|
|
|
| A study of tectonic framework of the Qinnan sag in Bohai Basin and its adjacent areas based on satellite gravity anomalies |
YANG Rong-Xiang1,2,3( ), WANG Wan-Yin1,2,3,4,5,6( ), WANG Wan-Yin1,2,3,4,5,6( ), CAI Meng-Ke1,2,3, WANG Ding-Ding1,2,3,7, LUO Xin-Gang1,2,3 ), CAI Meng-Ke1,2,3, WANG Ding-Ding1,2,3,7, LUO Xin-Gang1,2,3 |
1. Institute of Gravity and Magnetic Technology, Chang 'an University, Xi'an 710054, China
2. School of Geological Engineering and Geomatics, Chang'an University, Xi'an 710054, China
3. Key Laboratory of Western China's Mineral Resources and Geological Engineering of Ministry of Education, Chang'an University, Xi'an 710054, China
4. Key Laboratory of Marine Geology & Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
5. Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266071, China
6. National Engineering Research Center of Offshore Oil and Gas Exploration, Beijing 100028, China
7. Department of Earth Sciences, University of Naples Federico II, Naples 80138, Italy |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Bohai Basin has the most offshore oil and gas fields discovered in China. As a potential hydrocarbon-rich sag in the Bohai Basin, the Qinnan Sag is of high value in exploration. Therefore, the study of the tectonic framework of the sag and its adjacent areas is of great significance and application value. Based on satellite gravity anomalies, this study determined the Bouguer gravity anomalies by correcting the influences of land topography and seawater and obtained the planar distribution and apparent depths of faults, the thickness of Cenozoic strata, and the boundaries of tectonic units using methods such as the normalized vertical derivative of the total horizontal derivative (NVDR-THDR), the Euler deconvolution, the minimum curvature potential field separation, and the fast for the gravity field based in a dual interface model. Based on the geological and geophysical data, this study analyzed the distribution and geophysical characteristics of major faults and tectonic units in the study area. The results of this study are as follows: The faults in the Qinnan Sag and its adjacent areas mainly have NE, NEE, and NW strikes and an apparent depth of primarily 1~10 km, which is up to 15~25 km at some positions of the sag-controlling faults and the intersections of the faults; The Cenozoic strata have a thickness of 0~11 km. The Cenozoic tectonic units are distributed in alternating NE and NEE directions, and their boundaries are mostly controlled by faults; Through further investigation, this study classified the sub-sag on the west side of the Qinnan sag as the Laoting sag and adjusted the boundaries of other tectonic units. The results of this study on the distribution of the faults and tectonic units can provide geophysical data for hydrocarbon exploration in the Qinnan Sag.
|
|
Received: 21 September 2022
Published: 05 July 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
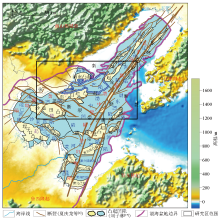
|
Regional geological background map of Bohai basin
|

| 地层 | 岩性 | 密度/(kg·m-3) | | 界 | 系 | 组 | | 新生界 | 第四系 | 平原组 | 黄土、黏土、粉砂岩 | 2050 | | 新近系 | 明化镇组 | 泥岩、砂岩 | 2110 | | 馆陶组 | 泥岩、砂砾岩 | 2190 | | 古近系 | 东营组 | 泥岩、砂岩、油页岩 | 2430 | | 沙河街组 | 泥岩、油页岩、 | 2450 | | 石灰岩、白云岩 | | 孔店组 | 砂岩、石灰岩 | 2450 | | 中生界 | 白垩系 | | 砂砾岩、泥岩、安山岩、 | 2580 | | 凝灰岩、玄武岩 | | 侏罗系 | | 砂岩、凝灰岩、 | 2560 | | 泥岩、砂砾岩 | | 古生界 | 二叠系 | | 砂岩、泥岩、煤层 | 2600 | | 石炭系 | | 泥岩、粉砂岩、石灰岩、 | 2700 | | 煤层、铝土岩 | | 奥陶系 | | 厚层白云岩、石灰岩 | 2660 | | 寒武系 | | 页岩、砂岩、石灰岩 | 2720 |
|
Stratum core density in Chengning uplift, Dagang region[19]
|
|
Topographic map of Qinnan Sag and its surrounding areas
|
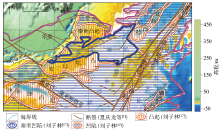
|
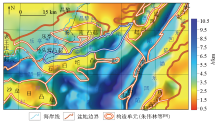
Satellite gravity anomaly of Qinnan Sag and its surrounding areas
|
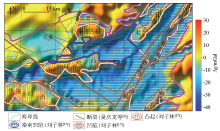
|
Bouguer gravity anomaly of Qinnan Sag and its surrounding areas
|
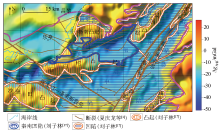
|
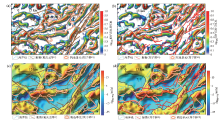
Comparison of previous fault division with Bouguer gravity anomaly NVDR-THDR(a and b) and residual Bouguer gravity anomaly zero line (c and d) in Qinnan Sag and its adjacent areas
|
|
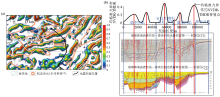
The contrast figure of seismic geological section position (a) and faults in Qinnan Sag and its adjesent areas (b)
|
|
The distribution of faults plane position in Qinnan Sag and its adjacent areas
|
|
The apparent depth in Qinnan Sag and its adjacent areas
|
|
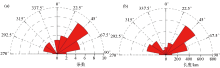
Rose diagrams of fault strike and frequency (a) and length (b) in Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas
|
|
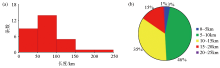
Statistical histogram of fracture length and number (a) in Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas (b)
|
17]; (b) Xia Qinglong et al.[1]; (c) Hu Zhiwei et al.[8]; (d) Yang Keji et al. [12]; the black lines are the result of this paper
">
|
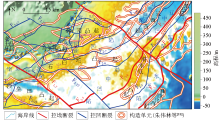
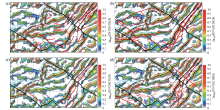
Comparison of main fracture distribution in Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas with previous results
the red lines are the faults deduced by (a) Liu Zilin[17]; (b) Xia Qinglong et al.[1]; (c) Hu Zhiwei et al.[8]; (d) Yang Keji et al. [12]; the black lines are the result of this paper
|
|
Thickness of Cenozoic in Qinnan Sag and its surrounding areas
|
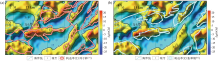
|
Residual bouguer gravity anomaly map of Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas
|
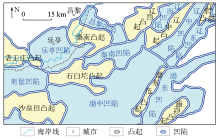
|
Division results of tectonic units in Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas
|
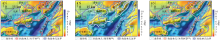
|
Comparison of the division results of tectonic units in Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas with previous studies
|
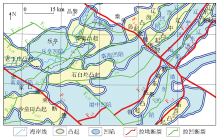
|
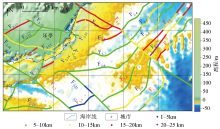
The relationship between faults and tectonic units in Qinnan Sag and adjacent areas
|

| 编号(名称) | 构造位置 | 识别标志 | 走向 | 长度/km | 视深度/km | 级别 | | F1-1 | 郯庐
断裂
东支 | 渤海盆地东部边界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NE | 71.4 | 5~20 | 控坳 | | F1-2 | 渤东凹陷与庙西北凸起分界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NE—近SN | 63.8 | 5~15 | 控坳 | | F1-3 | 郯庐
断裂
西支 | 辽中凹陷与辽东凸起分界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NE | 79.5 | 10~20 | 控坳 | | F1-4 | 渤东低凸起和渤中凹陷边界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值 | NE | 85.5 | 5~15 | 控坳 | | F1-5 | 渤中凹陷内 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值 | NE | 33.9 | 1~5 | 控坳 | | F1-6 | 秦皇岛—
旅顺断裂 | 辽东湾坳陷与辽中凹陷
分界断裂 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线及错断 | NW | 179.8 | 5~20 | 控坳 | | F1-7 | 张家口—
蓬莱断裂 | 渤中坳陷与济阳坳陷的分界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值错断 | NW | 106.9 | 5~10 | 控坳 | | F2-1 | 辽东凹陷和辽东凸起
及辽中凹陷分界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NE | 82.7 | 10~25 | 控凹 | | F2-2 | 辽中凸起和辽中凹陷分界 | NVDR-THDR脊值连线 | NE | 73.2 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | 编号(名称) | 构造位置 | 识别标志 | 走向 | 长度/km | 视深度/km | 级别 | | F2-3 | 辽西凹陷和辽中凸起分界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NE | 65.0 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-4 | 辽西凸起和辽西凹陷分界 | NVDR-THDR脊值连线 | NE | 49.8 | 5~10 | 控凹 | | F2-5 | 渤东凹陷内 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NE—近SN | 91.0 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-6 | 石臼坨凸起和渤中凹陷分界 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | 近EW | 137.4 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-7 | 石臼坨凸起北侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | 近EW—NEE | 119.6 | 5~20 | 控凹 | | F2-8 | 秦南凹陷南侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线 | NEE | 131.2 | 10~20 | 控凹 | | F2-9 | 昌黎凹陷南部 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NW | 49.0 | 15~20 | 控凹 | | F2-10 | 秦南凸起内部 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NNE | 36.5 | 10~15 | 控凹 | | F2-11 | 秦南凸起内部 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NNE | 33.2 | 10~15 | 控凹 | | F2-12 | 乐亭凹陷东侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NNW—NNE | 19.5 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-13 | 乐亭凹陷东南侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NNW | 13.7 | 10~15 | 控凹 | | F2-14 | 秦南凹陷西侧 | 剩余布格重力异常零值线 | NNE | 11.8 | 10~15 | 控凹 | | F2-15 | 乐亭凹陷内部 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NEE—NNE | 31.6 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-16 | 乐亭凹陷西北侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NE | 35.2 | 5~10 | 控凹 | | F2-17 | 乐亭凹陷西北侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NE | 34.7 | 15~20 | 控凹 | | F2-18 | 老王庄凸起东北侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-THDR
脊值连线与剩余布格
重力异常零值线 | NWW | 76.0 | 10~15 | 控凹 | | F2-19 | 乐亭凹陷东北侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NWW | 66.9 | 5~10 | 控凹 | | F2-20 | 老王庄凸起东南侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NE | 39.6 | 10~20 | 控凹 | | F2-21 | 石臼坨凸起西侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NEE | 27.6 | 5~10 | 控凹 | | F2-22 | 渤中凹陷内部 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值错断 | NW | 70.8 | 1~10 | 控凹 | | F2-23 | 沙垒田凸起南侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | EW—NE | 72.5 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-24 | 南堡凹陷南侧 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | 近EW | 43.0 | 5~15 | 控凹 | | F2-25 | 沙垒田凸起内部 | 布格重力异常NVDR-
THDR脊值连线 | NNE | 30.8 | 5~10 | 控凹 |
|
Statistical table of fracture properties in study area
|
| [1] |
夏庆龙, 徐长贵. 渤海海域复杂断裂带地质认识创新与油气重大发现[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(S1):22-33.
|
| [1] |
Xia Q L, Xu C G. New geological understandings and major hydrocarbon discoveries in the complex fault zone of Bo-hai Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(S1):22-33.
|
| [2] |
魏刚, 薛永安, 柴永波, 等. 秦南凹陷油气勘探思路创新与突破[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(3):7-11.
|
| [2] |
Wei G, Xue Y A, Chai Y B, et al. Philosophy innovations and a breakthrough in petroleum exploration in Qinnan Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(3):7-11.
|
| [3] |
庄新兵, 邹华耀, 李楠, 等. 秦南凹陷烃源岩特征与油气勘探新领域[J]. 断块油气田, 2011, 18(2):146-149.
|
| [3] |
Zhuang X B, Zou H Y, Li N, et al. Characteristics of source rock and new region of oil and gas exploration in Qinnan Sag[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2011, 18(2):146-149.
|
| [4] |
石文龙, 李慧勇, 茆利, 等. 渤海海域秦南凹陷油气地质特征及勘探潜力[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2014, 19(5):32-40.
|
| [4] |
Shi W L, Li H Y, Mao L, et al. Hydrocarbon geological characteristics and exploration potential of Qinnan depression in offshore area of Bohai Sea[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2014, 19(5):32-40.
|
| [5] |
杨海风, 魏刚, 王德英, 等. 秦南凹陷秦皇岛29-2油气田原油来源及其勘探意义[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(6):28- 31,112-113.
|
| [5] |
Yang H F, Wei G, Wang D Y, et al. Oil sources and exploration significance of Qinhuangdao29-2 oil-gas field[J]. Pe-troleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2011, 18(6):28-31,112-113.
|
| [6] |
蔡少武, 周东红, 王德英, 等. 渤海湾盆地秦南凹陷构造发育特征与有利勘探方向[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(5):532-541.
|
| [6] |
Cai S W, Zhou D H, Wang D Y, et al. Tectonic development characteristics and favorable exploration direction of Qinnan sag in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(5):532-541.
|
| [7] |
张震, 徐春强, 郭瑞, 等. 渤海秦南凹陷新生代断裂体系与构造演化[J]. 断块油气田, 2019, 26(2):158-161,167.
|
| [7] |
Zhang Z, Xu C Q, Guo R, et al. Cenozoic fault system and tectonic evolution of Qinan Sag in Bohai Sea[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2019, 26(2):158-161,167.
|
| [8] |
胡志伟, 王德英, 牛成民, 等. 辽西—秦南地区断裂体系形成与演化特征[J]. 成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 46(5):618-627.
|
| [8] |
Hu Z W, Wang D Y, Niu C M, et al. Characteristics of fault system and evaluation of hydrocarbon generation potential in western Liaoxi-Qinnan area,China[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2019, 46(5):618-627.
|
| [9] |
林晓星. 重磁资料在渤海前新生代油气盆地结构研究中的应用[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2012.
|
| [9] |
Lin X X. Application of gravity and magnetic data in the structural study of pre-cenozoic oil and gas basins in the Bohai Sea[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2012.
|
| [10] |
滕长宇, 邹华耀, 郝芳. 渤海湾盆地构造差异演化与油气差异富集[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(4):579-590.
|
| [10] |
Teng C Y, Zou H Y, Hao F. Differential evolution of tectonics and differential enrichment of oil and gas in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. China Science:Earth Sciences, 2014, 44(4):579-590.
|
| [11] |
王德英, 王清斌, 刘晓健, 等. 渤海湾盆地海域片麻岩潜山风化壳型储层特征及发育模式[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(4):1181-1193.
|
| [11] |
Wang D Y, Wang Q B, Liu X J, et al. Characteristics and development model of weathering crust reservoir of gneiss buried hill in Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Lithology, 2019, 35 (4) :1181-1193.
|
| [12] |
杨克基, 漆家福, 余一欣, 等. 渤海湾地区断层相关褶皱及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2016, 51(3):625-636.
|
| [12] |
Yang K J, Qi J F, Yu Y X, et al. Fault-related folds in the Bohai Bay area and their petroleum geological significance[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2016, 51(3):625-636.
|
| [13] |
周心怀, 余一欣, 汤良杰, 等. 渤海海域新生代盆地结构与构造单元划分[J]. 中国海上油气, 2010, 22(5):285-289.
|
| [13] |
Zhou X H, Yu Y X, Tang L J, et al. Structure and tectonic unit division of cenozoic basins in Bohai Sea[J]. Offshore Oil and Gas of China, 2010, 22 (5) :285-289.
|
| [14] |
侯贵廷, 钱祥麟, 蔡东升. 渤海湾盆地中、新生代构造演化研究[J]. 北京大学学报:自然科学版, 2001, 37(6):845-851.
|
| [14] |
Hou G T, Qian X L, Cai D S. Study on mesozoic-cenozoic tectonic evolution of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Journal of Peking University:Natural Science Edition, 2001, 37(6):845-851.
|
| [15] |
陈光希, 张明华, 张盛. 约束变密度界面反演法在渤海深部结构研究中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(6):2406-2413.
|
| [15] |
Chen G X, Zhang M H, Zhang S. Application of constrained variable density interface inversion method in the study of deep structure of the Bohai Sea[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34 (6) :2406-2413.
|
| [16] |
张翠梅. 渤海湾盆地南堡凹陷构造—沉积分析[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2010.
|
| [16] |
Zhang C M. Structural-sedimentary analysis of Nanpu Sag in Bohai Bay Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2010.
|
| [17] |
刘子林. 渤海湾盆地(海域)断裂系统及其与CO2气(藏)的关系[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2018.
|
| [17] |
Liu Z L. Bohai Bay Basin (sea area) fault system and its relationship with CO2 gas (reservoir)[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2018.
|
| [18] |
朱伟林, 米立军. 中国海域含油气盆地图集[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2010
|
| [18] |
Zhu W L, Mi L J. Atlas of petroliferous basins in China Sea[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2010.
|
| [19] |
郝天珧, 徐亚, 周立宏, 等. 前新生代残留盆地宏观分布的综合地球物理研究——以大港地区为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 2008, 51(2):491-502.
|
| [19] |
Hao T Y, Xu Y, Zhou L H, et al. A comprehensive geophysical study on the macroscopic distribution of pre-cenozoic residual basins—A case study of Dagang area[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2008, 51(2):491-502.
|
| [20] |
张功成, 贾庆军, 王万银, 等. 南海构造格局及其演化[J]. 地球物理学报, 2018, 61(10):4194-4215.
|
| [20] |
Zhang G C, Jia Q J, Wang W Y, et al. Tectonic framework and evolution of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2018, 61 (10):4194-4215.
|
| [21] |
雷受昱. 重力广义地形改正值和均衡改正值的一种计算方法[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1984, 4(1),101-111.
|
| [21] |
Lei S Y. A calculation method for generalized terrain correction and isostatic correction of gravity[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 1984, 4(1),101-111.
|
| [22] |
王万银, 邱之云, 杨永, 等. 位场边缘识别方法研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(1):196-210.
|
| [22] |
Wang W Y, Qiu Z Y, Yang Y, et al. Research progress of potential field edge recognition method[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(1):196-210.
|
| [23] |
Wang W Y, Pan Y, Qiu Z Y. A new edge recognition technology based on the normalized vertical derivative of the total horizontal derivative for potential data[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2009, 6(3):226-233.

|
| [24] |
王丁丁, 王万银, 朱莹洁, 等. 位场边缘识别特征点提取方法及应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 2021, 64(4):1401-1411.
|
| [24] |
Wang D D, Wang W Y, Zhu Y J, et al. Method and extraction methods and application of feature points of edge recognition for potential field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2021, 64(4):1401-1411.
|
| [25] |
纪晓琳, 王万银, 邱之云. 最小曲率位场分离方法研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(3):1042-1058.
|
| [25] |
Ji X L, Wang W Y, Qiu Z Y. Study on the separation method of minimum curvature potential field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(3):1042-1058.
|
| [26] |
Salem A, Williams S, Fairhead D, et al. Interpretation of magnetic data using tilt-angle derivatives[J]. Geophysics, 2008, 73(1):1-10.
|
| [27] |
刘强. 重磁反演中欧拉反褶积方法的分析与研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
|
| [27] |
Liu Q. Analysis and research of Euler deconvolution method in gravity and magnetic inversion[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosxiences (Beijing), 2009.
|
| [28] |
王万银, 潘作枢. 双界面模型重力场快速正反演问题[J]. 石油物探, 1993, 32(2):81-87,123.
|
| [28] |
Wang W Y, Pan Z S. Double interface model for fast forward and inverse problem of gravity field[J]. Petroleum Geophysics, 1993, 32(2):81-87,123.
|
| [1] |
XUE Dong-Xu, LIU Cheng, GUO Fa, WANG Jun, XU Duo-Xun, YANG Sheng-Fei, ZHANG Pei. Predicting the geothermal resources of the Tangyu geothermal field in Meixian County, Shaanxi Province, based on soil radon measurement and the controlled source audio magnetotelluric method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1169-1178. |
| [2] |
HU Xin-Jun, CHEN Xiao-Jing, WU Yang, BAI Ya-Dong, ZHAO Fu-Yuan. An analysis of the fault framework in southern Ningxia based on geophysical data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 916-925. |
|
|
|
|

