体特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(9):2085-2108.
|
| [30] |
Chen Y J, Ni P, Fan H R, et al. Diagnostic fluid inclusions of different types hydrothermal gold deposits[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(9): 2085-2108.
|
| [31] |
张静, 陈衍景, 李国平, 等. 河南内乡县银洞沟银矿地质和流体包裹体特征及成因类型[J]. 矿物岩石, 2004, 24(3):55-64.
|
| [31] |
Zhang J, Chen Y J, Li G P, et al. Geological and fluid inclusion characteristics and genetic types of Yindonggou silver deposit in Neixiang County,Henan Province[J]. Mineral Rocks, 2004, 24(3):55-64.
|
| [32] |
陈衍景. 造山型矿床、成矿模式及找矿潜力[J]. 中国地质, 2006, 33(6):1181-1196.
|
| [1] |
王义天, 毛景文. 碰撞造山作用期后伸展体制下的成矿作用——以小秦岭金矿集中区为例[J]. 地质通报, 2002(Z2):562-566.
|
| [1] |
Wang Y T, Mao J W. Mineralization under the extension system after the collision orogenic period:A case study of the Xiaoqinling gold deposit area[J]. Geological Bulletin, 2002(Z2):562-566.
|
| [2] |
王晋定, 王大钊, 詹小飞, 等. 小秦岭金成矿区南矿带构造控矿规律和矿床定位样式[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(6):1064-1077.
|
| [2] |
Wang J D, Wang D Z, Zhan X F, et al. Tectonic ore-controlling laws and deposit positioning styles in the southern ore belt of the Xiaoqinling gold metallogenic area[J]. Tectonics and Mineralization, 2018, 42(6):1064-1077.
|
| [3] |
刘宗彦, 张灯堂, 刘运华, 等. 小秦岭金矿田韧性剪切带的控矿规律及中深部成矿分析[J]. 矿产与地质, 2018, 32(4):605-615.
|
| [3] |
Liu Z Y, Zhang D T, Liu Y H, et al. Ore-controlling law and metallogenic analysis of the ductile shear zone in the Xiaoqinling gold ore field[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2018, 32(4):605-615.
|
| [4] |
吴晓贵. 小秦岭东桐峪金矿床稳定同位素地球化学及成矿物质来源[J]. 西北地质, 2016, 49(4):91-98.
|
| [4] |
Wu X G. Stable isotope geochemistry and source of ore-forming materials of Dongtongyu gold deposit in Xiaoqinling[J]. Northwest Geology, 2016, 49(4):91-98.
|
| [5] |
铁健康, 董少波, 马林霄, 等. 小秦岭文峪金矿床深部地质特征及成矿规律[J]. 山东国土资源, 2015, 31(3):7-11,15.
|
| [5] |
Tie J K, Dong S B, Ma L X, et al. Deep geological characteristics and metallogenic regularity of the Wenyu gold deposit in Xiaoqinling[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2015, 31(3):7-11,15.
|
| [6] |
Mao J W, Qiu Y M, Goldfarb R J, et al. Gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling-Xiong'ershan region,Qinling Mountains, Central China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2002, 37:306-325.

|
| [7] |
Bi S J, Li J W, Zhou M F, et al. Gold distribution in As-deficient pyrite and telluride mineralogy of the Yangzhaiyu gold deposit,Xiaoqinling district,southern North China craton[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2011, 46:925-941.

|
| [8] |
郭云成. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床包裹体特征与成矿物质来源研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.
|
| [8] |
Guo Y C. Characteristics of inclusions and source of ore-forming materials in the Xiaohuling Dahu gold-molybdenum deposit[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2018.
|
| [9] |
曾昊. 河南省小秦岭地区灵金一矿成矿流体研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.
|
| [9] |
Zeng H. Research on the ore-forming fluid of Lingjin No.1 Mine,Xiaoqinling area,Henan Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2016.
|
| [10] |
倪智勇, 李诺, 管申进, 等. 河南小秦岭金矿田大湖金—钼矿床流体包裹体特征及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(9):2058-2068.
|
| [10] |
Ni Z Y, Li N, Guan S J, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions and ore genesis of the Dahu Au-Mo deposit in the Xiaoqinling gold field,Henan Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(9):2058-2068.
|
| [11] |
周振菊, 蒋少涌, 秦艳, 等. 小秦岭文峪金矿床流体包裹体研究及矿床成因[J]. 岩石学报, 2011, 27(12):3787-3799.
|
| [11] |
Zhou Z J, Jiang S Y, Qin Y, et al. Study on fluid inclusions and genesis of Wenyu gold deposit in Xiaoqinling[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2011, 27(12):3787-3799.
|
| [12] |
赵海香, 嵇静, 赵智, 等. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿流体包裹体研究及矿床成因[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(1):72-82.
|
| [12] |
Zhao H X, Yun J, Zhao Z, et al. Research on fluid inclusions and genesis of Dahu gold and molybdenum deposit in Xiaoqinling[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(1):72-82.
|
| [13] |
黎世美, 瞿伦全, 苏振邦, 等. 小秦岭金矿地质和成矿预测[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1996.
|
| [13] |
Li S M, Qu L Q, Su Z B, et al. The geology and metallogenic prediction of the gold deposit in Xiaoqinling[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1996.
|
| [14] |
Jiang N, Xu J H, Song M X. Fluid inclusion characteristics of mesothermal gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling district,Shannxi and Henan Provinces,People’s Republic of China[J]. Mineralium Deposit, 1999, 34:150-162.

|
| [15] |
Fan H R, Xie Y H, Zhao R, et al. Dual origions of Xiaoqinling gold-bearing quartz veins:Fluid inclusion evidence[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(15):1424-1430.

|
| [16] |
Zhou Z J, Chen Y J, Jiang S Y, et al. Geology, geochemistry and ore genesis of the Wenyu gold deposit,Xiaoqinling gold field,Qinling Orogen, southern margin of North China Craton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 59(6):1-20.

|
| [17] |
Zhou Z J, Chen Y J, Jiang S Y, et al. Isotope and fluid inclusion geochemistry and genesis of the Qiangma gold deposit,Xiaoqinling gold field,Qinling Orogen,China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 66(2):47-64.

|
| [18] |
蒋少涌, 戴宝章, 姜耀辉, 等. 胶东和小秦岭:两类不同构造环境中的造山型金矿省[J]. 岩石学报, 2009, 25(11):2727-2738.
|
| [18] |
Jiang S Y, Dai B Z, Jiang Y H, et al. Jiaodong and Xiaoqinlinga:Two orogenic gold provinces formed in different tectonic settings[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2009, 25(11):2727-2738.
|
| [19] |
纵瑞, 董岘证, 张凯涛, 等. 豫西董家埝银矿床地质特征及矿床成因探讨[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(3):367-372.
|
| [19] |
Zong R, Dong D Z, Zhang K T, et al. Geological characteristics and genesis of Dongjiayu silver deposit in western Henan[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2018, 32(3):367-372.
|
| [20] |
郭保健, 徐孟罗, 王志光, 等. 熊耳山北坡拆离断层带地球化学特征及其与金银矿化的关系[J]. 矿产与地质, 1997, 11(1):21-26.
|
| [20] |
Guo B J, Xu M L, Wang Z G, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the detached fault zone on the northern slope of Xiong'er Mountain and its relationship with gold and silver mineralization[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 1997, 11(1):21-26.
|
| [21] |
栾世伟, 曹殿春, 方耀奎, 等. 小秦岭金矿床地球化学[J]. 矿物岩石, 1985(2):2-134.
|
| [21] |
Luan S W, Cao D C, Fang Y K, et al. Geochemistry of the Xiaoqinling gold deposit[J]. Mineral Rocks, 1985(2):2-134.
|
| [32] |
Chen Y J. Orogenictype deposits and their metallogenic model and exploration potential[J]. Geology in China, 2006, 33(6):1181-1196.
|
| [22] |
冯建之. 河南小秦岭金矿构造控矿规律及控矿模式[J]. 矿产与地质, 2009, 23(4): 302-307.
|
| [1] |
SONG Wei-Fang, LIU Jian-Zhong, WU Pan, LI Jun-Hai, WANG Ze-Peng, YANG Cheng-Fu, TAN Qin-Ping, WANG Da-Fu. A successful application of the tectono-geochemistry weak information extraction method in the prospecting of Carlin-type gold deposits in southwestern Guizhou Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6): 1338-1348. |
| [2] |
WEI Cong-Ling, CHEN Jian-Li, GUO Peng. Metallogenic prediction of gold deposits in Laowan area, Henan Province using the weight of evidence model and MRAS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3): 653-660. |
|
|
|
|

