|
|
|
| Landslide survey based on three-dimensional resistivity inversion: A case study of the Xuelang Mountain scenic spot, Wuxi, China |
JIANG Guo-Qing( ), HAO She-Feng, YU Yong-Xiang, Du Jian-Guo, LI Ming, SHANG Tong-Xiao, SONG Jing-Lei ), HAO She-Feng, YU Yong-Xiang, Du Jian-Guo, LI Ming, SHANG Tong-Xiao, SONG Jing-Lei |
| Geological Survey of Jiangsu Province,Nanjing 210018,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Effectively identifying the stratigraphic and landslide structures in landslide-prone areas is significant for disaster prevention and mitigation. By investigating the landslides in the Xuelang Mountain scenic spot in Wuxi, this study analyzed the differences between two-and three-dimensional inversion using the high-density resistivity method. Accordingly, this study explored methods for eliminating the banded effect in the three-dimensional inversion, performed three-dimensional resistivity inversion under the constraints of high-precision surface elevation data and borehole-derived prior information, and constructed a three-dimensional geological model for the study area. The results indicate that three-dimensional resistivity inversion enjoys distinct advantages in complex landslide surveys. The banded effect can be effectively suppressed by optimizing the grid spacing, damping coefficient, and filter parameters for inversion. Furthermore, the terrain-induced impacts and the multiplicity of solutions of the inversion can be significantly reduced using constraints of refined terrain data and prior information, thus improving the resolutions of stratigraphic boundaries and landslide structures. Through three-dimensional resistivity inversion and geological modeling, this study determined the three-dimensional stratigraphic structure, along with the spatial distributions of the landslide bodies and sliding surfaces, and investigated landslide mechanisms, providing important data for the survey and control of landslides in the study area.
|
|
Received: 26 March 2024
Published: 08 January 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
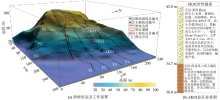
|
Landslide form and deployment of ERT in the study area
|

| 地层 | 岩性 | 电阻率ρ/ (Ω·m) | | 第四系(Q) | 黏土、泥质粉细砂 | 10~20 | | 粉细砂、细砂 | 20~30 | | 中、粗砂 | 30~50 | | 砂砾石 | 50~60 | 泥盆系上统五通组
(D3w) | 石英砂岩夹
粉砂质泥岩 | 800~3600 |
|
Statistical table of regional physical parameters
|
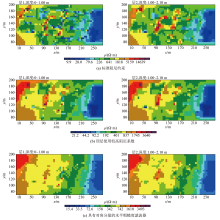
|
Comparison of resistivity images for reducing banding effect
|
|
Comparison of two-dimensional and three-dimensional resistivity inversion results
|
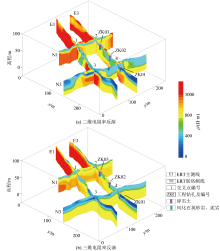
|
3D inverse resistivity and interpretation section of line E3
|
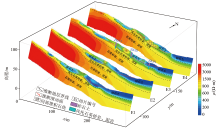
|
3D inverse resistivity and interpretation stereogram in key areas
|
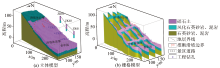
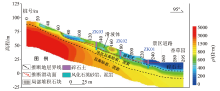
|
3D stratigraphic structure model in key area
|
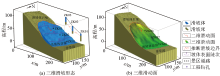
|
3D landslide morphology and structure model in key area
|
| [1] |
殷坤龙, 朱良峰. 滑坡灾害空间区划及GIS应用研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2001, 8(2):279-284.
|
| [1] |
Yin K L, Zhu L F. Landslide hazard zonation and application of GIS[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2001, 8(2):279-284.
|
| [2] |
殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2009, 17(1):29-38.
|
| [2] |
Yin Y P. Features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(1):29-38.
|
| [3] |
廖明生, 董杰, 李梦华, 等. 雷达遥感滑坡隐患识别与形变监测[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(1):332-341.
|
| [3] |
Liao M S, Dong J, Li M H, et al. Radar remote sensing for potential landslides detection and deformation monitoring[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(1):332-341.
|
| [4] |
薛翊国, 李术才, 苏茂鑫, 等. 厚层堆积层滑坡滑面的综合探测技术及其应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2013, 24(3):43-53.
|
| [4] |
Xue Y G, Li S C, Su M X, et al. Comprehensive detection technologies and their implementation on slip plane in thick colluvium landslide[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(3):43-53.
|
| [5] |
李振洪, 宋闯, 余琛, 等. 卫星雷达遥感在滑坡灾害探测和监测中的应用:挑战与对策[J]. 武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2019, 44(7):967-979.
|
| [5] |
Li Z H, Song C, Yu C, et al. Application of satellite radar remote sensing to landslide detection and monitoring:challenges and solutions[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7):967-979.
|
| [6] |
周越, 曾昭发, 唐海燕, 等. 公路勘察中滑坡体的地球物理特征与分析:以张榆线公路勘察为例[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2021, 51(2):638-644.
|
| [6] |
Zhou Y, Zeng Z F, Tang H Y, et al. Geophysical characteristics of landslide body in highway reconnaissance:A case study in highway prospecting of Zhangyu Line[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2021, 51(2):638-644.
|
| [7] |
孙红林, 化希瑞, 赵晋乾. 巨型深层岩质滑坡综合物探勘察模式探讨[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2022, 39(8):6-11.
|
| [7] |
Sun H L, Hua X R, Zhao J Q. Discussion on comprehensive geophysical exploration model of giant deep rock landslides[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2022, 39(8):6-11.
|
| [8] |
李华, 王东辉. 不同物理和几何参数条件下滑坡要素的地质雷达探测响应研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2017, 25(4):1057-1064.
|
| [8] |
Li H, Wang D H. GPR responses on different physical and geometrical parameters of landslide factors[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(4):1057-1064.
|
| [9] |
李富, 周洪福, 葛华. 不同类型滑坡体的高密度电阻率法勘察电性特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(1):215-221.
|
| [9] |
Li F, Zhou H F, Ge H. Electrical characteristics of different types of landslide bodies investigated by high-density electrical method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(1):215-221.
|
| [10] |
Cebulski J, Pasierb B, Wieczorek D, et al. Reconstruction of landslide movements using digital elevation model and electrical resistivity tomography analysis in the Polish Outer Carpathians[J]. Catena, 2020, 195:1-14.
|
| [11] |
王磊, 李孝波, 苏占东, 等. 高密度电法在黄土—泥岩接触面滑坡勘察中的应用[J]. 地质力学学报, 2019, 25(4):536-543.
|
| [11] |
Wang L, Li X B, Su Z D, et al. Application of high-density electrical method in loess-mudstone interface landslide investigation[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4):536-543.
|
| [12] |
林松, 王薇, 邓小虎, 等. 三峡库区典型滑坡地质与地球物理电性特征[J]. 吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2020, 50(1):273-284.
|
| [12] |
Lin S, Wang W, Deng X H, et al. Geological and geophysical electric characteristics of typical landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Jilin University:Earth Science Edition, 2020, 50(1):273-284.
|
| [13] |
Bellanova J, Calamita G, Giocoli A, et al. Electrical resistivity imaging for the characterization of the Montaguto landslide (southern Italy)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 243:272-281.
|
| [14] |
刘栋, 张帆宇, 陈立, 等. 高密度电法在黄土滑坡结构探测与三维建模中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 2022, 37(4):1742-1748.
|
| [14] |
Liu D, Zhang F Y, Chen L, et al. Application of high-density electrical method in detecting and 3D modeling of loess landslide[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 2022, 37(4):1742-1748.
|
| [15] |
黄俊革, 王家林, 阮百尧. 三维高密度电阻率E-SCAN法有限元模拟异常特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 2006, 49(4):1206-1214.
|
| [15] |
Huang J G, Wang J L, Ruan B Y. A study on FEM modeling of anomalies of 3-D high-density E-SCAN resistivity survey[J]. Chinese Jouranl of Geophysics, 2006, 49(4):1206-1214.
|
| [16] |
戴前伟, 肖波, 冯德山, 等. 基于二维高密度电阻率勘探数据的三维反演及应用[J]. 中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2012, 43(1):293-300.
|
| [16] |
Dai Q W, Xiao B, Feng D S, et al. 3D inversion of high density resistivity method based on 2D exploration data and its application[J]. Journal of Central South University:Science and Technology, 2012, 43(1):293-300.
|
| [17] |
Loke M H, Dahlin T. Methods to reduce banding effects in 3D resistivity inversion[C]// Near Surface 2010 16th European Meeting of Environmental and Engineering Geophysics, 2010.
|
| [18] |
Chambers J E, Kuras O, Meldrum P I, et al. Electrical resistivity tomography applied to geologic,hydrogeologic,and engineering investigations at a former waste-disposal site[J]. Geophysics, 2006, 71(6):B231-B239.
|
| [19] |
Loke M H, Dahlin T, Rucker D F. Smoothness-constrained time-lapse inversion of data from 3D resistivity surveys[J]. Near Surface Geophysics, 2014, 12(1):5-24.
|
| [20] |
黄瑶. 基于三维电阻率法的水电工程隧道地质条件探查[J]. 物探与化探, 2024, 48(1):281-286.
|
| [20] |
Huang Y. Exploring geological conditions for tunnel construction in hydropower engineering using a 3D resistivity method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(1):281-286.
|
| [21] |
吴小平, 刘洋, 王威. 基于非结构网格的电阻率三维带地形反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(8):2706-2717.
|
| [21] |
Wu X P, Liu Y, Wang W. 3D resistivity inversion incorporating topography based on unstructured meshes[J]. Chinese Jouranl of Geophysics, 2015, 58(8):2706-2717.
|
| [22] |
Li S C, Nie L C, Liu B, et al. 3D electrical resistivity inversion using prior spatial shape constraints[J]. Applied Geophysics, 2013, 10(4):361-372.
|
| [23] |
Kamiński M, Zientara P, Krawczyk M. Electrical resistivity tomography and digital aerial photogrammetry in the research of the “Bachledzki Hill” active landslide——in Podhale (Poland)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 285:1-17.
|
| [24] |
喻永祥, 何伟, 李勇, 等. 雪浪山横山寺西侧顺层岩质高边坡变形破坏机理与治理方案分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2020, 31(2):33-43.
|
| [24] |
Yu Y X, He W, Li Y, et al. Stability evaluation and treatment measure study of high bedding rock slope on the west side of Hengshan Temple in Xuelang Mountain[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(2):33-43.
|
| [25] |
Bentley L R, Gharibi M. Two-and three-dimensional electrical resistivity imaging at a heterogeneous remediation site[J]. Geophysics, 2004, 69(3):674-680.
|
| [26] |
Rucker D F, Loke M H, Levitt M T, et al. Electrical-resistivity characterization of an industrial site using long electrodes[J]. Geophysics, 2010, 75(4):WA95-WA104.
|
| [1] |
ZHAO Bai-Ru, LI Hou-Pu, ZHANG Heng-Lei. Application of three-dimensional magnetic anomaly inversion in magnetite exploration[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(6): 1626-1632. |
| [2] |
LIU Hong-Hua, ZHANG Hui, WANG Ru-Jie, YU Peng, QIN Sheng-Qiang, LI Wen-Yu, CHE Rong-Qi. 3D simulations of geological structures in coastal cities using a electrical resistivity method[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 1037-1044. |
|
|
|
|

