|
|
|
| Application of high-density electrical resistivity tomography and audio magnetotellurics for groundwater exploration in the karst area in southwestern China |
XIA Shi-Bin( ), LIAO Guo-Zhong, DENG Guo-Shi, YANG Jian, LI Fu ), LIAO Guo-Zhong, DENG Guo-Shi, YANG Jian, LI Fu |
| Chengdu Center of Geological Survey, China Geological Survey, Chengdu 610081, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Huize County of Yunnan Province is situated in the karst area in southwestern China, where karst groundwater is its primary water source. To conquer local difficulties in drinking water, this study constructed a conceptual model of groundwater occurrence by fully investigating the hydrogeological conditions of the Huize area. Moreover, this study evaluated the applicability and optimal combination of geophysical methods based on the measurement results of petrophysical properties. According to the actual local needs, this study deployed a comprehensive profile combining high-density electrical resistivity tomography (HDERT) and audio magnetotellurics (AMT) in Tuogu Village, Huize County. The groundwater enrichment site was delineated relying on resistivity anomalies, effectively guiding the layout of boreholes. The boreholes achieved the maximum single-borehole water yield of 20.76 m3/d, thus effectively alleviating the local drinking water problem. The HDERT-AMT combined exploration method proves to be optimal for prospecting for groundwater in carbonate rock areas. HDERT can accurately characterize weathered layer thicknesses, bedrock boundaries, fissure evolutionary degrees, and water-bearing properties of strata, constraining groundwater recharge channels, thus counteracting AMT's defects for identification of near-surface stratigraphic structures. AMT can accurately reflect the spatial structures of fracture zones and the macrostructures of strata, limiting the boundary conditions (aquicludes) of water-bearing structures, thus making up for the defects of insufficient detection depths of HDERT in high-resistivity stratigraphic regions. HDERT and AMT, which are complementary to each other in terms of accuracy and depth, can be applied to identify and constrain the spatial occurrence conditions of groundwater migration, storage, and enrichment.
|
|
Received: 30 May 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
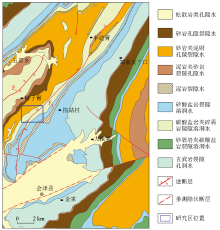
Groundwater type distribution map in Huize area
|
|
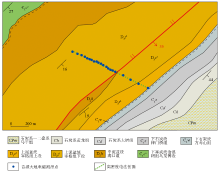
Geological map and electrical profile location in the study area
|

| 岩石类型 | 变化范围/(Ω·m) | 平均值/(Ω·m) | | 玄武岩 | 1182.1~2096.8 | 1885.4 | | 砂岩 | 105.7~1378.4 | 387.2 | | 灰岩 | 3485.2~3885.1 | 3245.7 | | 白云岩 | 3028.4~3765.5 | 3346.8 | | 泥岩 | 352.3~622.5 | 486.2 |
|
Rock resistivity statistics in Huize area
|
|
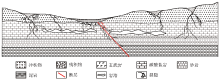
Conceptual model of groundwater deposition in study area
|
|
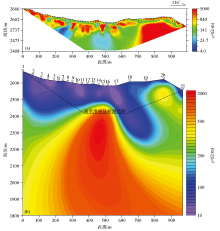
Inversion anomaly map of high density resistivity method profile(a) and audio magnetotelluric profile (b)
|
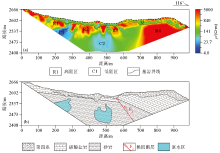
|
Inversion anomaly map (a) and inference diagram (b) of high density resistivity method profile
|
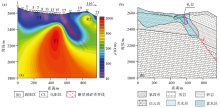
|
Inversion anomaly map (a) and inference diagram (b) of audio magnetotelluric profile
|
| [1] |
邹胜章, 朱明秋, 唐建生, 等. 西南岩溶区水资源安全与对策[J]. 地质学报, 2006, 80(10):1637-1642.
|
| [1] |
Zou S Z, Zhu M Q, Tang J S, et al. Water resources secirity in Karst area of southwest China:Problems and counterm easures[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2006, 80(10):1637-1642.
|
| [2] |
蒋忠诚, 夏日元, 时坚, 等. 西南岩溶地下水资源开发利用效应与潜力分析[J]. 地球学报, 2006, 27(5):495-502.
|
| [2] |
Jiang Z C, Xia R Y, Shi J, et al. The application effects and exploitation capacity of Karst underground water resources in southwest China[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2006, 27(5):495-502.
|
| [3] |
王宇. 岩溶找水与开发技术研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [3] |
Wang Y. Study on Karst water exploration and development technology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2007.
|
| [4] |
石应骏. 大地电磁测深法教程:高等学校教学用书[M]. 北京: 地震出版社,1985.
|
| [4] |
Shi Y J. Course of magnetotelluric sounding:A teaching book for colleges and universities[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press,1985.
|
| [5] |
林君. 核磁共振找水技术的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2010, 25(2):681-691.
|
| [5] |
Lin J. Situation and progress of nuclear magnetic resonance technique for groundwater investigations[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2010, 25(2):681-691.
|
| [6] |
Chirindja F J, Dahlin T, Juizo D, et al. Reconstructing the formation of a costal aquifer in Nampula Province,Mozambique,from ERT and IP methods for water prospection[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 76(1):36.
|
| [7] |
Kouadio K L, Xu Y X, Liu C M, et al. Two-dimensional inversion of CSAMT data and three-dimensional geological mapping for groundwater exploration in Tongkeng Area,Hunan Province,China[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2020,183:104204.
|
| [8] |
齐信, 黎清华, 张再天, 等. 海南省琼中县花岗岩地区含水层电性特征及地下水赋存规律[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(6):1001-1009.
|
| [8] |
Qi X, Li Q H, Zhang Z T, et al. Electrical characteristics and storage rules of groundwater in granite area of Qiongzhong County,Hainan Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40(6):1001-1009.
|
| [9] |
Metwaly M, Elawadi E, Moustafa S S R, et al. Groundwater contamination assessment in Al-Quwy’yia area of central Saudi Arabia using transient electromagnetic and 2D electrical resistivity tomography[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2014, 71(2):827-835.
|
| [10] |
屈利军, 李波, 周佩. 综合物探方法在湘中贫水山区找水中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2017, 41(5):835-839.
|
| [10] |
Qu L J, Li B, Zhou P. The application of multiple geophysical methods to water exploration in the arid areas of central Hunan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2017, 41(5):835-839.
|
| [11] |
刘春伟, 王重, 胡彩萍, 等. 综合物探方法在胶东岩浆岩缺水山区找水中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2023, 47(2):512-522.
|
| [11] |
Liu C W, Wang C, Hu C P, et al. Application of a comprehensive geophysical exploration methods to water exploration in magmatic rock mountainous areas with water shortage in Jiaodong Peninsula[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(2):512-522.
|
| [12] |
底青云, 石昆法, 王妙月, 等. CSAMT法和高密度电法探测地下水资源[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2001, 16(3):53-57,127.
|
| [12] |
Di Q Y, Shi K F, Wang M Y, et al. Water resources exploration with CSAMT and high density electric resistivity method[J]. Progress In Geophysics, 2001, 16(3):53-57,127.
|
| [13] |
郑智杰, 曾洁, 赵伟, 等. 高密度电法在岩溶区找水中的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2019, 34(3):1262-1267.
|
| [13] |
Zheng Z J, Zeng J, Zhao W, et al. Application research of high density resistivity method in water exploring in Karst area[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2019, 34(3):1262-1267.
|
| [14] |
董浩斌, 王传雷. 高密度电法的发展与应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2003, 10(1):171-176.
|
| [14] |
Dong H B, Wang C L. Development and application of 2d resistivity imaging surveys[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(1):171-176.
|
| [15] |
刘国兴. 电法勘探原理与方法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2005.
|
| [15] |
Liu G X. Principles and methods of electrical exploration[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2005.
|
| [16] |
陈乐寿, 王光锷. 大地电磁测深法[M]. 北京: 地质出版社,1990.
|
| [16] |
Chen L S, Wang G E. Magnetotelluric sounding[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House,1990.
|
| [17] |
李伟, 朱庆俊, 王洪磊, 等. 西南岩溶地区找水技术方法探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(5):918-923.
|
| [17] |
Li W, Zhu Q J, Wang H L, et al. On methods of finding water in the Karst zones of southwest China[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2011, 47(5):918-923.
|
| [18] |
李伟, 朱庆俊, 王洪磊, 等. 西南岩溶地区找水技术方法探讨[J]. 地质与勘探, 2011, 47(5):918-923.
|
| [18] |
Li W, Zhu Q J, Wang H L, et al. On methods of finding water in the Karst zones of southwest China[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2011, 47(5):918-923.
|
| [19] |
Romo J, Flores C, Vega R, et al. A closely-spaced magnetotelluric study of the Ahuachapán-Chipilapa geothermal field,El Salvador[J]. Geothermics, 1997, 26(5/6):627-656.
|
| [20] |
Tripaldi S, Siniscalchi A, Spitzer K. A method to determine the magnetotelluric static shift from DC resistivity measurements in practice[J]. Geophysics, 2010, 75(1):F23-F32.
|
| [21] |
Rodi W, Mackie R L. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 2001, 66(1):174-187.
|
|
|
|

