|
|
|
| Improvement in active-source surface wave acquisition device and its application in subway construction exploration |
QIN Chang-Chun1( ), WANG Guo-Shun2, LI Jing1 ), WANG Guo-Shun2, LI Jing1 |
1. The Second Geophysical Brigade,Shaanxi Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources,Xi’an 710016,China
2. School of Geological Engineering and Geomatics,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710054,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract With the rapid development of cities and the accelerated construction of subway tunnels,there is an urgent demand for the detection of unfavorable geological bodies ahead of tunnel excavation.It is difficult for traditional electromagnetic methods to yield excellent detection results in an urban environment with high electromagnetic interference.Active-source surface wave exploration has gained increasing popularity in shallow superficial exploration and engineering geophysical prospecting in cities due to its strong anti-interference,convenient acquisition devices,and low construction cost.However,the traditional active-source reflection seismic method uses only a heavy hammer with limited excitation energy as a seismic source,and the collected signals are prone to be disturbed by urban activities.Meanwhile,the asphalt or cement pavement in urban areas is unfavorable for the placement of geophones and the excitation of seismic signals from a hammer.Given these,this study improved the geophones and seismic source devices at low costs,obtaining a more efficient and user-friendly surface wave acquisition device.As confirmed by practical engineering exploration,the improved device can collect surface-wave signals with strong energy and high signal-to-noise ratios,resulting in high-quality data,desirable inversion and imaging results,and high consistency between the geological defects and actual geological conditions.The improved acquisition device can be extensively promoted and referenced in active-source surface wave exploration in cities.
|
|
Received: 20 April 2023
Published: 26 February 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
Conventional detector
|

|
Triangular bracket
|

|
Triangular bracket where the geophone is installed
|
|
Comparison of surface wave records
a—surface waves records on hard pavement when the geophone is on a triangular bracket;b—surface wave records when the geophone is inserted into the soil
|

|
Normal heavy hammer
|

|
Perforated heavy hammer
|

|
Emergency rescue tripod
|

|
Permanent magnet crane
|

|
Optimized and improved source device system
|
|
Comparison of surface wave records
a—surface wave records obtained by hammering the source with 15 pounds;b—surface wave records obtained by improved hypocenter
|

|
Comparison of surface wave records
a—surface wave records in soil;b—surface wave records on cement pavement;c—surface wave records on cement pavement obtained by improved hypocenter
|

| 土层编号 | 土层名称
与时代成因 | 范围值/m | 岩性描述 | | 层厚 | 层底深度 | 层底高程 | 颜色 | 密实度 | 包含物及其它特征 | | 1-1( ) | 杂填土 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 391.99 | 杂色 | 稍密 | 杂色,稍湿,土质不均,成份以建筑垃圾为主,含少量黏性土。地表0.2m为混凝土路面。 | | 1-2( ) | 素填土 | 1.8~3.0
(平均2.44) | 1.8~3.0 | 391.18~389.49 | 褐黄色 | 稍密 | 以黏性土为主,含少量碎砖块,土质疏密不均,顶部通常有0.2~0.3 m的砼地面。 | | 3-1-1( ) | 新黄土 | 9.5~13.1
(平均10.89) | 12.5~14.2 | 380.35~378.29 | 褐黄色 | / | 土质均匀,大孔、针孔及垂直节理发育,含钙膜,偶见蜗牛壳。具湿陷性。IL=0.05, a1-2=0.49 MPa-1,属中偏高压缩性土。 | | 3-2( ) | 古土壤 | 1.1~5.2
(平均4.46) | 17.0~18.5 | 375.98~374.19 | 黄褐~黄褐色 | / | 土质较均,局部略显团粒结构,具大孔、针孔。含较多钙质条斑,底部0.2 m含较多钙质结核,粒径一般0.5~1 cm,大者2~3 cm,具湿陷性;IL=0.27, a1-2=0.28 MPa-1,属中等压缩性土。 | | 3-4( ) | 粉质黏土 | 1.1~14.8
(平均4.47) | 30.8~56.4 | 361.73~335.56 | 灰黄~黄灰色 | / | 土质均匀,含氧化铁条纹及锰质斑点,局部含钙质粉末。液性指数IL=0.25,a1-2=0.23 MPa-1,属中等压缩性土。 | | 3-5( ) | 粉土 | 0.5~0.9
(平均4.47) | 18.4~19.0 | 373.69~373.59 | 褐黄色 | 密实 | 厚度小,不连续。分布于3-2层古土壤之下。土质均匀,较纯净,含钙质条斑,具针孔。W=18.5%,e=0.543,a1-2=0.13 MPa-1,属中偏低压缩性土。 | | 3-6( ) | 细砂 | 1.5~6.6
(平均3.54) | 18.5~33.6 | 374.18~359.38 | 灰黄~褐黄 | 密实 | 以透镜体状分布于3-7层中,稍湿~饱和,颗粒成分以石英、长石为主,局部夹粉质粘土、粉土薄层。N=55.4击;属低压缩性土,密实。 | | 3-7( ) | 中砂 | 1.2~11.2
(平均4.09) | 27.5~53.0 | 364.49~338.96 | 灰黄色 | 密实 | 分布于场地中部,与3-4粉质黏土交互出现,局部地段相变为粗砂。颗粒成分以石英、长石为主,局部含砾,分选好,级配不良,夹粉质黏土、粉细砂、粗砂、砾砂等夹层,含砾。N=58.1击,密实;属低压缩性土 | | 3-8( ) | 粗砂 | 9.4 | 29.6 | 362.93 | 灰黄色 | 密实 | 以透镜体状夹于3-7中砂层中。颗粒成分以石英、长石为主,局部含砾,分选好,级配不良,夹粉质黏土、粉细砂、砾砂等夹层,含砾。N=63.5击,密实。低压缩性土。 |
|
Stratigraphic comprehensive description of the exploration area
|
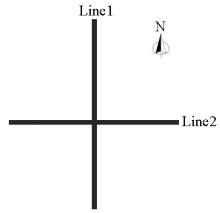
|
Schematic diagram of the orientation of the survey line layout
|
|
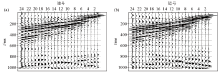
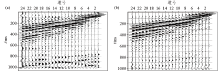
Surface wave records and corresponding dispersion curve
a—surface wave records of 1 Line 2 point;b—dispersion curve of 1 Line 2 point;c—surface wave records of 2 Line 2 point;d—dispersion curve of 2 Line 2 point
|
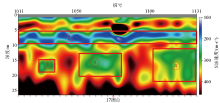
|
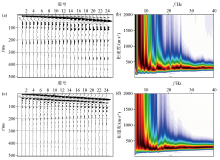
1 Line surface wave dispersion curve inverts two-dimensional shear wave velocity-depth profile
|
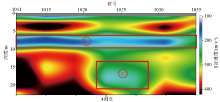
|
2 Line surface wave dispersion curve inverts two-dimensional shear wave velocity-depth profile
|
| [1] |
秦长春, 毛鹏宇, 韩要记, 等. 确定地下金属管线弯头位置和埋深的实用技术[J]. 工程地球物理学报, 2018, 15(5):655-659.
|
| [1] |
Qin C C, M P Y, H Y J, et al. Practical Techniques for determining the elbow position and depth of underground metal pipes[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Geophysics, 2018, 15(5):655-659.
|
| [2] |
黄果, 刘争平, 刘茂洋. 地下空洞的面波场地效应数值模拟研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 2021, 43(2):468-475.
|
| [2] |
Huang G, Liu Z P, Liu M Y. Numerical simulation of site effect of surface wave in underground cavities[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2021, 43(2):468-475.
|
| [3] |
杨道煌, 刘江平, 程飞, 等. 超声面波法在混凝土强度检测中的应用研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(3):626-634.
|
| [3] |
Yang D H, Liu J P, Cheng F, et al. The application of ultrasonic surface wave method to concrete strength testing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(3):626-634.
|
| [4] |
杨成林. 瑞雷波法勘探原理及其应用[J]. 物探与化探, 1989, 13(6):465-468.
|
| [4] |
Yang C L. The principle and application of Rayleigh wave exploration method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1989, 13(6):465-468.
|
| [5] |
刘云祯, 王振东. 瞬态面波法的数据采集处理系统及其应用实例[J]. 物探与化探, 1996, 20(1):28-34.
|
| [5] |
Liu Y Z, Wang Z D. Data collection and processing system of transient surface wave method and examples of its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1996, 20(1):28-34.
|
| [6] |
赵勇刚, 刘江. 瞬态面波剖面法在滑坡探查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2007, 31(S1):116-118.
|
| [6] |
Zhao Y G, Liu J. The application of the transient surface wave to the landslide exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 31(S1):116-118.
|
| [7] |
刘江平, 罗银河, 何伟兵. 相邻道瞬态瑞雷面波法与压实度检测[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2009, 31(11):1652-1659.
|
| [7] |
Liu J P, Luo Y H, He W B. Method of neighboring trace transient Rayleigh wave and its application in compactness inspection[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2009, 31(11):1652-1659.
|
| [8] |
郑立宁, 谢强, 冯治国, 等. 瞬态瑞雷面波法岩溶路基注浆质量检测现场试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(12):1934-1937.
|
| [8] |
Zheng L N, Xie Q, Feng Z G, et al. Field tests on grouting effect of Karst roadbed based on transient Rayleigh wave method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(12):1934-1937.
|
| [9] |
杨天春, 肖巧玲. 多层层状介质的瑞利面波频散特性[J]. 物探与化探, 2009, 33(3) :299-303.
|
| [9] |
Yang T C, Xiao Q L. Dispersion characteristics of Rayleigh waves in multilayered media[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 33(3):299-303.
|
| [10] |
Tsai W H, Lin Y, Cheng C C. Detecting the depth of weak layer in concrete using R-wave dispersion techniques[J]. NDT&E International, 2018, 98:161-170.

|
| [11] |
宋先海, 肖柏勋, 黄荣荣, 等. 用等厚薄层权重自适应迭代阻尼最小二乘法反演瑞雷波频散曲线[J]. 物探与化探, 2003, 27(3):212-216.
|
| [11] |
Song X H, Xiao B X, Huang R R, et al. The inversion of dispersion curves using self-adaptively iterative damping least square method by combining equal thinner layers with weighting matrix[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2003, 27(3):212-216.
|
| [12] |
凡友华, 刘雪峰, 陈晓非. 面波频散反演地下层状结构的拟牛顿法[J]. 物探与化探, 2006, 30(5):456-459.
|
| [12] |
Fan Y H, Liu X F, Chen X F. The QUASI Newton method in the inversion of the dispersion curve of Rayleigh wave in multilayered media[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 30(5):456-459.
|
| [13] |
程飞, 刘江平, 毛茂, 等. 参数自适应差分演化算法在面波频散曲线反演中的应用[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(1):147-154.
|
| [13] |
Cheng F, Liu J P, Mao M, et al. Self-adapting control parameters-based differential evolution algorithm for inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion curves[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2016, 38(1):147-154.
|
| [14] |
邵广周, 岳亮, 李远林, 等. 被动源瑞利波两道法提取频散曲线的质量控制方法[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6):1297-1308.
|
| [14] |
Shao G Z, Yue L, Li Y L, et al. A study of quality control of extracting dispersion curves by two-channel method of passive Rayleigh waves[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6):1297-1308.
|
| [15] |
吴华, 李庆春, 邵广周. 瑞利波波形反演的发展现状及展望[J]. 物探与化探, 2018, 42(6):1103-1111.
|
| [15] |
Wu H, Li Q C, Shao G Z. Development status and prospect of Rayleigh waveform inversion[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2018, 42(6):1103-1111.
|
| [16] |
邵广周, 李远林, 岳亮. 主动源与被动源面波联合勘探在黄土覆盖区三维成像中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(4):897-903.
|
| [16] |
Shao G Z, Li Y L, Yue L. Joint application of active and passive surface wave in 3D imaging of loess covered area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4):897-903.
|
| [1] |
LIU Tie-Hua, LIU Tie, ZHANG Bang, BIAN You-Yan, ZHANG Zhan-Rong, HUA Xi-Rui. Inhomogeneous media-based forward modeling technique of spectrum ratio curves and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5): 1276-1282. |
| [2] |
SHAO Guang-Zhou, LI Yuan-Lin, YUE Liang. Joint application of active and passive surface wave in 3D imaging of loess covered area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(4): 897-903. |
|
|
|
|

