|
|
|
| Application of wave impedance inversion technology based on wavelet edge analysis and combined well-seismic modeling in reservoir prediction of Luliang uplift zone |
SHI Quan-Dang1, KONG Ling-Ye1, WU Chao1( ), DING Yan-Xue1, LIU Ze-Min1, YU Xue1, WANG Jiang2( ), DING Yan-Xue1, LIU Ze-Min1, YU Xue1, WANG Jiang2( ) ) |
1. PetroChina Xinjiang Oilfield Company Gas Production Plant No.1,Karamay 834000,China
2. Exploration and Development Research Institute of Daqing Oilfield Co.,Ltd.,Daqing 163712,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The Luliang uplift zone in the Junggar Basin exhibits intricate fault structures,laterally heterogeneous reservoirs,and small-scale and thin gas-bearing sand bodies,presenting challenges in reservoir prediction.Hence,this study applied the wave impedance inversion technology based on wavelet edge analysis and well-seismic joint modeling to directly extract seismic attributes' characteristic parameters that reflect structural and lithological changes from seismic records.These seismic attribute characteristic parameters were used to build the initial model together with acoustic impedance logs and participated in disturbance modification of the wave impedance model.This inversion technology counteracted the lack of inter-well high-frequency components and the inter-well local lithologic changes during the inter-well interpolation modeling and avoided error information caused by the inaccurate initial model in the conventional wave impedance inversion,thus improving the resolution of seismic data in identifying small-scale and thin sand bodies.The results show that under the control of the provenance of the Kelameili Mountain in the east,a fan delta-semideep (deep) lacustrine sedimentary system formed in the Wutonggou Formation in the DX14 well area of the Luliang uplift zone,hosting many fan delta-front sand bodies.The comparison between the actual drilling results and the pre-drilling prediction results indicates that the absolute error and relative mean error of sandstone thickness prediction at the well site were less than 0.60 m and less than 2.84%,respectively,suggesting that the prediction accuracy meets the requirements of fine-scale reservoir prediction.The research results provide a guide for fine-scale reservoir description and well deployment.
|
|
Received: 16 December 2022
Published: 23 January 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
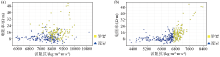
|
Intersection of resistivity and wave impedance before(a) and after(b) wave impedance reconstruction
|
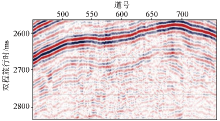
|
L1036 seismic profile in DX14 well area
|
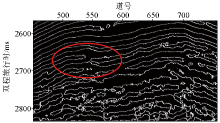
|
L1036 edge detection feature point profile in DX14 well area
|
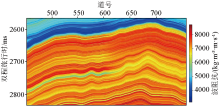
|
Low frequency logging impedance model of L1036 line
|
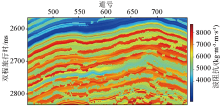
|
AIW wave impedance inversion model for well seismology unification
|
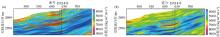
|
Comparison between AIW wave impedance inversion section and conventional model-based wave impedance inversion section
|
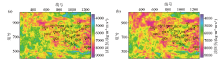
|
P3wt2 1 AIW wave impedance inversion(a) and conventional model-based wave impedance inversion(b) wave impedance plan of the first member of Wutonggou Formation in DX14 well area
|
| [1] |
Li G F, Zhou H, Zhao C. Potential risks of spectrum whitening deconvolution—Compared with well-driven deconvolution[J] .Petroleum Science, 2009, 6(2):146-152.

|
| [2] |
王江, 涂国田, 王杰. 基于载波调制的高分辨率地震双向拓频技术及其应用[J]. 石油物探, 2021, 60(6):954-963.
|
| [2] |
Wang J, Tu G T, Wang J. High-resolution seismic bidirectional frequency extension based on carrier modulation[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2021, 60(6):954-963.
|
| [3] |
王华忠, 盛燊. 走向精确地震勘探的道路[J]. 石油物探, 2021, 60(5):693-708,720.
|
| [3] |
Wang H Z, Sheng S. Pathway toward accurate seismic exploration[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2021, 60(5):693-708,720.
|
| [4] |
纪永祯, 张渝悦, 朱立华, 等. 基于SBL-WVD 的地震高分辨率时频分析[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(1):80-86,107.
|
| [4] |
Ji Y Z, Zhang Y Y, Zhu L H, et al. High-resolution seismic time-frequency analysis based on sparse Bayesian learning combined with Wigner-Ville distribution[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(1):80-86,107.
|
| [5] |
肖张波, 雷永昌, 于骏清, 等. 基于宽频资料的扩展弹性阻抗反演方法在陆丰22洼陷低勘探区古近系岩性预测中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(2):392-401.
|
| [5] |
Xiao Z B, Lei Y C, Yu J Q, et al. Application of broadband data-based extended elastic impedance inversion method in Paleogene lithology prediction of areas at a low exploration level in Lufeng 22 subsag[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2):392-401.
|
| [6] |
张德明, 刘志刚, 臧殿光, 等. 基于叠前同时反演的致密砂岩储层预测及含气性识别——以苏里格S区块为例[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(3):645-652.
|
| [6] |
Zhang D M, Liu Z G, Zang D G, et al. Prediction and identification of gas-bearing properties of tight sandstone reservoirs through simultaneous prestack inversion:A case study of block S in Sulige gas field[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(3):645-652.
|
| [7] |
姜勇, 秦德文, 俞伟哲, 等. 东海某凹陷大型砂体优势储层预测技术研究与应用[J]. 石油物探, 2020, 59(6):949-960.
|
| [7] |
Jiang Y, Qin D W, Yu W Z, et al. Prediction of favorable reservoirs in large sandstone reservoirs in a sag of the East China Sea[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2020, 59(6):949-960.
|
| [8] |
杜向东. 中国海上地震勘探技术新进展[J]. 石油物探, 2018, 57(3):321-331.
|
| [8] |
Du X D. Progress of seismic exploration technology in offshore China[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2018, 57(3):321-331.
|
| [9] |
宁宏晓, 唐东磊, 皮红梅, 等. 国内陆上“两宽一高”地震勘探技术及发展[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(5):645-653.
|
| [9] |
Ning H X, Tang D L, Pi H M, et al. The technology and development of "WBH" seismic exploration in land,China[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(5):645-653.
|
| [10] |
董世泰, 张研. 成熟探区物探技术发展方向——以中石油成熟探区为例[J]. 石油物探, 2019, 58(2):155-161,186.
|
| [10] |
Dong S T, Zhang Y. Geophysical technical development direction of mature exploration areas:A case study from a mature exploration area of PetroChina[J]. Geophysical Prospecting for Petroleum, 2019, 58(2):155-161,186.
|
| [11] |
姚逢昌, 甘利灯. 地震反演的应用与限制[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2000, 27(2):53-56.
|
| [11] |
Yao F C, Gan L D. Application and restriction of seismic inversion[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2000, 27(2):53-56.
|
| [12] |
李国发, 王艳仓, 熊金良, 等. 地震波阻抗反演实验分析[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 2010, 45(6):868-872.
|
| [12] |
Li G F, Wang Y C, Xiong J L, et al. Experimental analysis on seismic wave impedance inversion[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 2010, 45(6):868-872.
|
| [13] |
刘海宁, 韩宏伟, 魏文, 等. YD高密度三维区沙四段灰岩有利储层地震预测[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(5):1281-1287.
|
| [13] |
Liu H N, Han H W, Wei W, et al. Seismic prediction of favorable limestone reservoirs in the fourth member of Shahejie Formation in YD high density 3D area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(5):1281-1287.
|
| [14] |
许崇宝, 刘东源. 小波边缘分析建模波阻抗反演方法在煤层解释中的应用[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2008, 20(2):43-45.
|
| [14] |
Xu C B, Liu D Y. Application of wavelet marginal analytical modeling wave impedance inversion in coal seam interpretation[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2008, 20(2):43-45.
|
| [15] |
崔永福, 彭更新, 李国会, 等. 基于小波边缘分析建模的波阻抗反演技术[J]. 新疆石油地质, 2009, 30(2):261-263.
|
| [15] |
Cui Y F, Peng G X, Li G H, et al. Acoustic impedance inversion based on wavelet edge analysis and modeling[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2009, 30(2):261-263.
|
| [16] |
谢裕江, 刘高. 小波边缘分析与建模的波阻抗反演算法的改进——以中国MOU气田盒8段储层分布预测为例[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2013, 47(9):1680-1684,1696.
|
| [16] |
Xie Y J, Liu G. Algorithmic modification of acoustic impedance inversion based on wavelet edge analysis and modelling:a case of reservoir distribution prediction in h8 segment of MOU gas field,China[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University:Engineering Science, 2013, 47(9):1680-1684,1696.
|
| [17] |
Ingber L. Very fast simulated re-annealing[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 1989, 12(8):967-973.

|
| [18] |
Huang X R, Chopra A, Yang C T. Wavelet sensitivity study on inversion using heuristic combinatorial algorithms[J]. Seg Technical Program Expanded Abstracts, 1995:1088-1090.
|
| [1] |
WANG Kang, LIU Cai-Yun, XIONG Jie, WANG Yong-Chang, HU Huan-Fa, KANG Jia-Shuai. Seismic wave impedance inversion based on the fully convolutional residual shrinkage network[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1538-1546. |
| [2] |
CHEN Ren-Jie, Xu Le-Yi, LIU Ling, ZHU Huan, YI Hao, JIANG Man. A low frequency model construction method for continental strata inversion based on co-kriging technique[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(6): 1595-1601. |
|
|
|
|

