|
|
|
| Evaluating the nutritional and safety quality of camellia oil, oil content of camellia oleifera fruits, and site soils in Youyang |
LI Yu1( ), ZHANG Yu-Han1( ), ZHANG Yu-Han1( ), GUAN Kai-Jiang2, BAO Li-Ran1 ), GUAN Kai-Jiang2, BAO Li-Ran1 |
1. Chongqing Key Laboratory of Land Quality Geological Survey, Southeast Sichuan Geological Group, Chongqing Geological and Mineral Resource Exploration and Development Bureau, Chongqing 400038, China
2. Agriculture and Rural Committee of Shapingba District, Chongqing Municipality, Chongqing 400038, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To ascertain the nutritional quality, oil content characteristics, and growing environment of camellia oleifera in Youyang, Chongqing, China, this study analyzed the fatty acid composition of camellia oil and the oil content of camellia oleifera fruits produced in different strata. Furthermore, this study evaluated the soil nutrients and environmental quality of the site. The results indicate that the camellia oil from Youyang exhibited a similar fatty acid composition to olive oil, suggesting that camellia oleifera seeds are valuable high-grade oilseeds. The oil content of camellia oleifera fruits is significantly associated with strata. Camellia oleifera fruits produced in the Permian strata exhibit the highest oil content, followed by those in the Silurian and Ordovician strata sequentially. The cause of the differences lies in the varying geochemical composition of soils in different strata. The camellia oleifera site in Youyang manifests average soil nutrients but relatively high soil environmental quality, with only slightly over-limit Cd content. Therefore, camellia oleifera should be cultivated by applying various fertilizers in a scientific manner to ensure its healthy growth.
|
|
Received: 28 February 2023
Published: 16 April 2024
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
ZHANG Yu-Han
E-mail: Rachilee@163.com;15034119711@163.com
|
|
|
|
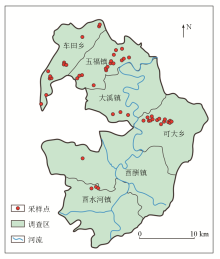
|
Sampling sites of camellia oleifera and soil-in-root in Youyang County
|

| 指标 | 方法名称 | 检出限 | | Se | 原子荧光光谱法 | 0.01 | | Hg | 0.002 | | As | 0.01 | | B | 发射光谱法 | 1 | | P | X射线荧光光谱法 | 8 | | S | 20 | | Cr | 0.4 | | Pb | 1.4 | | Zn | 1 | | CaO | 等离子体发射光谱法 | 0.02 | | K2O | 0.01 | | MgO | 0.02 | | Cu | 1 | | Ni | 0.4 | | Mn | 5 | | Mo | 极谱法 | 0.3 | | Cd | 等离子体质谱法 | 0.012 | | N | 酸碱滴定容量法 | 15 | | OrgC | 氧化还原法 | 0.05 |
|
Analysis supporting scheme and detection limit of each index of soil-in-root in Youyang County
|

| 脂肪酸 | 酉阳油茶籽油1 | 油茶籽油2 | 红松籽油2 | 茶叶籽油2 | 核桃油2 | 香榧油2 | 国内橄榄油2 | 进口橄榄油2 | | 硬脂酸 | 1.57 | 2.16 | 2.38 | 3.15 | 2.18 | 3.06 | 1.86 | 3.40 | | 棕榈酸 | 8.16 | 8.26 | 4.86 | 16.22 | 4.97 | 8.55 | 14.38 | 10.03 | | 油酸 | 78.63 | 80.55 | 26.52 | 53.24 | 25.82 | 27.57 | 70.33 | 75.69 | | 棕榈油酸 | 0.08 | 0.23 | | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.07 | 1.85 | 0.69 | | 亚油酸 | 8.42 | 8.11 | 46.70 | 25.92 | 59.13 | 44.05 | 10.12 | 7.78 | | 亚麻酸 | 0.78 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 6.61 | 0.79 | 0.90 | 0.83 | | 饱和脂肪酸总量 | 9.73 | 10.42 | 7.24 | 19.37 | 7.15 | 11.61 | 16.24 | 13.43 | | 不饱和脂肪酸总量 | 87.91 | 89.20 | 73.47 | 79.52 | 91.63 | 72.48 | 83.20 | 84.99 |
|
Composition of fatty acid for eight different kinds of woody oil
|

| 主要脂肪酸 | 限值/% | | 硬脂酸 | 0.3~4.8 | | 棕榈酸 | 3.9~14.5 | | 油酸 | 68.0~87.0 | | 棕榈油酸 | ≤0.2 | | 亚油酸 | 3.8~14.0 | | 亚麻酸 | ≤1.4 |
|
Standard limits of various fatty acids in camellia oleifera seed oil
|

| 地层 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 中位值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | | 二叠系 | 27.23 | 38.87 | 32.24 | 31.87 | 4.66 | 0.15 | | 志留系 | 21.68 | 35.12 | 28.53 | 28.51 | 3.93 | 0.14 | | 奥陶系 | 19.94 | 28.92 | 27.77 | 26.10 | 4.19 | 0.16 | | 全区 | 19.94 | 38.87 | 28.57 | 28.93 | 4.37 | 0.16 |
|
Oil content characteristics for oil-tea camellia fruit in the study area
|

评价标准
GT/T 37917—2019 | 不同地层各等级比例/% | 全区/%
(n=17) | | 等级 | 出油率/% | 二叠系
(n=5) | 志留系
(n=8) | 奥陶系
(n=4) | | 1级 | ≥32 | 60 | 12.5 | 0 | 23.5 | | 2级 | ≥29 | 0 | 37.5 | 0 | 17.6 | | 3级 | ≥26 | 40 | 37.5 | 75 | 47.1 | | 4级 | ≥23 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 等级外 | <23 | 0 | 12.5 | 25 | 11.8 |
|
Probability distribution of oil yield rating for camellia oleifera seeds in the study area
|
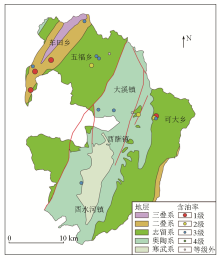
|
Stratigraphic distribution and oil conent of camellia oleifera in the study area
|

| 指标 | 含量范围 | 平均值 | 营养等级 | | 有机质 | 5.91~192.74 | 19.41 | 较缺乏 | | N | 0.57~12.21 | 1.36 | 中等 | | P | 0.18~2.07 | 0.52 | 较缺乏 | | K | 5.95~40.10 | 21.95 | 较丰富 | | CaO | 0.09~6.13 | 0.26 | 缺乏 | | MgO | 0.34~10.93 | 1.34 | 中等 | | S | 57.90~947.40 | 228.71 | 中等 | | B | 29.70~217.90 | 70.74 | 丰富 | | Mn | 55.00~13456.00 | 801.52 | 丰富 | | Mo | 0.14~40.19 | 1.32 | 丰富 | | Cu | 4.70~97.90 | 24.93 | 较丰富 | | Zn | 24.10~841.90 | 89.27 | 丰富 | | Se | 0.103~7.84 | 0.42 | 富硒 |
|
Distribution of mineral elements in soil of Youyang camellia oleifera producer
|

| 元素 | 含量/10-6 | 比例/% | | 平均值 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 清洁 | 轻微超标 | 轻度超标 | 中度超标 | 重度超标 | | Cd | 0.262 | 0.036 | 1.040 | 37 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 | | Hg | 0.114 | 0.037 | 0.298 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Pb | 30.83 | 11.80 | 67.90 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | As | 13.36 | 3.20 | 28.80 | 47 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cr | 82.80 | 17.30 | 119.60 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cu | 25.34 | 4.41 | 43.20 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | 89.86 | 24.60 | 144.60 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Ni | 34.04 | 8.00 | 96.10 | 49 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | 综合 | | | | 37 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 0 |
|
Characteristics of environmental quality and contents of heavy metal elements of soil-in-root in the study area
|
| [1] |
邓三龙, 陈永忠. 中国油茶[M]. 长沙: 湖南科学技术出版社, 2019.
|
| [1] |
Deng S L, Chen Y Z. Chinese camellia oleifera[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 2019.
|
| [2] |
李丽, 吴雪辉, 寇巧花. 茶油的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 中国油脂, 2010, 35(3):10-14.
|
| [2] |
Li L, Wu X H, Kou Q H. Research advance and application prospect of camellia seed oil[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2010, 35(3):10-14.
|
| [3] |
邓小莲, 谢光盛, 黄树根. 保健油茶的研制及其调节血脂的作用[J]. 中国油脂, 2002, 27(5):96-98.
|
| [3] |
Deng X L, Xie G S, Huang S G. Preparation of healthy tea oil and its function of adjusting blood fat[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2002, 27(5):96-98.
|
| [4] |
邓建平, 张永慧, 黄俊新, 等. 油茶对正常人血脂影响的研究[J]. 营养学报, 1993, 15(3):289-291.
|
| [4] |
Deng J P, Zhang Y H, Huang J X, et al. A study on the effect of camellia oleifera on blood lipids in normal people[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 1993, 15(3):289-291.
|
| [5] |
冯翔, 周韫珍. 油茶、玉米油和鱼油对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J]. 营养学报, 1996, 18(4):412-417.
|
| [5] |
Feng X, Zhou Y Z. Influences of feeding teaseed oil,corn oil and fish oil on immune status in mice[J]. Acta Nutrimenta Sinica, 1996, 18(4):412-417.
|
| [6] |
Mattson F H, Grundy S M. Comparison of effects of dietary saturated monounasturated and polyunsaturated faity acids on plasm a lipids and lipoproteins in man[J]. Journal of Lipid R eaearch, 1985, 26:194-202.
|
| [7] |
Barrads M A, Christofides J A, Jeremy J Y, et al. The effect of oil supplem entation on human platele function,serum cholesterol related variables and plasm a libinogen concentrations[J]. Nutrition Research, 1990(10):403-411.
|
| [8] |
李健, 范学珍. 农产品产地环境采样中土壤样品采集点的布设[J]. 现代农业科技, 2020(1):175-180.
|
| [8] |
Li J, Fan X Z. Layout of soil sample collection points in environmental sampling agricultural production areas[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology, 2020(1):175-180.
|
| [9] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0258—2014多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250 000)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014.
|
| [9] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0258—2014 Specification for multi objective regional geochemical survey(1∶250 000)[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press,2018.
|
| [10] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 14488.1—2008植物油料含油率测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.
|
| [10] |
General Administration of Quality Supervision,inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China,Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 14488.1—2018 Determination of oil content in vegetable oilseeds[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008.
|
| [11] |
中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会, 国家食品药品监督管理总局.GB 5009.168—2016食品安全国家标准食品中脂肪酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [11] |
National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China,Food and Drug Administration. GB 5009.168—2016 National food safety standard,Determination of fatty acids in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press,2016.
|
| [12] |
国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 11765—2018油茶籽油[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [12] |
State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 11765—2018 Camellia oleifera seed oil[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
|
| [13] |
潘盈伟, 于晏同, 刘增革, 等. 橄榄油生物活性成分功能研究及加工技术的探讨[C]// 中国粮油学会油脂分会第二十二届学术年会暨产品展示会论文集, 2013:49-52.
|
| [13] |
Pan Y W, Yu Y T, Liu Z G, et al. Study on function and processing technology of bioactive ingredients in olive oil[C]// Proceedings of the 22nd academic annual conference and product exhibition of the oil and fat branch of the china grain and oil society, 2013:49-52.
|
| [14] |
陈振超, 倪张林, 莫润宏, 等. 7种木本油料油脂品质综合评价[J]. 中国油脂, 2018, 43(11):80-85.
|
| [14] |
Chen Z C, Ni Z L, Mo R H, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on quality of oils from seven kinds of woody oilcrops[J]. China Oils and Fats, 2018, 43(11):80-85.
|
| [15] |
肖正春, 袁昌齐, 束成杰, 等. 三种木本植物果肉类植物油的开发与利用[J]. 中国野生植物资源, 2017, 36(3):7-9,26.
|
| [15] |
Xiao Z C, Yuan C Q, Shu C J, et al. Development and utilization of fatty oil from three kinds of woody plants's pulp[J]. Chinese Wild Plant Resources, 2017, 36(3):7-9,26.
|
| [16] |
国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 37917—2019油茶籽[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2019.
|
| [16] |
State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration of China. GB/T 37917—2019 Camellia oleifera seeds[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2019.
|
| [17] |
中华人民共和国国土资源部. DZ/T 0295—2016土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016.
|
| [17] |
Ministry of Land and Resources of the People's Republic of China. DZ/T 0295—2016 Specification for land quality geochemical evaluation[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
|
| [18] |
生态环境部, 国家市场监督管理总局.国家市场监督管理总局. GB 15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [18] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment, State Administration for Market Regulation. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018.
|
| [1] |
Peng WANG, Tuo LIU. Variational weight effect in the geochemical evaluation of soil nutrients in Baota District of Yan'an City[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(4): 847-854. |
| [2] |
Ming-Shu YAN, Chun-Mei WU, Li MENG, Xiang-Lun DING, Pan DONG, Hai DENG, Jia-Li LEI, Yuan-Yuan GONG, Li-Ran BAO. An analysis of soil nutrient status of kiwifruit orchard in Qianjiang, Chongqing[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(5): 1123-1130. |
|
|
|
|

