|
|
|
| Distributions, enrichment characteristics, and sources of heavy metals in soils in Fangshan District, Beijing |
HAN Bing( ), HUANG Yong( ), HUANG Yong( ), LI Huan, AN Yong-Long ), LI Huan, AN Yong-Long |
| Beijing Institute of Ecological Geology, Beijing 100120, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Heavy metal pollution in soils has become increasingly prominent. To explore the distributions of heavy metals in soils in Fangshan District, Beijing, China, this study collected 152 topsoil samples and 240 deep soil samples from this district. Based on these samples, this study statistically analyzed the distributions and enrichment factors (EF) of seven heavy metal elements, namely As, Cd, Cr, Cu, Hg, Ni, and Pb. Furthermore, this study investigated the correlations, sources, and contribution rates of these elements through principal component analysis (PCA) and positive matrix factorization (PMF). The results show that: ① Elements As, Cd, Cu, Ni, and Pb exhibit high contents in the topsoil of the Shidu, Shijiaying, Xiayunling, and Puwa areas. Besides, elements Cr, Ni, and As manifest high contents locally in Zhoukoudian, Nanjiao, and Hebei Town. Element Hg displays high content in the eastern plain areas including Doudian, Yancun, and Changyang; ② Elements Hg and Cd are highly enriched, and there exist strong corrections among elements As, Cr, and Ni; ③ These elements primarily originate from natural sources (soil parent materials), which contribute to 73.6% to 78.6% of the elements. Element Cd is mostly sourced from an anthropogenic mixed source, which contributes 83.3% of Cd. The mixed source predominantly consists of industrial and mining activities, agricultural production, and traffic emissions. Elements Cu and Pb showed similar contribution rates of natural and mixed sources, both about 50%. Element Hg in soils primarily stems from dry and wet atmospheric deposition, which yields a contribution rate of 72.4%.
|
|
Received: 06 April 2023
Published: 27 June 2024
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distribution of mineral resources in the study area
|
|
Point distribution of the study area
|

| 指标 | 规范要求 | 检出限 | 测试方法 | | As | 1 | 0.2 | 微波消解/
原子荧光法(AFS) | | Hg | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | | Cd | 0.03 | 0.017 | 电感耦合等离
子质谱法(ICP-MS) | | Cr | 5 | 1.5 | 电感耦合等离子
质谱法(ICP-OES) | | Cu | 1 | 0.1 | | Ni | 2 | 0. 2 | | Pb | 2 | 1 | | Al2O3 | 0.05 | 0.03 | X射线荧光
光谱(XRF) | | Fe2O3 | 0.05 | 0.02 | | SiO2 | 0.1 | 0.05 | | pH | 0.10 | 0.03 | pH计(ISE) |
|
The analysis method and detection limit of each index
|

| 含量范围 | 准确度
ΔlgC | 精密度
λ | ΔlgC=
| λ= | | 检出限3倍以内 | ≤0.12 | 0.17 | | 检出限3倍以外 | ≤0.10 | 0.15 | | 1%~5% | ≤0.07 | 0.10 | | >5% | ≤0.05 | 0.08 |
|
Accuracy and precision requirements for analysis
|

| 参数 | As | Cd | Cr | Cu | Hg | Ni | Pb | | 表层 | /10-6 | 9.47 | 0.189 | 58.8 | 25.8 | 0.095 | 27.8 | 28.0 | | Xmed/10-6 | 9.45 | 0.156 | 58.0 | 21.9 | 0.055 | 26.8 | 25.2 | | S/10-6 | 2.72 | 0.148 | 9.3 | 14.8 | 0.144 | 7.0 | 13.0 | | CV/% | 28.7% | 78.2% | 15.8% | 57.6% | 151.8% | 25.2% | 46.5% | | Xmin/10-6 | 2.27 | 0.058 | 33.85 | 9.2 | 0.012 | 11.6 | 11.7 | | Xmax/10-6 | 20.33 | 1.395 | 99.97 | 125.4 | 1.093 | 66.1 | 123.5 | | 深层 | /10-6 | 10.01 | 0.139 | 58.0 | 22.1 | 0.051 | 26.9 | 22.3 | | Xmed/10-6 | 10.16 | 0.103 | 59.6 | 21.8 | 0.034 | 26.9 | 20.4 | | S/10-6 | 4.34 | 0.108 | 12.3 | 8.9 | 0.081 | 7.7 | 10.7 | | Cv/% | 43.3% | 77.4% | 21.3% | 40.3% | 159.3% | 28.7% | 48.0% | | Xmin/10-6 | 2.46 | 0.040 | 12.51 | 6.2 | 0.008 | 8.5 | 6.5 | | Xmax/10-6 | 24.76 | 0.564 | 81.69 | 48.5 | 0.533 | 46.0 | 75.9 | | 北京市表层土壤Xmed/10-6[16] | 8.50 | 0.140 | 58.0 | 23.0 | 0.066 | 25.0 | 24.0 | | 北京市深层土壤Xmed/10-6[16] | 8.40 | 0.095 | 58.0 | 20.0 | 0.017 | 26.0 | 20.0 | | 海河流域表层土壤Xmed/10-6[16] | 9.70 | 0.140 | 66.0 | 23.0 | 0.035 | 28.0 | 22.0 | | 海河流域深层土壤Xmed/10-6[16] | 9.70 | 0.100 | 65.0 | 22.0 | 0.016 | 29.0 | 19.0 |
|
Geochemical parameters of soil heavy metal elements
|
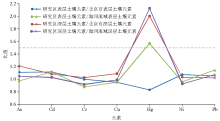
|
Comparison of mean values of heavy metal elements in soil of the study area with that in Beijing and Haihe River Basin
|
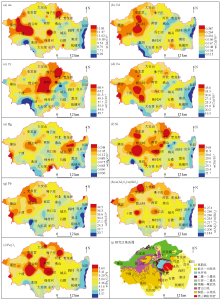
|
Geochemical distribution of heavy metal elements in topsoil
|
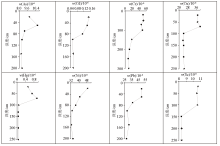
|
Vertical distribution characteristics of elements in soil profile
|

| 项目 | EF<1 | 1≤EF<2 | 2≤EF<3 | 3≤EF<5 | EF≥5 | | 污染级别 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | | 富集程度 | 无 | 轻微 | 中度 | 偏重度 | 重度 |
|
Classification of enrichment factors
|
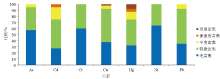
|
Statistical diagram of element enrichment ration
|
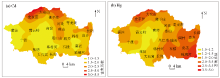
|
Spatial distribution of enrichment coefficient of Cd (a) and Hg (b)
|

| 主成分 | Cd | Pb | Cu | Cr | Ni | As | Hg | | F1 | 0.900 | 0.649 | 0.595 | 0.067 | 0.579 | 0.468 | 0.110 | | F2 | 0.120 | 0.071 | 0.295 | 0.933 | 0.734 | 0.694 | 0.015 | | F3 | 0.073 | 0.540 | 0.366 | 0.113 | 0.049 | 0.005 | 0.909 |
|
Rotated component matrix of heavy metal elements
|
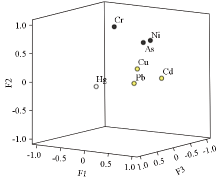
|
Components graph of heavy metal elements in rotated space
|

|
Environmental characteristics of natural source
|

| 元素 | 斜率 | R2 | | As | 0.65 | 0.82 | | Cd | 0.90 | 0.94 | | Cr | 0.89 | 0.81 | | Cu | 0.57 | 0.65 | | Hg | 1.01 | 1.00 | | Ni | 0.79 | 0.86 | | Pb | 0.71 | 0.82 |
|
Fitting results of measured values and predictedvalues of PMF model
|
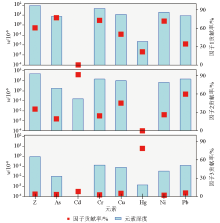
|
Analytical contribution of heavy metal PMF source
|
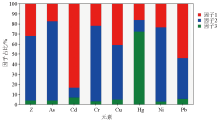
|
Factor contribution proportion of heavy metal elements
|
| [1] |
Zhang X Y, Zhong T Y, Chen D M, et al. Assessment of arsenic (As) occurrence in arable soil and its related health risk in China[J]. Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2016, 38(3):691-702.
|
| [2] |
Zhu Y G, Sun G X, Lei M, et al. High percentage inorganic arsenic content of mining impacted and nonimpacted Chinese rice[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008, 42(13):5008-5013.
|
| [3] |
黄勇, 段续川, 袁国礼, 等. 北京市延庆区土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及其来源分析[J]. 现代地质, 2022, 36(2):634-644.
|
| [3] |
Huang Y, Duan X C, Yuan G L, et al. Geochemistry and source identification of heavy metals in the top and subsoil of Yanqing District in Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 2022, 36(2):634-644.
|
| [4] |
段续川, 李苹, 黄勇, 等. 北京市密云区农业土壤重金属元素地球化学特征及生态风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(1):95-104.
|
| [4] |
Duan X C, Li P, Huang Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soils in Miyun District of Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(1):95-104.
|
| [5] |
辜敏, 赵靓, 陈倩, 等. 密云水库土壤重金属污染与生态风险评价[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2020, 42(11):1398-1404,1442.
|
| [5] |
Gu M, Zhao L, Chen Q, et al. Heavy metal pollution and ecological risk assessment of soil in Miyun Reservoir[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2020, 42(11):1398-1404,1442.
|
| [6] |
韩平, 王纪华, 冯晓元, 等. 北京顺义区土壤重金属污染生态风险评估研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2015, 34(1):103-109.
|
| [6] |
Han P, Wang J H, Feng X Y, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in soils in Shunyi,Beijing[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2015, 34(1):103-109.
|
| [7] |
李苹, 黄勇, 林赟, 等. 北京市怀柔区土壤重金属的分布特征、来源分析及风险评价[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(1):86-94.
|
| [7] |
Li P, Huang Y, Lin Y, et al. Distribution,source identification and risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil of Huairou District in Beijing[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(1):86-94.
|
| [8] |
姚世厅, 李玉倩, 王德利, 等. 北京万庄金矿区土壤重金属分布特征及污染评价[J]. 中国矿业, 2018, 27(S2):59-65.
|
| [8] |
Yao S T, Li Y Q, Wang D L, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution assessment of soil heavy metals in Wanzhuang gold mining area,Beijing[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2018, 27(S2):59-65.
|
| [9] |
胡克林, 张凤荣, 吕贻忠, 等. 北京市大兴区土壤重金属含量的空间分布特征[J]. 北京市大兴区土壤重金属含量的空间分布特征[J]. 环境科学学报, 2004, 24(3):463-468.
|
| [9] |
Hu K L, Zhang F R, Lyu D Z, et al. Spatial distribution of concentrations of soil heavy metals in Daxing County,Beijing[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2004, 24(3):463-468.
|
| [10] |
唐莹, 武相林, 孙敏, 等. 北京市门头沟风化煤矸石中汞的赋存形态与溶出特征分析[J]. 环境化学, 2022, 41(3):962-976.
|
| [10] |
Tang Y, Wu X L, Sun M, et al. Analysis on the occurrence and dissolution characteristics of mercury in weathered coal gangue in Mentougou,Beijing[J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2022, 41(3):962-976.
|
| [11] |
董騄睿, 胡文友, 黄标, 等. 南京沿江典型蔬菜生产系统土壤重金属异常的源解析[J]. 土壤学报, 2014, 51(6):1251-1261.
|
| [11] |
Dong L R, Hu W Y, Huang B, et al. Sources of heavy metals in soils of a typical vegetable production system along Yangtze River in Nanjing[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2014, 51(6):1251-1261.
|
| [12] |
北京市地质志编纂委员会. 北京志·地质矿产水利气象卷·地质矿产志[M]. 北京: 北京出版社, 2001.
|
| [12] |
Beijing Geological Records Compilation Committee. Beijing Records·Geological and mineral water conservancy meteorological volume·Geological and mineral records[M]. Beijing: Beijing Press, 2001.
|
| [13] |
钱静. 北京山区开发建设的路径依赖及其对策——以北京市房山区为例[J]. 北京农业职业学院学报, 2014, 28(2):44-48.
|
| [13] |
Qian J. Path dependence of development and construction in mountainous areas of Beijing and its countermeasures—Taking Fangshan district of Beijing as an example[J]. Journal of Beijing Agricultural Vocation College, 2014, 28(2):44-48.
|
| [14] |
DZ/T 0258—2014多目标区域地球化学调查规范(1∶250 000)[S].
|
| [14] |
DZ/T 0258—2014 Specification for multi-target regional geochemical survey(1∶250,000)[S].
|
| [15] |
DD2005-03 生态地球化学评价样品分析技术要求[S].
|
| [15] |
DD2005- 03 Technical requirements for analysis of ecological geo- chemical evalution samples[S].
|
| [16] |
侯青叶, 杨忠芳, 余涛, 等. 中国土壤地球化学参数[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2020.
|
| [16] |
Hou Q Y, Yang Z F, Yu T, et al. Soil geochemical dataset of China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2020.
|
| [17] |
李廷芳. 北京土壤的地球化学过程与元素背景含量的关系[J]. 环境科学, 1987, 8(4):57-61.
|
| [17] |
Li T F. Relationship between geochemical process of soil and background content of elements in Beijing[J]. Environmental Science, 1987, 8(4):57-61.
|
| [18] |
叶盼青, 阿不都艾尼·阿不里, 孙小丽, 等. 天山北坡经济带土壤重金属来源及污染评价[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(10):4704-4712.
|
| [18] |
Ye P Q, Abdugheni Abliz, Sun X L, et al. Source analysis and pollution assessment of soil heavy metals in the economic belt on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains[J]. China Environmental Science, 2022, 42(10):4704-4712.
|
| [19] |
Lin Y, Han P, Huang Y, et al. Source identification of potentially hazardous elements and their relationships with soil properties in agricultural soil of the Pinggu district of Beijing,China:Multivariate statistical analysis and redundancy analysis[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2017,173:110-118.
|
| [20] |
Shen G H, Ru X, Gu Y T, et al. Pollution characteristics,spatial distribution,and evaluation of heavy metal(loid)s in farmland soils in a typical mountainous hilly area in China[J]. Foods, 2023, 12(3):681.
|
| [21] |
苏海民, 孙朋, 张勇. 宿州市煤矿区土壤重金属地球化学基线及污染评价研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(12):1568-1572,1601.
|
| [21] |
Su H M, Sun P, Zhang Y. Study on geochemical baseline and contamination evaluation of soil heavy metals in Suzhou coal mining area[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(12):1568-1572,1601.
|
| [22] |
张沁瑞, 李欢, 邓宇飞, 等. 北京东南郊土壤重金属元素分布及其在表层土壤中的富集特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(2):490-501.
|
| [22] |
Zhang Q R, Li H, Deng Y F, et al. Distribution of heavy metal elements in soil of the Southeastern suburbs of Beijing and their enrichment characteristics in surface soil[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(2):490-501.
|
| [23] |
李霞, 张慧鸣, 徐震, 等. 农田Cd和Hg污染的来源解析与风险评价研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(7):1314-1320.
|
| [23] |
Li X, Zhang H M, Xu Z, et al. Source apportionment and risk assessment of Cd and Hg pollution in farmland[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(7):1314-1320.
|
| [24] |
李晓岚, 高秉博, 周艳兵, 等. 基于时空不确定性分析的北京市农田土壤重金属镉含量等级划分[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(2):307-316.
|
| [24] |
Li X L, Gao B B, Zhou Y B, et al. Classification of soil heavy metal cadmium content grade in Beijing farmland based on spatio-temporal uncertainty analysis[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(2):307-316.
|
| [25] |
李欢, 张沁瑞, 闫广新, 等. 2005-2018年北京市平原区土壤汞时空特征及影响因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2023, 45(1):93-100.
|
| [25] |
Li H, Zhang Q R, Yan G X, et al. Tempo-spatial characteristics of soil mercury in Beijing plain,China from 2005 to 2018 and their influence factors[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environ-ment, 2023, 45(1):93-103.
|
| [26] |
李科, 刘清伟. 煤中汞的来源分布与燃煤烟气中汞的形态及脱除技术[J]. 中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(10):104-106.
|
| [26] |
Li K, Liu Q W. Source distribution of mercury in coal and form and removal technology of mercury in flue gas of coal burning[J]. China Resources Comprehensive Utilization, 2019, 37(10):104-106.
|
| [27] |
成杭新, 庄广民, 赵传冬, 等. 北京市土壤Hg污染的区域生态地球化学评价[J]. 地学前缘, 2008, 15(5):126-145.
|
| [27] |
Cheng H X, Zhuang G M, Zhao C D, et al. Regional eco-geochemical assessment of mercury in soils in Beijing[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(5):126-145.
|
| [28] |
朱琳, 王雅南, 韩美, 等. 武水河水质时空分布特征及污染成因的解析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2018, 38(6):2150-2156.
|
| [28] |
Zhu L, Wang Y N, Han M, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of water quality and source identification of pollution in Wushui River Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2018, 38(6):2150-2156.
|
| [29] |
韩存亮, 罗炳圣, 常春英, 等. 基于多种方法的区域农业土壤重金属污染成因分析研究[J]. 生态与农村环境学报, 2022, 38(2):176-183.
|
| [29] |
Han C L, Luo B S, Chang C Y, et al. Identifying the source of soil heavy metal pollution in regional agricultural area based on multiple methods[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment, 2022, 38(2):176-183.
|
| [30] |
崔慧敏. 拒马河悬浮沉积物对重金属的吸附—解吸研究[J]. 水资源保护, 2000, 16(1):25-28,46.
|
| [30] |
Cui H M. Study on adsorption of heavy metals by suspended sediment of Juma River[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2000, 16(1):25-28,46.
|
| [31] |
Gao J W, Gong J J, Yang J Z, et al. Spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in a typical volcanic area:Influence of parent materials[J]. Heliyon, 2023, 9(1):e12993.
|
| [32] |
Qin Y L, Zhang F G, Xue S D, et al. Heavy metal pollution and source contributions in agricultural soils developed from Karst landform in the southwestern region of China[J]. Toxics, 2022, 10(10):568.
|
| [33] |
Chen L, Ma K, Ma J, et al. Risk assessment and sources of heavy metals in farmland soils of Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia[J]. Huan Jing Ke Xue, 2023, 44(1):356-366.
|
| [34] |
陈林, 马琨, 马建军, 等. 宁夏引黄灌区农田土壤重金属生态风险评价及来源解析[J]. 环境科学, 2023, 44(1):356-366.
|
| [34] |
Chen L, Ma K, Ma J J, et al. Risk assessment and sources of heavy metals in farmland soils of Yellow River irrigation area of Ningxia[J]. Environmental Science, 2023, 44(1):356-366.
|
| [35] |
Smolík J, Hartman M, Sýkorová I, et al. Emission fluxes of heavy metals from the fluidized bed combustion of fossil fuels[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science,1995,26:S655-S656.
|
| [36] |
Jacobsen A P, Blumenthal R S. Cardiovascular disease is the condition,air pollution the risk factor,fossil fuel combustion the cause[J]. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2022, 79(2):e131.
|
| [37] |
Xu J, Niehoff N M, White A J, et al. Fossil-fuel and combustion-related air pollution and hypertension in the Sister Study[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2022,315:120401.
|
| [38] |
Guan Q Y, Wang F F, Xu C Q, et al. Source apportionment of heavy metals in agricultural soil based on PMF:A case study in Hexi Corridor,Northwest China[J]. Chemosphere, 2018,193:189-197.
|
| [39] |
付昱萌. 基于PMF模型鄂州市大气挥发性有机物污染特征及来源解析[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2020.
|
| [39] |
Fu Y M. Analysis of pollution characteristics and sources of vocs in Ezhou City based on PMF[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2020.
|
| [40] |
邹长伟, 江玉洁, 黄虹. 重金属镉的分布、暴露与健康风险评价研究进展[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2022, 17(6):225-243.
|
| [40] |
Zou C W, Jiang Y J, Huang H. Distribution,exposure and health risk assessment of heavy metal cadmium:A review[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2022, 17(6):225-243.
|
| [41] |
石文静, 周翰鹏, 孙涛, 等. 矿区周边土壤重金属污染优先控制因子及健康风险评价研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2022, 31(8):1616-1628.
|
| [41] |
Shi W J, Zhou H P, Sun T, et al. Research on priority control factors and health risk assessment of heavy metal pollution in soil around mining areas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2022, 31(8):1616-1628.
|
| [42] |
Giersz J, Bartosiak M, Jankowski K. Sensitive determination of Hg together with Mn,Fe,Cu by combined photochemical vapor generation and pneumatic nebulization in the programmable temperature spray chamber and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry[J]. Talanta, 2017,167:279-285.
|
| [43] |
董丽君, 张展华, 张彤. 土壤环境汞污染现状及其影响因素研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2022, 50(3):397-414,319.
|
| [43] |
Dong L J, Zhang Z H, Zhang T. Mercury pollution in soil environment:Current status and its influencing factors[J]. Earth and Environment, 2022, 50(3):397-414,319.
|
| [44] |
王鑫, 刘冬跃, 钱松山, 等. 大气沉降对环境污染研究现状及进展[J]. 北京水务, 2021(2):16-20.
|
| [44] |
Wang X, Liu D Y, Qian S S, et al. Research progress of atmospheric deposition on environmental pollution[J]. Beijing Water, 2021(2):16-20.
|
| [45] |
王林江, 刘廷吉, 林则鑫, 等. 土壤—作物系统重金属迁移转化研究进展[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2021, 27(22):147-154.
|
| [45] |
Wang L J, Liu T J, Lin Z X, et al. Research progress on the migration and transformation of heavy metals in soil-crop system[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 27(22):147-154.
|
| [1] |
SUN Hong-Lin, LIU Tie-Hua, LIU Tie, ZHANG Zhan-Rong, CHEN Zhi-Xing. Multi-source frequency-domain seismic exploration technique and its application[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 618-628. |
| [2] |
CHEN Xing-Peng, WANG Liang, LONG Xia, XI Zhen-Zhu, QI Qing-Xin, XUE Jun-Ping, DAI Yun-Feng, HU Zi-Jun. Distribution patterns of the electromagnetic fields of orthogonal horizontal magnetic dipoles as sources in CSRMT[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(3): 721-735. |
|
|
|
|

