|
|
|
| A method for quality classification of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Ordos Basin based on pore structures and multiphase seepage capacity |
XU Feng1( ), SI Zhao-Wei1( ), SI Zhao-Wei1( ), LIANG Zhong-Kui1, TIAN Chao-Guo1, LUO Lan1, GUO Yu-Hang2 ), LIANG Zhong-Kui1, TIAN Chao-Guo1, LUO Lan1, GUO Yu-Hang2 |
1. Exploration and Development Research Institute, Jidong Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Tangshan 063000, China
2. College of Geo-Exploration Science and Technology, Jilin University, Changchun 130026, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract With the advancement of social economy and science and technology, the demand for oil and gas resources has been increasing in daily life and industry. Tight sandstone reservoirs have been the priority targets for the exploration and production of oil and gas resources. However, there still exist many challenges in assessing the parameters and quality of tight sandstone reservoirs. This study conducted experiments on the physical properties, pore structures, and electrical properties of rock samples from the Taiyuan Formation in the Shenmu gas field of the Ordos Basin. Based on this, it established a porosity-permeability relationship model, a capillary pressure prediction model, and a classification saturation assessment model. Besides, it obtained the relative permeability of gas and water phases, which varied point by point, from wells based on the I-Kr model. This study proposed the factors for assessing reservoir quality, which were applied to the target interval in the study area considering the physical properties, pore structures, and multiphase seepage capacity, yielding satisfactory assessment results. Therefore, the method of this study provides a reliable basis for the log-based assessment of the quality of tight sandstone reservoirs.
|
|
Received: 13 October 2023
Published: 26 February 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|

| 标号 | 岩性 | 层组 | 长度/mm | 直径/mm | 孔隙度/% | 渗透率/mD | RQI | 束缚水饱和度 | | X37-1 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 45.12 | 25.25 | 5.21 | 0.1328 | 0.1597 | 0.7000 | | X37-2 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 43.79 | 25.23 | 8.09 | 0.3935 | 0.2205 | 0.5693 | | X37-3 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 42.21 | 25.22 | 10.39 | 0.5527 | 0.2306 | 0.4709 | | X37-4 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 41.85 | 25.21 | 9.65 | 0.4676 | 0.2201 | 0.4101 | | X37-5 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 45.12 | 25.22 | 9.76 | 0.6157 | 0.2512 | 0.4333 | | X37-6 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 44.45 | 25.24 | 9.75 | 0.5235 | 0.2317 | 0.4601 | | X37-7 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 41.79 | 25.19 | 10.08 | 0.4847 | 0.2193 | 0.4030 | | X37-8 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 43.83 | 25.22 | 11.89 | 1.4168 | 0.3452 | 0.5264 | | X37-9 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 41.06 | 25.22 | 11.12 | 0.7265 | 0.2556 | 0.3559 | | X37-10 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 44.11 | 25.27 | 9.26 | 0.5261 | 0.2384 | 0.4198 | | X37-11 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 47.12 | 25.25 | 10.88 | 1.1125 | 0.3198 | 0.4162 | | X37-12 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 45.23 | 25.30 | 10.44 | 1.0861 | 0.3225 | 0.4399 | | X37-13 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 42.50 | 25.29 | 8.58 | 0.6948 | 0.2846 | 0.4029 | | X37-14 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 45.90 | 25.26 | 11.26 | 1.0869 | 0.3107 | 0.3425 | | X37-15 | 砂岩 | 太原组 | 43.58 | 25.28 | 10.34 | 1.2611 | 0.3492 | 0.3831 |
|
Basic information of rock samples from X37-2c1 well in Taiyuan Formation
|
|
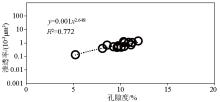
Relationship between porosity and permeability of 15 samples from Taiyuan Formation
|
|
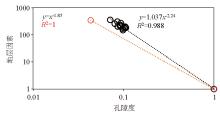
Relationship between Stratigraphic factors and porosity for 15 samples from Taiyuan Formation
|
|
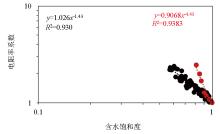
Relationship between resistivity coefficient and water saturation for 15 samples from Taiyuan Formation
|
|
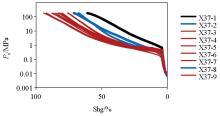
Classification of capillary pressure curves for 15 samples from Taiyuan group
|
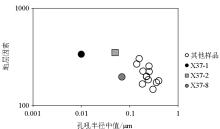
|
Intersection of stratigraphic factors and median pore throat radius for 15 samples from Taiyuan Formation
|

| 标号 | AC/
(μs·m-1) | CNL/
% | DEN/
(g·cm-3) | GR/
API | RT/
(Ω·m) | RXO/
(Ω·m) | Shg60/
MPa | Shg40/
MPa | Shg30/
MPa | Shg20/
MPa | Shg10/
MPa | Shg5/
MPa | Shg1/
MPa | | X37-1 | 208.2 | 9.25 | 2.57 | 111.85 | 52.83 | 39.77 | 175.11 | 24.24 | 7.54 | 2.79 | 1.20 | 0.75 | 0.01 | | X37-2 | 217.3 | 8.35 | 2.5 | 84.04 | 44.02 | 31.92 | 52.50 | 5.77 | 2.24 | 0.97 | 0.45 | 0.26 | 0.01 | | X37-3 | 218.02 | 8.1 | 2.51 | 67.95 | 39.54 | 28.42 | 19.42 | 2.26 | 1.19 | 0.85 | 0.62 | 0.51 | 0.01 | | X37-4 | 216.3 | 8.0 | 2.53 | 63.66 | 39.13 | 28.05 | 8.40 | 1.76 | 1.01 | 0.83 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.01 | | X37-5 | 208.53 | 10.24 | 2.59 | 83.86 | 54.8 | 37.21 | 10.74 | 1.94 | 1.08 | 0.70 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.01 | | X37-6 | 217.03 | 7.91 | 2.5 | 80.54 | 40.99 | 27.54 | 17.26 | 2.01 | 1.14 | 0.80 | 0.54 | 0.38 | 0.01 | | X37-7 | 218.55 | 7.54 | 2.48 | 65.38 | 39.03 | 25.7 | 7.86 | 1.51 | 0.95 | 0.71 | 0.52 | 0.39 | 0.01 | | X37-8 | 219.66 | 6.91 | 2.47 | 55.85 | 42.87 | 27.96 | 57.15 | 3.23 | 1.33 | 0.70 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.01 | | X37-9 | 214.09 | 7.5 | 2.52 | 56.29 | 41.97 | 26.64 | 4.81 | 1.16 | 0.83 | 0.63 | 0.48 | 0.33 | 0.01 | | X37-10 | 214.51 | 6.62 | 2.49 | 63.31 | 44.59 | 28.04 | 9.50 | 1.62 | 0.96 | 0.74 | 0.55 | 0.34 | 0.01 | | X37-11 | 215.51 | 6.74 | 2.48 | 63.22 | 44.87 | 28.27 | 9.31 | 1.45 | 0.82 | 0.52 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.01 | | X37-12 | 215.32 | 6.51 | 2.49 | 61.31 | 44.62 | 28.58 | 11.63 | 1.85 | 0.96 | 0.61 | 0.39 | 0.22 | 0.01 | | X37-13 | 215.13 | 6.63 | 2.49 | 59.68 | 44.59 | 28.78 | 7.83 | 1.47 | 0.85 | 0.54 | 0.35 | 0.21 | 0.01 | | X37-14 | 215.69 | 7.22 | 2.46 | 57.4 | 44.6 | 30.52 | 4.10 | 1.01 | 0.65 | 0.47 | 0.36 | 0.22 | 0.01 | | X37-15 | 208.11 | 9.38 | 2.54 | 70.68 | 54.42 | 38.48 | 6.22 | 1.27 | 0.70 | 0.42 | 0.25 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
|
Sample predicted capillary pressure curves for Taiyuan Formation
|
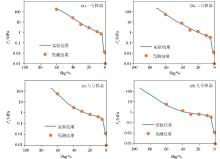
|
Effectiveness of the prediction of the capillary pressure curve
|
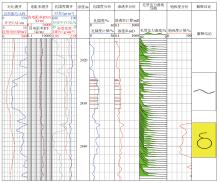
|
Example of application of capillary pressure curve prediction for well X37-2C1
|
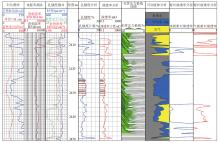
|
Example of continuous gas-water relative permeability calculation based on the I-Kr model
|

| 分类 | 物性 | 孔隙结构 | 渗流性能 | | 一类 | RQI>0.3 | 毛管压力一类 | Krg/Krw>10 | | 二类 | 0.3>RQI>0.2 | 毛管压力二类 | 10>Krg/Krw>0.01 | | 三类 | RQI<0.2 | 毛管压力三类 | Krg/Krw<0.01 |
|
Classification thresholds for physical properties, pore structure and seepage performance of Taiyuan Formation
|

| 因子 | ωpc | ωQ | ωKS | | 权重 | 0.35 | 0.4 | 0.25 |
|
Factor weight settings
|
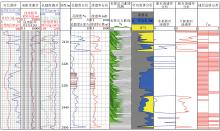
|
Example of calculation of integrated reservoir quality classification based on pore structure and seepage capacity
|
| [1] |
何庆, 韩学彬, 吴建东, 等. 低孔低渗储层参数解释模型的建立[J]. 西部探矿工程, 2009, 21(10):99-104.
|
| [1] |
He Q, Han X B, Wu J D, et al. Establishment of parameter interpretation model for low porosity and low permeability reservoirs[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2009, 21(10):99-104.
|
| [2] |
石玉江. 低渗透岩性油藏含油性与富集区测井评价研究——以鄂尔多斯盆地姬塬地区长8油层组为例[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2011.
|
| [2] |
Shi Y J. Study on oil-bearing property and logging evaluation of enriched areas in low permeability lithologic reservoirs—Taking Chang-8 reservoir group in Jiyuan area of Ordos Basin as an example[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2011.
|
| [3] |
丁圣, 钟思瑛, 周方喜, 等. 高邮凹陷成岩相约束下的低渗透储层物性参数测井解释模型[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(6):1012-1017.
|
| [3] |
Ding S, Zhong S Y, Zhou F X, et al. A logging interpretation model of physical property parameters confined by diagenetic facies of low-permeability reservoirs in Gaoyou sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(6):1012-1017.
|
| [4] |
杜元凯, 吴寒, 马强, 等. 鄂尔多斯东部低渗砂岩储层饱和度解释方法[J]. 石油化工应用, 2017, 36(1):93-96.
|
| [4] |
Du Y K, Wu H, Ma Q, et al. Reservoir saturation interpretation method of low permeability sandstone reservoir in eastern Ordos[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2017, 36(1):93-96.
|
| [5] |
Guo Y H, Pan B Z, Liu W B. A research on the relationship between resistivity index and relative permeability at different measurement conditions based on the pore structure[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 16(6):1129-1141.
|
| [6] |
王振阳. CX坳陷DY地区须家河组致密砂岩气储层测井评价方法研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2023.
|
| [6] |
Wang Z Y. Study on logging evaluation method of tight sandstone gas reservoir in Xujiahe Formation in DY area of CX depression[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2023.
|
| [7] |
刘瑞林, 朱广生. 用神经网络建立孔隙度预测模型[J]. 江汉石油学院学报, 1993(1):28-31.
|
| [7] |
Liu R L, Zhu G S. An application of neural network to reservoir evaluating from seismic data:Express porosity prediction model[J]. Journal of Jianghan Petroleum Institute, 1993(1):28-31.
|
| [8] |
赵仕俊, 任荣亭, 马绍国. 基于线性拟合方法测量岩心孔隙度研究[J]. 石油仪器, 1997(4):10-11,62.
|
| [8] |
Zhao S J, Ren R T, Ma S G. Study on measurement of core porosity based on linear fitting[J]. Petroleum Instruments, 1997(4):10-11,62.
|
| [9] |
张松扬, 严建文. 非线性声波孔隙率模型及其应用[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1998, 33(5):671-678,690-706.
|
| [9] |
Zhang S Y, Yan J W. Non-linear acoustic porosity model and its application[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1998, 33(5):671-678,690-706.
|
| [10] |
肖亮, 毛志强, 孙中春, 等. 最优化方法在复杂岩性储集层测井评价中的应用[J]. 断块油气田, 2011, 18(3):342-345.
|
| [10] |
Xiao L, Mao Z Q, Sun Z C, et al. Application of optimization method in log evaluation of complex lithologic reservoir[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2011, 18(3):342-345.
|
| [11] |
童强. 鄂尔多斯盆地史家湾—堡子湾地区长82-长9砂体构型及多因素耦合储层综合评价[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2021.
|
| [11] |
Tong Q. Sand body configuration of Chang 82-Chang 9 in Shijiawan-Baoziwan area of Ordos Basin and comprehensive evaluation of multi-factor coupling reservoir[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2021.
|
| [12] |
张雁, 柳成志, 秦秋寒, 等. 利用人工神经网络预测砂岩储层渗透率[J]. 大庆石油学院学报, 2005, 29(4):10-11,32-137.
|
| [12] |
Zhang Y, Liu C Z, Qin Q H, et al. Predicting reservoir permeability of sandstone by means of artificial neural network[J]. Journal of Daqing Petroleum Institute, 2005, 29(4):10-11,32-137.
|
| [13] |
石萍, 唐俊. 遗传算法在致密砂岩储层渗透率计算公式优化中的应用—以鄂尔多斯盆地环县地区延长组长8段为例[J]. 内蒙古大学学报:自然科学版, 2014, 45(4):365-371.
|
| [13] |
Shi P, Tang J. Application of genetic algorithm to the optimization of the calculation formula for permeability of tight sandstone reservoir:Taking the number 8 of the Yanchang formation of Huan County oilfield in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University:Natural Science Edition, 2014, 45(4):365-371.
|
| [14] |
成志刚, 宋子齐, 景成, 等. 苏里格东区致密气储层成岩储集相分类及特征[J]. 断块油气田, 2012, 19(5):577-582.
|
| [14] |
Cheng Z G, Song Z Q, Jing C, et al. Classfication and characteristics of reservoir diagenetic facies for tight gas reservoir in eastern area of Sulige[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2012, 19(5):577-582.
|
| [15] |
尹帅, 丁文龙, 单钰铭, 等. 利用致密砂岩储层电导率参数求取渗透率[J]. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(6):117-124.
|
| [15] |
Yin S, Ding W L, Shan Y M, et al. Permeability calculation of tight sandstone reservoir by conductivity parameters[J]. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2016, 28(6):117-124.
|
| [16] |
萧高健. 鄂尔多斯盆地红河油田长8段致密裂缝砂岩储层表征及“甜点油层” 综合评价研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2022.
|
| [16] |
Xiao G J. Study on reservoir characterization of tight fractured sandstone in Chang 8 member of Honghe Oilfield in Ordos Basin and comprehensive evaluation of “dessert reservoir”[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2022.
|
| [17] |
Purcell W R. Capillary pressures-their measurement using mercury and the calculation of permeability therefrom[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1949, 1(2):39-48.
|
| [18] |
Burdine N T. Relative permeability calculations from pore size distribution data[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1953, 5(3):71-78.
|
| [19] |
杨博. 致密油储层微观结构及甜点评价——以鄂尔多斯盆地定边东南部三叠系延长组长7油层组为例[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2022.
|
| [19] |
Yang B. Evaluation of reservoir microstructure and dessert in tight oil—A case study of Chang 7 oil formation in Yanchang Formation of Triassic in southeastern Dingbian,Ordos Basin[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2022.
|
| [20] |
钟新宇. 河套盆地临河坳陷西部白垩系固阳组砂砾岩储层不同模态孔喉结构及渗流特征响应[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2021.
|
| [20] |
Zhong X Y. Pore throat structure and seepage characteristics response of glutenite reservoir of Cretaceous Guyang Formation in the west of Linhe Depression,Hetao Basin[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2021.
|
| [21] |
邹佳儒, 霍守东. 基于测井数据驱动的相渗曲线预测方法研究[C]// 2021年中国地球科学联合学术年会, 2021.
|
| [21] |
Zou J R, Huo S D. Research on phase permeability curve prediction based on logging data[C]// China Earth Science Joint Annual Conference, 2021.
|
| [22] |
白新庄. 神木气田新增探明储量区地震预测技术及应用效果[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2015.
|
| [22] |
Bai X Z. Seismic prediction technology and its application effect in the newly proven reserves area of Shenmu gas field[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Shiyou University, 2015.
|
| [23] |
习丽英. 神木气田储层评价及井位优化部署[D]. 西安: 西安石油大学, 2015.
|
| [23] |
Xi L Y. Reservoir evaluation and well location optimization in Shenmu gas field[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an Shiyou University, 2015.
|
| [24] |
Li K, Williams W. Deter mination of capillary pressure fuction form resistivity data[J]. Transport in Porous Media, 2007, 67(1):1-15.
|
| [25] |
Bian H Y, Li K W, Yang J H, et al. A modified method and experimental verification for estimating relative permeability from resistivity logging data[C]// Kuala Lumpur, 2014.
|
| [26] |
郭宇航. 基于渗流与导电特性的致密砂岩储层测井解释与产能预测[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.
|
| [26] |
Guo Y H. Logging interpretation and productivity prediction of tight sandstone reservoir based on seepage and conductivity characteristics[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017.
|
| [1] |
HE Xiao-Long, ZHANG Bing, YANG Kai, HE Yi-Fan, LI Zhuo. A log-based lithofacies identification method based on random forest and sedimentary microfacies characteristics:A case study of tight sandstones in the second member of the Xujiahe Formation in the Xinchang area[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(5): 1337-1347. |
| [2] |
CAO Shao-He, REN Feng-Ru, WANG Xiao-Xiao. Critical techniques for sweet spot prediction for tight sandstone reservoirs in the Dongsheng gas field and their application effects[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2024, 48(4): 954-961. |
|
|
|
|

