|
|
|
| Research progress in the influencing factors and correction methods of XRF-CS |
HUANG Ping-An1,2( ), WANG Xia-Qing2( ), WANG Xia-Qing2( ), TANG Xiang-Ling1, WANG Yu-Tang1,2, LI Wei2, LUO Zeng2, Lyu Fei-Ya2 ), TANG Xiang-Ling1, WANG Yu-Tang1,2, LI Wei2, LUO Zeng2, Lyu Fei-Ya2 |
1. College of Earth Science, Guilin University of Technology, Guilin 541004, China
2. College of Geography and Tourism, Hunan University of Arts and Science, Changde 415000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract With more than 20 years of development, the X-ray fluorescence core scanners (XRF-CS) have been widely applied in the elemental analysis of multi-type sediment cores, the paleoenvironment reconstruction, and the exploration of mineral reservoirs and their abundance, exhibiting great potential for application. However, there is a lack of studies on the influencing factors and correction of the elemental signals output by XRF-CS (especially in China), which restricts the proper use of XRF-CS and the accurate interpretation of their data. Compared with conventional XRF techniques, XRF-CS enjoy a high processing speed (only 1/10 of the time for conventional analysis), high continuity, non-destructive scanning, and a high resolution (up to 0.02 mm). However, XRF-CS only output semi-quantitative values of elemental signals and thus fail to accurately identify the element compositions. This study summarized the influencing factors of the values of the elemental signals output by XRF-CS in terms of instruments and cores, together with the degrees of the influences. On this basis, this study proposed achieving the balance between the intensity of elemental signals output by XRF-CS and cost by selecting appropriate scanning steps and exposure time on the premise of the optimal instrument setting. This study also suggested that the influences of water content and particle sizes on elemental signals should be eliminated as far as possible by drying in the air and smoothing the core surface during the scanning. To improve the accuracy of elemental signals output by XRF-CS, this study systematically introduced three types of international common calibration models and their application potential, namely the normalized median-scaled (NMS) model, the log-ratio calibration equation (LRCE) model, the improved multivariate log-ratio calibration (MLC) model, the normalized polynomial-scaled calibration (NPS) model, and polynomial-corrected multivariate log-ratio calibration (P-MLC) model. Finally, this study proposed further enhancing research on the comparative analysis of the influence exerted by the same factor among multiple types of XRF-CS; the optimization of calibration models and development of visual software packages; the equipment of multiple sensors for integrated scanning, and the extensive applications in the exploration and evaluation of geological and mineral resources.
|
|
Received: 01 June 2022
Published: 05 July 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
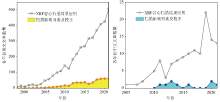
|
Statistics of the number of Chinese and English papers on XRF-CS scanning applications from 1998 to 2021 (source Google Scholar)
|

| 参数 | Itrax XRF-CS | WD-XRF | | 仪器要求 | 三相电源、液态水
冷却 | 一相或三相电源、
液态水冷却 | | X-ray光管 | Mo、Cr、Cu | Rh | | 高分辨率X光照相 | 是 | 否 | | 高精度光学图像 | 是 | 否 | | X光照相分辨率 | ≥0.1mm | 否 | | 可添加传感器 | 是 | 否 | X光照相和光学图像
的获取时间# | 0.5h | 否 | 样品处理和准备
要求 | 无损坏、平坦和光
滑的表面,并覆盖
4μm聚乙烯薄膜 | 分离样品烘干、研
磨、压片或融化,
约需5g左右 | | 真空系统要求 | 可选 | 是 | 对挥发或研磨样品
的He气系统要求 | 否 | 是 | | 样品扫描分辨率 | ≥0.02mm | ≥5mm | | 测量元素 | Al-U | Na-U | 获取数据所需时间
(K、Ca、Fe) | 2h# | 10个工作日§ | 获取数据所需时间
(Si、Al、K、Ca、Ti、
Fe、Mn、Zn、Sr、Zr) | 15h# | 10个工作日§ | 获取数据所需时间
(Si、Al、S、Cl、K、Ca、
Fe、As、Pb、Zn、Br、
Rb、Sr、Zr) | 48h# | 10个工作日§ | | 分析数据质量 | 较好 | 高精度 |
|
Comparison between Itrax XRF-CS and traditional WD-XRF[13]
|
87]
">
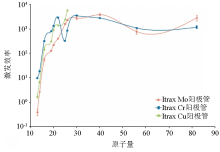
|
Comparison of excitation efficiency for X-ray tubes with different anode targets in the Itrax XRF-CS [87]
|
87]
">
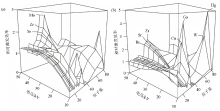
|
Relative counts recorded per element in a set of geochemical reference samples with different tube voltages for Cr anode tube (a) and Mo anode tube (b) [87]
|
87]);b—transmission properties of the Ultralene foil used for the XRF core scanner analyses, and the Kα fluorescence energies of elements Al, Si, and Cl,cited in [11]
">
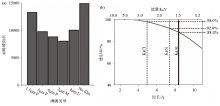
|
Effect of plastic film on XRF peak areas
a—a comparison of recorded Al peak areas using a range of available XRF films and no film (scanned with Mo anode tube at 30 kV and 30 mA, with 100 s count time,cited in [87]);b—transmission properties of the Ultralene foil used for the XRF core scanner analyses, and the Kα fluorescence energies of elements Al, Si, and Cl,cited in [11]
|
| [1] |
Yu J M, Oppo D W, Jin Z D, et al. Millennial and centennial CO2 release from the Southern Ocean during the last deglaciation[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2022, 15:293-299.
|
| [2] |
Wilhelm B, Rapuc W, Amann B, et al. Impact of warmer climate periods on flood hazard in the European Alps[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2022, 15(2):118-123.
|
| [3] |
廖时理, 陶春辉, 赵江南, 等. 基于便携式X射线荧光光谱(PXRF)分析的西南印度洋脊龙角区沉积物地球化学找矿研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3):264-272.
|
| [3] |
Liao S L, Tao C H, Zhao J N, et al. Application of PXRF in sediment analysis for geochemical prospecting in Dragon Horn area on the southwestern Indian Ridge[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(3):264-272.
|
| [4] |
Jansen J H F, Van der Gaast S J, Koster B, et al. CORTEX,a shipboard XRF-scanner for element analyses in split sediment cores[J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 151(1-4):143-153.

|
| [5] |
Yi L, Wang H F, Deng X G, et al. Geochronology and geochemical properties of Mid-Pleistocene sediments on the Caiwei Guyot in the Northwest Pacific imply a surface-to-deep linkage[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(3):253.

|
| [6] |
Gregory B R B, Patterson R T, Galloway J M, et al. The impact of cyclical,multi-decadal to centennial climate variability on arsenic sequestration in lacustrine sediments[J]. Palaeogeography,Palaeoclimatology,Palaeoecology, 2021, 565:110189.

|
| [7] |
Guo F, Clemens S C, Wang T, et al. Monsoon variations inferred from high-resolution geochemical records of the Linxia loess/paleosol sequence,western Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Catena, 2021, 198:105019.

|
| [8] |
Henares S, Bloemsma M R, Donselaar M E, et al. The role of detrital anhydrite in diagenesis of aeolian sandstones (upper Rotliegend,the Netherlands):Implications for reservoir-quality prediction[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 2014, 314:60-74.

|
| [9] |
吴兰军, 黎刚. XRF岩心扫描估算海洋沉积物有机碳含量的适用性[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(2):112-120.
|
| [9] |
Wu L J, Li G. The estimation of organic contents in marine sediments based on bromine intensity by the XRF scanner[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2022, 41(2):112-120.
|
| [10] |
张玉枝, 张家武, 毛春晖, 等. 湖泊沉积物含水量和结构对XRF扫描结果影响的评估及校正──以西藏阿翁错为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(5):1145-1153.
|
| [10] |
Zhang Y Z, Zhang J W, Mao C H, et al. Accuracy assessment and calibration of the impact of water content and structure of lake sediments on the XRF scanning data—A case study of Aweng Co in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(5):1145-1153.
|
| [11] |
Tjallingii R, Röhl U, Kolling M, et al. Influence of the water content on X-ray fluorescence core-scanning measurements in soft marine sediments[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems, 2007, 8(2):Q02004.
|
| [12] |
Richter T O, Van der Gaast S, Koster B, et al. The Avaatech XRF core scanner:Technical description and applications to NE Atlantic sediments[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 2006, 267:39-50.

|
| [13] |
Croudace I W, Rindby A, Rothwell R G. ITRAX:Description and evaluation of a new multi-function X-ray core scanner[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 2006, 267:51-63.

|
| [14] |
Hennekam R, de Lange G. X-ray fluorescence core scanning of wet marine sediments:Methods to improve quality and reproducibility of high-resolution paleoenvironmental records[J]. Limnology and Oceanography:Methods, 2012, 10:991-1003.

|
| [15] |
Zuo R G. ITRAX:A potential tool to explore the physical and chemical properties of mineralized rocks in mineral resource exploration[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 132:149-155.

|
| [16] |
Halim A Y, Kelloway S J, Marjo C, et al. A Hylogger-Itrax core-scanner comparison for multi-scale high-resolution petrophysical characterisation workflow[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2021, 133:104956.

|
| [17] |
Haschke M. The Eagle III BKA system,a novel sediment core X-ray fluorescence analyser with very high spatial resolution[J]. Geological Society of London Special Publication, 2006, 267:31-37.

|
| [18] |
Sakamoto T, Kuroki K, Sugawara T, et al. Non-destructive X-Ray fluorescence (XRF) core-imaging scanner,TATSCAN-F2[J]. Scientific Drilling, 2006, 2:37-39.

|
| [19] |
Boyle J F, Chiverrell R C, Schillereff D. Approaches to water content correction and calibration for μXRF core scanning:Comparing X-ray scattering with simple regression of elemental concentrations[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:373-390.
|
| [20] |
陈宇亮, 郑洪波. XRF岩心扫描在第四纪沉积物研究中的应用[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2014, 30(4):51-59.
|
| [20] |
Chen Y L, Zheng H B. The application of XRF core scanning to Quaternary sediments[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2014, 30(4):51-59.
|
| [21] |
Mondal M N, Horikawa K, Seki O, et al. Investigation of adequate calibration methods for X-ray fluorescence core scanning element count data:A case study of a marine sediment piston core from the Gulf of Alaska[J]. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2021, 9(5):540.

|
| [22] |
Nowaczyk N R, Liu J B, Plessen B, et al. A high-resolution paleosecular variation record for marine isotope stage 6 from Southeastern Black Sea sediments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2021, 126(3): e2020JB021350.
|
| [23] |
Hansen K E, Giraudeau J, Limoges A, et al. Characterization of organic matter in marine sediments to estimate age offset of bulk radiocarbon dating[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2022, 67:101242.

|
| [24] |
Johnson J E, Phillips S C, Clyde W C, et al. Isolating detrital and diagenetic signals in magnetic susceptibility records from methane-bearing marine sediments[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems, 2021, 22(9): e2021GC009867.
|
| [25] |
Lyle M, Lyle A O, Gorgas T, et al. Data report:Raw and normalized elemental data along the Site U1338 splice from X-ray fluorescence scanning[J]. Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program, 2012, 320/321:1-19.
|
| [26] |
张喜林, 范德江, 王亮, 等. X射线岩心扫描系统对海洋沉积物成分测定质量的综合评价和校正[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(6):86-95.
|
| [26] |
Zhang X L, Fan D J, Wang L, et al. The calibration and quality evaluation of elemental analysis results of marine sediment measured by an X-ray fluorescence core scanner[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013, 35(6):86-95.
|
| [27] |
Shackford J K, Lyle M, Wilkens R H, et al. Data report:Raw and normalized elemental data along the Site U1335,U1336,and U1337 splices from X-ray fluorescence scanning[J]. Proceedings of the Integrated Ocean Drilling Program, 2014, 320/321:1-19.
|
| [28] |
Lefebvre P, Sabatier P, Mangeret A, et al. Climate-driven fluxes of organic-bound uranium to an alpine lake over the Holocene[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2021, 783:146878.

|
| [29] |
Hagemans K, Nooren K, de Hass T, et al. Patterns of alluvial deposition in Andean lake consistent with ENSO trigger[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2021, 259:106900.

|
| [30] |
Zhao Y T, An C B, Zhou A F, et al. Late Pleistocene hydroclimatic variabilities in arid north-west China:Geochemical evidence from Balikun Lake,eastern Tienshan,China[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2021, 36(3):415-425.

|
| [31] |
Knierzinger W, Huang J J S, Strasser M, et al. Late Holocene periods of copper mining in the Eisenerz Alps (Austria) deduced from calcareous lake deposits[J]. Anthropocene, 2021, 33:100273.

|
| [32] |
杨涵菲, 赵艳, 崔巧玉, 等. 基于XRF岩芯扫描的Rb/Sr比值的古气候意义探讨──以青藏高原东部若尔盖盆地为例[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2021, 51(1):73-91.
|
| [32] |
Yang H F, Zhao Y, Cui Q Y, et al. Paleoclimatic indication of X-ray fluorescence core-scanned Rb/Sr ratios:A case study in the Zoige Basin in the eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2021, 51(1):73-91.
|
| [33] |
崔巧玉, 赵艳. 大兴安岭阿尔山天池湖泊沉积物记录的全新世气候突变[J]. 第四纪研究, 2019, 39(6):1346-1356.
|
| [33] |
Cui Q Y, Zhao Y. Climatic abrupt events implied by lacustrine sediments of Arxan Crater Lake,in the central Great Khingan Mountains,NE China during Holocene[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2019, 39(6):1346-1356.
|
| [34] |
范鹏飞, 邓述培, 邹源, 等. XRF半定量分析技术在矿石光片鉴定中的作用[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2021, 51(3):783-791.
|
| [34] |
Fan P F, Deng S P, Zou Y, et al. Application of XRF semi-quantitative analysis technology in identifying ore on polished section[J]. Journal of Jinlin University:Earth Science Edition, 2021, 51(3):783-791.
|
| [35] |
Wang X Q, Wang Z S, Xiao J, et al. Soil erosion fluxes on the central Chinese Loess Plateau during CE 1811 to 1996 and the roles of monsoon storms and human activities[J]. Catena, 2021, 200:105148.

|
| [36] |
Sun Y B, Clemens S C, Guo F, et al. High-sedimentation-rate loess records:A new window into understanding orbital- and millennial-scale monsoon variability[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2021, 220:103731.

|
| [37] |
Wang X Q, Jin Z D, He Z, et al. New insights into dating the sediment sequence within a landslide-dammed reservoir on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. The Holocene, 2019, 29(6):1020-1029.

|
| [38] |
Sun Y B, Liang L J, Bloemendal J, et al. High-resolution scanning XRF investigation of Chinese loess and its implications for millennial-scale monsoon variability[J]. Journal of Quaternary Science, 2016, 31(3):191-202.

|
| [39] |
Wang X Q, Jin Z D, Zhang X B, et al. High-resolution geochemical records of deposition couplets in a palaeolandslide-dammed reservoir on the Chinese Loess Plateau and its implication for rainstorm erosion[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2018, 18(3):1147-1158.

|
| [40] |
Wang X Q, Jin Z D, Chen L M, et al. High-resolution X-ray fluorescence core scanning of landslide-dammed reservoir sediment sequences on the Chinese Loess Plateau:New insights into the information and geochemical processes of annual freeze-thaw layers[J]. Geoderma, 2016, 279:122-131.

|
| [41] |
Liang L J, Sun Y B, Yao Z Q, et al. Evaluation of high-resolution elemental analyses of Chinese loess deposits measured by X-ray fluorescence core scanner[J]. Catena, 2012, 92:75-82.

|
| [42] |
Xue G, Cai Y J, Lu Y B, et al. Speleothem-based hydroclimate reconstructions during the penultimate deglaciation in Northern China[J]. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 2021, 36(4): e2020PA004072.
|
| [43] |
Liu X X, Sun Y B, Vandenberghe J, et al. Centennial- to millennial-scale monsoon changes since the last deglaciation linked to solar activities and North Atlantic cooling[J]. Climate of the Past, 2020, 16(1):315-324.

|
| [44] |
Tan L C, Cai Y J, Cheng H, et al. Centennial- to decadal-scale monsoon precipitation variations in the upper Hanjiang River region,China over the past 6650 years[J]. Earth and Planetary Sciences Letters, 2018, 482:580-590.

|
| [45] |
李东, 谭亮成, 郭飞, 等. Avvatech XRF岩芯扫描分析方法在石笋Sr/Ca测试中的应用[J]. 中国科学:地球科学, 2019, 49(6):1014-1023.
|
| [45] |
Li D, Tan L C, Guo F, et al. Application of Avaatech X-ray fluorescence core-scanning in Sr/Ca analysis of speleothems[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2019, 49(6):1014-1023.
|
| [46] |
Finné M, Kylander M, Boyd M, et al. Can XRF scanning of speleothems be used as a non-destructive method to identify paleoflood events in caves?[J]. International Journal of Speleology, 2015, 44(1):17-23.

|
| [47] |
谭亮成, 蔡演军, 安芷生, 等. 石笋氧同位素和微量元素记录的陕南地区4200-2000 a B.P.高分辨率季风降雨变化[J]. 第四纪研究,2014, 34(6):1238-1245.
|
| [47] |
Tan L C, Cai Y J, An Z S, et al. High-resolution monsoon precipitation variations in southern Shaanxi,Central China during 4200-2000 a B.P.as revealed by speleothem δ18O and Sr/Ca records[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(6):1238-1245.
|
| [48] |
杨欢, 曾蒙秀, 彭海军, 等. 基于XRF岩芯扫描的贵州喀斯特地区晚全新世泥炭古环境研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2020, 40(5):1154-1169.
|
| [48] |
Yang H, Zeng M X, Peng H J, et al. Application of XRF core scanning method in Late Holocene environment change study derived from a peat core from southwestern Guizhou,Southwestern China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2020, 40(5):1154-1169.
|
| [49] |
Kern O A, Koutsodendris A, Süfke F, et al. Persistent,multi-sourced lead contamination in Central Europe since the Bronze Age recorded in the Füramoos peat bog,Germany[J]. Anthropocene, 2021, 36:100310.

|
| [50] |
Longman J, Veres D, Wennrich V. Utilisation of XRF core scanning on peat and other highly organic sediments[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 514:85-96.
|
| [51] |
Kern O A, Koutsodendris A, Mächtle B, et al. XRF core scanning yields reliable semiquantitative data on the elemental composition of highly organic-rich sediments:Evidence from the Füramoos peat bog (Southern Germany)[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 697:134110.

|
| [52] |
Chawchai S, Kylander M E, Chabangborn A, et al. Testing commonly used X-ray fluorescence core scanning-based proxies for organic-rich lake sediments and peat[J]. Boreas, 2016, 45(1):180-189.

|
| [53] |
Poto L, Gabrieli J, Crowhurst S, et al. Cross calibration between XRF and ICP-MS for high spatial resolution analysis of ombrotrophic peat cores for palaeoclimatic studies[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2015, 407(2):379-385.
|
| [54] |
Kang S J, Kim J H, Joe Y J, et al. Long-term environmental changes in the Geum Estuary (South Korea):Implications of river impoundments[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2021, 168:112383.

|
| [55] |
Zhou L, Shi Y, Zhao Y Q, et al. Extreme floods of the Changjiang River over the past two millennia:Contributions of climate change and human activity[J]. Marine Geology, 2021, 433:106418.

|
| [56] |
Perez L, Crisci C, Lüning S, et al. Last millennium intensification of decadal and interannual river discharge cycles into the Southwestern Atlantic Ocean increases shelf productivity[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 2021, 196:103367.

|
| [57] |
Chen J H, Chyi S J, Yen J Y, et al. Holocene fluvial landscape evolution driven by sea level and tectonic controls in the Gangkou River,Hengchun Peninsula[J]. Terrestrial Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, 2021, 32(3):339-360.

|
| [58] |
韦璐, 范代读, 吴伊婧, 等. 近百年来长江水下三角洲高分辨率洪水沉积记录及其控制机理[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(5):707-720.
|
| [58] |
Wei L, Fan D D, Wu Y J, et al. High resolution flood records in the Yangtze subaqueous delta during the past century and control mechanism[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(5):707-720.
|
| [59] |
Turner J N, Jones A F, Brewer P A, et al. Micro-XRF applications in fluvial sedimentary environments of Britain and Ireland:Progress and prospects[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:227-265.
|
| [60] |
庞红丽, 高红山, 刘晓鹏, 等. 河流沉积物原位XRF岩芯扫描结果定量估算的初步研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(1):237-246.
|
| [60] |
Pang H L, Gao H S, Liu X P, et al. Preliminary study on calibration of X-ray fluorescence core scanner for quantitative element records in the yellow river sediments[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(1):237-246.
|
| [61] |
Gardes T, Portet-Koltalo F, Debret M, et al. Historical and post-ban releases of organochlorine pesticides recorded in sediment deposits in an agricultural watershed,France[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2021, 228:117769.
|
| [62] |
Cerdà-Domènech M, Frigola J, Sanchez-Vidal A, et al. Calibrating high resolution XRF core scanner data to obtain absolute metal concentrations in highly polluted marine deposits after two case studies off Portmán Bay and Barcelona,Spain[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 717:134778.

|
| [63] |
Croudace I W, Teasdale P A, Cundy A B. 200-year industrial archaeological record preserved in an Isle of Man saltmarsh sediment sequence:Geochemical and radiochronological evidence[J]. Quaternary International, 2019, 514:195-203.
|
| [64] |
Croudace I W, Romano E, Ausili A, et al. X-ray core scanners as an environmental forensics tool:A case study of polluted harbour sediment (Augusta Bay,Sicily)[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:393-421.
|
| [65] |
Miller H, Croudace I W, Bull J M, et al. Modern pollution signals in sediments from Windermere,NW England,determined by Micro-XRF and lead isotope analysis[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:423-442.
|
| [66] |
Roethlin R L, Gilli A, Wehrli B, et al. Tracking the legacy of early industrial activity in sediments of Lake Zurich,Switzerland:Using a novel multi-proxy approach to find the source of extensive metal contamination[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2022, 29:85789-85801.
|
| [67] |
Bertrand S, Hughen K, Giosan L. Limited influence of sediment grain size on elemental XRF core scanner measurements[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:473-490.
|
| [68] |
Maclachlan S E, Hunt J E, Croudace I W. An empirical assessment of variable water content and grain-size on X-ray fluorescence core-scanning measurements of deep sea sediments[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:173-185.
|
| [69] |
Weltje G J, Tjallingii R. Calibration of XRF core scanners for quantitative geochemical logging of sediment cores:Theory and application[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 274(3/4):423-438.

|
| [70] |
Weltje G J, Bloemsma M R, Tjallingii R, et al. Prediction of geochemical composition from XRF core scanner data:A new multivariate approach including automatic selection of calibration samples and quantification of uncertainties[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:507-534.
|
| [71] |
Chen Q, Kissel C, Govin A, et al. Correction of interstitial water changes in calibration methods applied to XRF core-scanning major elements in long sediment cores:Case study from the South China Sea[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems, 2016, 17(5):1925-1934.

|
| [72] |
Xu F J, Hu B Q, Wang C, et al. Comparison and calibration of elemental measurements in sediments using X-ray fluorescence core scanning with ICP methods:A case study of the South China Sea deep basin[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2021, 20(4):845-856.
|
| [73] |
杨明太, 张连平. WDXRF光谱仪与EDXRF光谱仪之异同[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2008, 28(5):1008-1011.
|
| [73] |
Yang M T, Zhang L P. Comparison of WDXRF and EDXRF spectrometry[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2008, 28(5):1008-1011.
|
| [74] |
李迎春, 张磊, 尚文郁. 粉末压片—X射线荧光光谱法分析富硒土壤样品中的硒及主次量元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2022, 41(1):145-152.
|
| [74] |
Li Y C, Zhang L, Shang W Y. Determination of selenium,major and minor elements in selenium-rich soil samples by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with powder pellet preparation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2022, 41(1):145-152.
|
| [75] |
周伟, 曾梦, 王健, 等. 熔融制样—X射线荧光光谱法测定稀土矿石中的主量元素和稀土元素[J]. 岩矿测试, 2018, 37(3):298-305.
|
| [75] |
Zhou W, Zeng M, Wang J, et al. Determination of major and rare earth elements in rare earth ores by X-ray fluorescence spectrometry with fusion sample preparation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2018, 37(3):298-305.
|
| [76] |
周锐, 李珍, 宋兵, 等. 长江三角洲平原湖沼沉积物XRF岩芯扫描结果的可靠性分析[J]. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(4):697-704.
|
| [76] |
Zhou R, Li Z, Song B, et al. Reliability analysis of X-ray fluorescence core-scanning in the Yangtze River delta limnetic sediments[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(4):697-704.
|
| [77] |
张鹏, 张寿庭, 邹灏, 等. 便携式X荧光分析仪在萤石矿勘查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2012, 36(5):718-722.
|
| [77] |
Zhang P, Zhang S T, Zou H, et al. The application of portable X-ray fluorescence analyzer to fluorite prospecting[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2012, 36(5):718-722.
|
| [78] |
孙伟涛, 郑有业, 牛学瑶, 等. 手持式X射线荧光光谱分析仪在斑岩铜矿快速勘查中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2021, 40(2):206-216.
|
| [78] |
Sun W T, Zheng Y Y, Niu X Y, et al. Practicality of hand-held XRF analyzer in rapid exploration of porphyry copper deposit[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2021, 40(2):206-216.
|
| [79] |
马德锡, 杨进, 陈孝强, 等. 便携式X荧光仪在多金属矿区的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2013, 37(1):63-66.
|
| [79] |
Ma D X, Yang J, Chen X Q, et al. The application of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument to the polymetallic ore district[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 37(1):63-66.
|
| [80] |
袁兆宪, 周树斌, 常浩, 等. 基于pXRF原位分析的内蒙古兴和曹四夭钼矿床深部岩石地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39(5):973-982.
|
| [80] |
Yuan Z X, Zhou S B, Chang H, et al. Lithogeochemistry characterization based on the in-Situ pXRF analyses of rocks in depth of the Caosiyao molybdenum deposit,Inner Mongolia,China[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39(5):973-982.
|
| [81] |
罗斌, 葛良全, 王卓, 等. 手持式X荧光分析仪在空气颗粒物分析中的应用[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2013, 13(6):112-114.
|
| [81] |
Luo B, Ge L Q, Wang Z, et al. Application of handheld X-ray fluorescence in the analysis of air particulate matter[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2013, 13(6):112-114.
|
| [82] |
李秋实, 葛良全, 王卓, 等. 手持式XRF分析仪快速检测大气颗粒物中Cu、Zn、Pb含量[J]. 核电子学与探测技术, 2014, 34(5):667-670.
|
| [82] |
Li Q S, Ge L Q, Wang Z, et al. Determination of Cu,Zn, Pb in atmospheric particulate matter by the handheld X-ray fluorescence analyzer[J]. Nuclear Electronics & Detection Technology, 2014, 34(5):667-670.
|
| [83] |
胡明情. 便携式XRF仪在土壤重金属检测中的应用[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2015, 38(S2):269-272.
|
| [83] |
Hu M Q. Application of portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer analyzer in field detection of heavy metal[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 38 (S2):269-272.

|
| [84] |
王豹, 余建新, 黄标, 等. 便携式X射线荧光光谱仪快速监测重金属土壤环境质量[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析[J]. 2015, 35(6):1735-1740.
|
| [84] |
Wang B, Yu J X, Huang B, et al. Fast monitoring soil environmental qualities of heavy metal by portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(6):1735-1740.
|
| [85] |
Li H Y, Sun J, Ma C M, et al. Paleoenvironmental evolution and human activities at the Hejia Site on the Ningshao coastal plain in Eastern China[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 8:609912.

|
| [86] |
Yang H F, Huang Y J, Ma C, et al. Recognition of Milankovitch cycles in XRF core-scanning records of the Late Cretaceous Nenjiang Formation from the Songliao Basin (northeastern China) and their paleoclimate implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2020, 194:104183.

|
| [87] |
Jarvis S, Croudace I W, Rothwell R G. Parameter optimisation for the ITRAX core scanner[G]//Croudace I W,Rothwell R G.Micro-XRF studies of sediment cores:Applications of a non-destructive tool for the environmental sciences.Dordrecht,Netherlands:Springer, 2015:535-562.
|
| [88] |
Gupta S, Deep K, Jain L, et al. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) set-up with a low power X-ray tube[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2010, 68(10):1922-1927.
|
| [89] |
Távora L M N, Morton E J, Gilboy W B. Enhancing the ratio of fluorescence to bremsstrahlung radiation in X-ray tube spectra[J]. Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 2001, 54(1):59-72.
|
| [90] |
Huang J J, Löwemark L, Chang Q, et al. Choosing optimal exposure times for XRF core-scanning:Suggestions based on the analysis of geological reference materials[J]. Geochemistry,Geophysics,Geosystems, 2016, 17(4):1558-1566.

|
| [91] |
雷国良, 张虎才, 常凤琴, 等. 湖泊沉积物XRF元素连续扫描与常规ICP-OES分析结果的对比及校正——以兹格塘错为例[J]. 湖泊科学, 2011, 23(2):287-294.
|
| [91] |
Lei G L, Zhang H C, Chang F Q, et al. Comparison and correction of element measurements in lacustrine sediments using X-ray fluorescence core-scanning with ICP-OES method:A case study of Zigetang Co[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2011, 23(2):287-294.

|
| [92] |
凌媛, 孙青, 朱庆增, 等. 同步辐射X射线荧光光谱法测定沉积物中元素含量的归一方法研究——以四海龙湾纹层沉积物为例[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34(6):1327-1335.
|
| [92] |
Ling Y, Sun Q, Zhu Q Z, et al. Research on normalization method for element analysis of sediment with Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray Fluorescence(SRXRF)——An example of varved sediment in Lake Sihailongwan,Northeast China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(6):1327-1335.
|
| [1] |
Duo-Ji-Wei-Se , Ci-Ren-Wang-Dui , Ni-Ma-Luo-Zhuo , ZHOU Peng, Ni-Ma-Ci-Ren . Characteristics and influencing factors of Se content in the farmland system in Bailang County, Tibet, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1118-1126. |
| [2] |
LI Shi-Bao, YANG Li-Guo, XIONG Wan-Li, MA Zhi-Chao, YUAN Hong-Wei, DUAN Ji-Xue. Speciation of selenium in the selenium-rich cultivated land in Linhe District, Bayannur City, Inner Mongolia and its influencing factors[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2): 477-486. |
|
|
|
|

