|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics of soil nutrient elements in cultivated land within a typical agricultural area, Liaocheng City, China |
ZHANG Wen-Qiang1,2( ), LI Chang-Suo1,2, LIU Jin-Xin1,2,3, CHENG Shi-Yue1,2,3, TENG Yue1,2, LI Gen-Lin1,2,3( ), LI Chang-Suo1,2, LIU Jin-Xin1,2,3, CHENG Shi-Yue1,2,3, TENG Yue1,2, LI Gen-Lin1,2,3( ) ) |
1. Shandong Provincial Geo-mineral Engineering Exploration Institute (No. 801 Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology Institute, Shandong Exploration Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources), Ji'nan 250014, China
2. Shandong Engineering Research Center for Environmental Protection and Remediation on Groundwater, Ji'nan 250014, China
3. Shandong Hydrogeology Engineering Geology and Environment Geology Corporation, Ji'nan 250014, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Assessing the abundance and deficiency of soil nutrient elements holds critical referential significance for guiding agricultural production, improving the planting structure, and implementing location-specific scientific fertilization. This study investigated Tangyi Town, a typical agricultural area in Liaocheng City. First, this study tested 15 nutrient indicators in 84 topsoil samples from representative cultivated land. Second, using the geographic information system (GIS) and geostatistical analysis, this study revealed the spatial distribution patterns of various geochemical elements. Third, this study conducted single-indicator and comprehensive assessments of soil nutrient geochemistry. The results show that the soils from cultivated land in Tangyi Town exhibited relatively abundant to abundant P and CaO contents, and moderate to relatively abundant K2O content. Their S content displayed overall relatively abundant to a higher level and a non-uniform distribution, with local excess observed. Additionally, they manifested relatively deficient N and organic matter contents and generally moderate trace element content. This study identified a Se-rich soil area of approximately 2.98 km2, representing about 4.76% of the total cultivated land area, with Se content ranging from 0.49×10-6 to 2.03×10-6. The comprehensive geochemical grades of soil nutrients in the study area are predominantly of grades Ⅱ (relatively abundant) and Ⅲ (moderate), covering areas of 54.11% and 40.47%, respectively, indicating favorable conditions for agricultural production. This study ascertained the soil nutrient status of cultivated land in the study area and identified Se-rich land resources, providing fundamental geochemical data for guiding the development and utilization of land resources and developing distinctive agriculture.
|
|
Received: 26 November 2024
Published: 23 October 2025
|
|
|
|
|
|
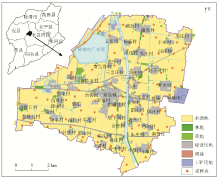
|
Distribution of land types and sampling points in the study area
|

| 指标 | 分析方法 | 仪器型号 | 检出限 | 单位 | | K2O、TFe2O3 | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | ZSXPrimusⅡ | 0.05(K2O、TFe2O3) | 10-2 | | P | X射线荧光光谱法(XRF) | ZSXPrimusⅡ | 10 | 10-6 | | N、S | 容量法(VOL) | | 20(N)、30(S) | 10-6 | | 有机质 | 容量法(VOL) | | 0.1 | 10-2 | | CaO | 电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | iCAP6300 | 0.05 | 10-2 | | Mn | 电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(ICP-OES) | iCAP6300 | 10 | 10-6 | | Cu、Mo、Zn | 电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS) | XSeriesII | 1(Cu)、0.3(Mo)、4(Zn) | 10-6 | | Se | 原子荧光光谱法(AFS) | AFS-8330 | 0.01 | 10-6 | | B | 交流电弧—发射光谱法(ES) | WP1 | 1 | 10-6 | | I | 催化分光光度法(COL) | UV1902PC | 0.5 | 10-6 | | F | 离子选择性电极法(ISE) | PXJ-1B | 100 | 10-6 |
|
Elementalan alysis methods and detection limits
|

养分
元素 | 一级
(丰富) | 二级
(较丰富) | 三级
(中等) | 四级
(较缺乏) | 五级
(缺乏) | 上限
值 | | N | >2000 | 1500~2000 | 1000~1500 | 750~1000 | ≤750 | | | P | >1000 | 800~1000 | 600~800 | 400~600 | ≤400 | | | K2O | >3.0 | 2.4~3.0 | 1.8~2.4 | 1.2~1.8 | ≤1.2 | | | SOM | >4.0 | 3.0~4.0 | 2.0~3.0 | 1.0~2.0 | ≤1.0 | | | CaO | >5.54 | 2.68~5.54 | 1.16~2.68 | 0.42~1.16 | ≤0.42 | | | TFe2O3 | >5.30 | 4.60~5.30 | 4.15~4.60 | 3.40~4.15 | ≤3.40 | | | S | >343 | 270~343 | 219~270 | 172~219 | ≤172 | ≥2000 | | B | >65 | 55~65 | 45~55 | 30~45 | ≤30 | ≥3000 | | Mo | >0.85 | 0.65~0.85 | 0.55~0.65 | 0.45~0.55 | ≤0.45 | ≥4 | | Mn | >700 | 600~700 | 500~600 | 375~500 | ≤375 | ≥1500 | | Cu | >29.0 | 24.0~29.0 | 21~24 | 16.0~21.0 | ≤16.0 | ≥50 | | Zn | >84 | 71.0~84.0 | 62~71 | 50~62.0 | ≤50.0 | ≥200 |
|
Classification Standards for Soil Nutrient Index Grades
|

| 指标 | 缺乏 | 边缘 | 适量 | 高 | 过剩 | | Se | ≤0.125 | 0.125~0.175 | 0.175~0.40 | 0.40~3.0 | >3.0 | | I | ≤1.0 | 1.0~1.5 | 1.5~5.0 | 5~100 | >100 | | F | ≤400 | 400~500 | 500~550 | 550~700 | >700 |
|
Classification standards for soil Selenium, Iodine, and Fluoride levels 10-6
|

| 等级 | 一 | 二 | 三 | 四 | 五 | | f养综 | ≥4.5 | 4.5~3.5 | 3.5~2.5 | 2.5~1.5 | <1.5 |
|
Classification of soil nutrient geochemistry comprehensive evaluation grades
|

| 指标 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 变异系数 | 背景值 | | 东昌府区[13] | 聊城市[14] | 山东省[14] | | B | 35.20 | 62.70 | 48.64 | 6.40 | 0.13 | 54.76 | 50.0 | 42.7 | | Cu | 14.90 | 41.90 | 22.64 | 4.16 | 0.18 | 23.82 | 21.3 | 22.6 | | F | 408.00 | 705.00 | 564.98 | 66.84 | 0.12 | 649 | 552 | 521 | | I | 1.09 | 10.60 | 3.61 | 1.88 | 0.52 | 3.854 | 1.94 | 1.96 | | Mn | 448.00 | 841.00 | 575.24 | 73.54 | 0.13 | 622 | 540 | 576 | | Mo | 0.34 | 1.23 | 0.65 | 0.15 | 0.23 | 0.712 | 0.57 | 0.58 | | N | 390 | 1340 | 890 | 230 | 0.26 | 1250 | 920 | 890 | | P | 631.00 | 3648.00 | 1657.82 | 579.17 | 0.35 | 1606 | 1101 | 824 | | S | 91.00 | 4324.00 | 473.39 | 590.53 | 1.25 | 308 | 234 | 211 | | Se | 0.10 | 2.03 | 0.24 | 0.22 | 0.92 | 0.223 | 0.19 | 0.18 | | Zn | 48.10 | 132.00 | 70.31 | 13.39 | 0.19 | 70.95 | 63.3 | 63.3 | | TFe2O3 | 3.20 | 5.66 | 4.01 | 0.44 | 0.11 | 4.683 | 4.1 | 4.31 | | CaO | 5.08 | 9.68 | 6.60 | 0.85 | 0.13 | 5.187 | 5.24 | 3.36 | | K2O | 2.22 | 2.81 | 2.42 | 0.12 | 0.05 | 2.299 | 2.29 | 2.47 | | SOM | 0.55 | 3.21 | 1.35 | 0.48 | 0.36 | 1.93 | 1.31 | 1.362 |
|
Statistics of soil geochemical element content characteristic parameters in study area
|
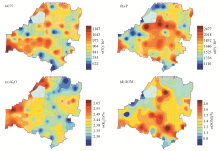
|
Distribution of macro-nutrients content in the soil of the study area
|
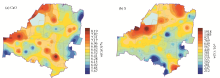
|
Distribution of middle-nutrients content in the soil of the study area
|
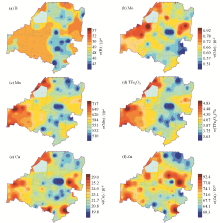
|
Distribution of micro-nutrients content in the soil of the study area
|
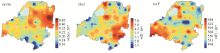
|
Distribution of characteristic nutrient elements in the soil of the study area
|
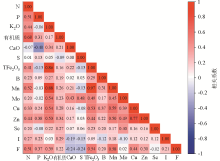
|
Correlation matrix of soil nutrient elements
|
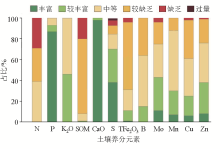
|
Proportion of samples of soil nutrient elements at different levels in the study area
|
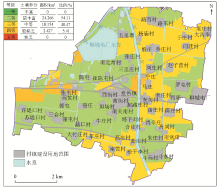
|
Comprehensive evaluation of surface soil nutrients in the study area
|
| [1] |
于林松, 万方, 范海印, 等. 姜湖贡米产地土壤重金属空间分布、源解析及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(8):4199-4211.
|
| [1] |
Yu L S, Wan F, Fan H Y, et al. Spatial distribution,source apportionment,and ecological risk assessment of soil heavy metals in Jianghugongmi producing area,Shandong Province[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(8):4199-4211.
|
| [2] |
刘立芬, 栾欣婷. 寒地黑土养分元素地球化学特征及丰缺评价——以抚远市为例[J]. 土壤, 2024, 56 (3):681-688.
|
| [2] |
Liu L F, Luan X T. Geochemical characteristics and assessment of nutrient elements in the cold region black soil:A case study of Fuyuan City[J]. Soils, 2024, 56 (3):681-688.
|
| [3] |
陈玉茹, 胡江龙, 胡绍祥, 等. 随州北部土地质量地球化学评价及空间分布研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2019, 33(S1):22-26.
|
| [3] |
Chen Y R, Hu J L, Hu S X, et al. Research on geochemical assessment and space distribution in northern Suizhou[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2019, 33(S1):22-26.
|
| [4] |
裴佳晨, 杨良波, 刘冬碧, 等. 江西省广昌县莲田土壤中、微量元素含量及空间变异性评价[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2022(3):50-57.
|
| [4] |
Pei J C, Yang L B, Liu D B, et al. Medium and trace element contents in lotus field soils at Guangchang County of Jiangxi Province and spatial variability evaluation[J]. China Vegetables, 2022(3):50-57.
|
| [5] |
张哲寰, 刘凯, 赵君, 等. 黑龙江省逊克平原土壤质量及绿色产地适宜性评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(5):1087-1096.
|
| [5] |
Zhang Z H, Liu K, Zhao J, et al. Evaluation of the soil quality and the suitability for green food-producing areas in the Xunke Plain,Heilongjiang Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(5):1087-1096.
|
| [6] |
喻超, 王英鹏, 王增辉, 等. 山东省聊城市“聊茌东” 都市区地球化学背景值研究[J]. 山东国土资源, 2021, 37(12):56-64.
|
| [6] |
Yu C, Wang Y P, Wang Z H, et al. Study on geochemical background values of Liaochidong metropolital area in Liaocheng City in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2021, 37(12):56-64.
|
| [7] |
庞绪贵, 代杰瑞, 陈磊, 等. 山东省17市土壤地球化学背景值[J]. 山东国土资源, 2019, 35(1):46-56.
|
| [7] |
Pang X G, Dai J R, Chen L, et al. Soil geochemical background value of 17 cities in Shandong Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2019, 35(1):46-56.
|
| [8] |
曹建荣, 刘衍君, 于洪军, 等. 聊城市土壤重金属含量特征分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2010, 38(12):6436-6437,6508.
|
| [8] |
Cao J R, Liu Y J, Yu H J, et al. Research on the characteristics of heavy metal contents in soil in Liaocheng City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2010, 38(12):6436-6437,6508.
|
| [9] |
罗庆芳, 张菊, 蒋磊, 等. 聊城市水岸带土壤重金属含量及污染评价[J]. 生态科学, 2017, 36(1):209-214.
|
| [9] |
Luo Q F, Zhang J, Jiang L, et al. Heavy metal concentrations and pollution assessment of riparian soils in Liaocheng City[J]. Ecological Science, 2017, 36(1):209-214.
|
| [10] |
常彬, 郭忠华, 刘根驿, 等. 黄河下游流域土壤硒元素分布特征及影响因素研究—以山东省聊城茌平地区为例[J]. 上海国土资源, 2022(3):93-98.
|
| [10] |
Chang B, Guo Z H, Liu G Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of soil selenium in the Lower Yellow River Basin:Take Chiping District of Liaocheng Shandong for example[J]. Shanghai Land & Resources, 2022(3):93-98.
|
| [11] |
段腾, 刘佳琦, 刘延龙, 等. 基于GIS的县级土地利用总体规划实施评价——以聊城市东昌府区为例[J]. 聊城大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 30(3):59-63.
|
| [11] |
Duan T, Liu J Q, Liu Y L, et al. The general land use planning implementation evaluation based on GIS at county level:Dongchangfu of Liaocheng as example[J]. Journal of Liaocheng University:Natural Science Edition, 2017, 30(3):59-63.
|
| [12] |
姜冰, 张海瑞, 刘阳, 等. 青州市南张楼村土地质量地球化学特征及特色土地资源评价[J]. 山东国土资源, 2022, 38(1):54-59.
|
| [12] |
Jiang B, Zhang H R, Liu Y, et al. Geochemical characteristic of land quality and typical land resources evaluation in Nanzhanglou Village in Qingzhou City[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2022, 38(1):54-59.
|
| [13] |
黄勇, 杨忠芳. 中国土地质量评价的研究现状及展望[J]. 地质通报, 2008, 27(2):207-211.
|
| [13] |
Huang Y, Yang Z F. Land quality evaluation in China:Present status and prospect[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2008, 27(2):207-211.
|
| [14] |
武春林, 王瑞廷, 丁坤, 等. 中国土壤质量地球化学调查与评价的研究现状和进展[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(3):240-252.
|
| [14] |
Wu C L, Wang R T, Ding K, et al. Geochemical survey and evaluation on soil quality in China:Research status and advances[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(3):240-252.
|
| [15] |
汪媛媛, 杨忠芳, 余涛. 土壤质量评价研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2011, 39(36):22617-22622,22657.
|
| [15] |
Wang Y Y, Yang Z F, Yu T. Research progress of soil quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 39(36):22617-22622,22657.
|
| [16] |
姜冰, 王松涛, 孙增兵, 等. 潍坊市土壤大量营养元素有效量及其影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2023, 55 (1):218-223.
|
| [16] |
Jiang B, Wang S T, Sun Z B, et al. Available contents of soil macronutrients and their influencing factors in Weifang[J]. Soils, 2023, 55 (1):218-223.
|
| [17] |
骆振华, 王彪, 陈昌阔, 等. 水城区猕猴桃产业园区土壤养分元素地球化学特征及地质环境[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2024, 52(5):159-165.
|
| [17] |
Luo Z H, Wang B, Chen C K, et al. Geochemical characteristics and geological environment of soil nutrient elements in the kiwifruit industrial park of Shuicheng District[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 52(5):159-165.
|
| [18] |
李巧玲, 苏建平, 阚建鸾, 等. 江苏省如皋市土壤中量元素含量有效性评价[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(2):263-268.
|
| [18] |
Li Q L, Su J P, Kan J L, et al. Availability assessment of medium elements contents in soils of Rugao,Jiangsu[J]. Soils, 2019, 51(2):263-268.
|
| [19] |
徐杰, 张亚, 王浩宇, 等. 滇中元谋土壤养分元素分布特征及异常分析[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(5):1151-1158.
|
| [19] |
Xu J, Zhang Y, Wang H Y, et al. Distribution characteristics and anomaly analysis of soil nutrient elements in Yuanmou County,Central Yunnan Province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(5):1151-1158.
|
| [20] |
曾美玲, 张中瑞, 李小川, 等. 云浮市油茶适生区土壤中量元素分析[J]. 林业与环境科学, 2017, 33(6):98-103.
|
| [20] |
Zeng M L, Zhang Z R, Li X C, et al. Soil calcium,magnesium and sulfur content of camellia oleifera suitable areas in Yunfu City[J]. Forestry and Environmental Science, 2017, 33(6):98-103.
|
| [21] |
于龙龙, 吴磊, 张志敏, 等. 富硒区土壤养分质量评价:以陕西省紫阳县闹热村为例[J]. 现代地质, 2021, 35(4):923-930.
|
| [21] |
Yu L L, Wu L, Zhang Z M, et al. Evaluation of soil nutrient quality in selenium-rich area:A case study of Naore Village,Ziyang County,Shanxi Province[J]. Geoscience, 2021, 35(4):923-930.
|
| [22] |
李德胜, 杨忠芳, 靳职斌. 太原盆地土壤微量元素的地球化学特征[J]. 地质与勘探, 2004, 40(3):86-89.
|
| [22] |
Li D S, Yang Z F, Jin Z B. Geochemical characters of trace elements of soil from the Taiyuan Basin[J]. Geology and Prospecting, 2004, 40(3):86-89.
|
| [23] |
郭莉, 杨忠芳, 阮起和, 等. 北京市平原区土壤中硒的含量和分布[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(5):859-864.
|
| [23] |
Guo L, Yang Z F, Ruan Q H, et al. Content and distribution of selenium in soil of Beijing Plain[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(5):859-864.
|
| [24] |
龚晶晶, 高健翁, 杨剑洲, 等. 琼中黎母山—湾岭地区土壤硒、碘分布特征及其影响因素探讨[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6):255-267.
|
| [24] |
Gong J J, Gao J W, Yang J Z, et al. Distribution and influencing factors of soil selenium and iodine in Limushan-Wanling,Qiongzhong area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6):255-267.
|
| [25] |
马常莲, 周金龙, 曾妍妍, 等. 新疆若羌县农用地表层土壤硒氟碘地球化学特征[J]. 物探与化探, 2022, 46(6):1573-1580.
|
| [25] |
Ma C L, Zhou J L, Zeng Y Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics of selenium,fluorine,iodine in surface soil of the agricultural land in Ruoqiang County,Xinjiang[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(6):1573-1580.
|
| [26] |
陈文静, 蔡奎, 栾文楼, 等. 河北省任丘市表层土壤元素地球化学评价[J]. 地质论评, 2023, 69 (2):809-815.
|
| [26] |
Chen W J, Cai K, Luan W L, et al. Geochemical evaluation of surface soil elements in Renqiu City,Hebei Province[J]. Geological Review, 2023, 69 (2):809-815.
|
| [27] |
崔邢涛, 栾文楼, 宋泽峰, 等. 石家庄城市土壤重金属空间分布特征及源解析[J]. 中国地质, 2016, 43(2):683-690.
|
| [27] |
Cui X T, Luan W L, Song Z F, et al. A study of the spatial distribution and source of heavy metals in urban soil in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Geology in China, 2016, 43(2):683-690.
|
| [28] |
Kunkel M L, Flores A N, Smith T J, et al. A simplified approach for estimating soil carbon and nitrogen stocks in semi-arid complex terrain[J]. Geoderma, 2011, 165(1):1-11.
|
| [29] |
吴涵, 张志远, 贾琳娜, 等. 秸秆还田量及破碎程度影响下的农田土壤碳氮淋失特征[J]. 中国海洋大学学报:自然科学版, 2025, 55(4):120-133.
|
| [29] |
Wu H, Zhang Z Y, Jia L N, et al. Impact of straw return quantity and fragmentation degree on carbon and nitrogen leaching characteristics in the farmland soil[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2025, 55(4):120-133.
|
| [30] |
刘家齐, 梁燕, 肖凡, 等. 西南喀斯特区域不同植被恢复阶段土壤磷主要来源及其季节变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2023, 34(12):3313-3321.
|
| [30] |
Liu J Q, Liang Y, Xiao F, et al. Main sources of soil phosphorus and their seasonal changes across different vegetation restoration stages in karst region of southwest China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2023, 34(12):3313-3321.
|
| [31] |
刘学, 杨继松, 王志康, 等. 辽河口湿地土壤中铁和锰元素含量的分布特征[J]. 湿地科学, 2022, 20(3):435-442.
|
| [31] |
Liu X, Yang J S, Wang Z K, et al. Distribution characteristics of iron and manganese contents in soils in the Liaohe River Estuary wetland[J]. Wetland Science, 2022, 20(3):435-442.
|
| [32] |
邵莉, 肖化云, 吴代赦, 等. 交通源重金属污染研究进展[J]. 地球与环境, 2012, 40(3):445-459.
|
| [32] |
Shao L, Xiao H Y, Wu D S, et al. Review on research on traffic-related heavy metals pollution[J]. Earth and Environment, 2012, 40(3):445-459.
|
|
|
|

