|
|
|
| The application of X-ray fluorescence rapid measurement to the exploration of the Dalu manganese deposit in Songtao |
| Song LIU |
| Geophysical and Geochemical Party, Non-ferrous Metals and Nuclear Industry Geological Exploration Bureau of Guizhou, Duyun 558000, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract In the field prospecting work, the most important thing for geologists is to wait for the data of sample test results. The test period is generally relatively long. In the exploration work of the Dalu manganese deposit, the author's group quickly surveyed the drilling cores of the manganese deposit by X-ray fluorescence instrument. It is found that the measurement data of this method have high accuracy in judging the enriched strata of manganese ore and the interpretation accuracy of orebody. Moreover, the instrument is precise. After calibration, the results of measurement are compared with those of laboratory data. The degree of approximation is very high. Especially for manganese ore (chemical) layer whose grade is more than 5%, the error between the results of measurement and laboratory results is generally less than 7%. It has objective and efficient guiding significance for orebody confirmation, core sampling section and sampling length determination in the field.
|
|
Received: 18 March 2019
Published: 28 November 2019
|
|
|
|
|
|
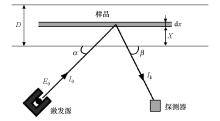
|
Working schematic diagram of hand-held X-ray fluorescence instrument
|

原位测量
钾(K)~铀(U) | 检出限/10-6 | | Cu、Zn、Ga、Ge、As、Se | ≤10 | | Co、Ni、Br到Mo、Ag到U | 11~100 | | K、Ca、Sc、Cr、Mn、Fe、Tc、Ru、Rh、Pd | 101~1000 | | Al、Si、P、S、Cl、Ar | >1000 |
|
Detection limit characteristic of IED-2000T hand-held multi-element rapid analyser
|

| 地层 | 岩性 | Mn含量范围/% | Mn平均含量/% | 备注 | | $\epsilon$2-3ls | 白云岩 | 0.19~1.33 | 0.59 | 高值位于层间页岩互层与白云岩接触部位 | | $\epsilon$2p | 砂质白云岩 | 0.25~0.84 | 0.65 | | | $\epsilon$2g | 白云岩 | 0.15~0.92 | 0.52 | | | $\epsilon$1q | 白云质灰岩 | 0.32~0.89 | 0.45 | | | $\epsilon$1p | 页岩夹砂岩 | 0.13~1.89 | 0.85 | 最高值位于层间页岩与砂岩接触部位 | | $\epsilon$1b | 炭质页岩夹砂岩 | 0.53~1.02 | 0.87 | 最高值位于层间页岩与砂岩接触部位 | | $\epsilon$1j | 灰岩夹炭质页岩 | 0.12~2.07 | 0.93 | 最高值位于层间页岩与砂岩接触部位 | | Z2l | 炭质、粉沙质页岩 | 0.78~2.67 | 1.36 | 最高值位于层间页岩与砂岩接触部位 | | Z2d | 白云岩夹砂质页岩 | 0.16~0.98 | 0.79 | 最高值位于层间页岩与白云岩接触部位 | | Nh2n | 含砾粉砂质黏土岩 | 0.84~2.98 | 1.19 | 最高值位于砾岩与粘土岩接触部位 | | Nh1d | 炭质、砂质页岩 | 1.95~36.04 | 5.19 | 最高值位于地层底部块状棱锰矿中 | | Nh1t | 含砾砂岩 | 1.63~3.06 | 2.23 | 最高值位于地层分界接触部位 | | Qbh | 砂质板岩 | 0.86~1.06 | 0.96 | 最高值位于地层分界接触部位 |
|
Manganese content characteristic for X-ray fluorescence measurement in working area
|
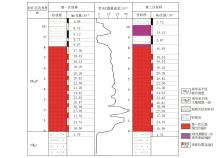
|
Comparison of sampling result after geological judgment sampling and X-ray fluorescence measurement
|

| 化验号 | X荧光测量结果 | 化验室结果 | | 岩心Mn含量/% | 几何平均Mn含量/% | 副样中Mn含量/% | Mn含量/% | | H29 | 0.92~4.15 | 1.98 | 2.36 | 1.72 | | H28 | 10.06~18.85 | 15.74 | 14.81 | 14.12 | | H27 | 2.52~8.58 | 3.06 | 4.99 | 3.87 | | H26 | 12.63~19.74 | 16.43 | 15.13 | 16.93 | | H25 | 17.56~21.45 | 18.01 | 19.65 | 18.62 | | H24 | 17.78~18.63 | 18.15 | 16.78 | 16.15 | | H23 | 17.64~19.23 | 20.18 | 21.56 | 19.23 | | H22 | 18.85~22.98 | 21.08 | 21.42 | 20.29 | | H21 | 19.76~22.65 | 19.87 | 19.87 | 20.82 | | H20 | 19.55~23.06 | 22.16 | 22.16 | 22.06 | | H9 | 20.45~24.24 | 22.46 | 22.46 | 21.26 | | H8 | 23.18~26.79 | 28.11 | 28.11 | 24.62 | | H7 | 25.87~30.15 | 28.01 | 28.64 | 26.87 | | H6 | 14.65~30.23 | 22.44 | 19.12 | 18.08 | | H5 | 30.25~36.04 | 34.04 | 29.59 | 27.09 | | H4 | 15.48~27.65 | 18.56 | 16.89 | 17.35 | | H3 | 27.65~30.12 | 28.88 | 25.15 | 24.31 | | H2 | 23.12~11.87 | 17.49 | 16.86 | 16.06 | | H1 | 1.45~7.73 | 3.59 | 2.93 | 1.76 |
|
Comparison of manganese content measured by hand-held X-ray fluorescence in core and accessory sample of ZK103 bore with laboratory results
|
| [1] |
林延畅, 葛良全, 赖万昌 . 新一代手提式多元素X荧光仪在地质普查中的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2002,26(4):325-328.
|
| [1] |
Lin Y C, Ge L Q, Lai W C . Application of new generation portable multi-element X-ray fluorescence instrument in geological survey[J]. Geophysical and geochemical exploration, 2002,26(4):325-328.
|
| [2] |
李欣宇, 邹灏, 张强 , 等. 便携式X荧光元素分析法在浅覆盖区萤石矿勘查中的应用与分析——以内蒙古乌力吉敖包萤石矿为例[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2018,40(5):125-132.
|
| [2] |
Li X Y, Zou H, Zhang Q , et al. Application and analysis of portable X-ray fluorescence element analysis in fluorite exploration in shallow covered area—Taking Wuliji Aobao fluorite deposit in Inner Mongolia as an example[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Prospecting Computing Technology, 2018,40(5):125-132.
|
| [3] |
钱建平, 吴高海, 陈宏毅 . 便携式X射线荧光光谱仪应用条件试验及效果[J]. 物探与化探, 2010,34(4):497-502.
|
| [3] |
Qian J P, Wu G H, Chen H Y . Application conditions test and effect of portable X-ray fluorescence spectrometer[J]. Geophysical and geochemical exploration, 2010,34(4):497-502.
|
| [4] |
林延畅, 葛良全, 姜海静 , 等. 铜钴矿样品X荧光快速测定技术的初步研究[J]. 物探化探计算技术, 2007,29(3):256-259.
|
| [4] |
Lin Y C, Ge L Q, Jiang H J , et al. Preliminary study on rapid X-ray fluorescence determination of copper and cobalt ore samples[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Prospecting Computing Technology, 2007,29(3):256-259.
|
| [5] |
李强, 张学华 . 手持式X射线荧光光谱仪测定富钴结壳样品中锰铁钴镍铜锌[J]. 岩矿测试, 2013,32(5):724-728.
|
| [5] |
Li Q, Zhang X H . Determination of ferromanganest, cobalt, nickel, copper and zing in cobalt-rich crust samples with hand-hand X-ray fluorescence[J]. Rock and Mineral Testing, 2013,32(5):724-728.
|
| [6] |
马德锡, 杨进, 陈孝强 , 等. 便携式X荧光仪在多金属矿区的应用[J]. 物探与化探, 2013,37(1):63-66.
|
| [6] |
Ma D X, Yang J, Chen X Q , et al. Application of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument in polymetallic mines[J]. Geophysical and geochemical exploration, 2013,37(1):63-66.
|
| [7] |
Civici N . A field-portable X-ray fluorescence instrument: Design and applications[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007.
|
| [8] |
Civici N . A field-portable X-ray fluorescence instrument: Design and applications[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2007.
|
| [9] |
吴小勇, 陈永君 . Si-PIN探测器便携式X荧光分析仪在海洋多金属结核结壳分析中的应用[J]. 岩矿测试, 2002,01.
|
| [9] |
Wu X Y, Chen Y J . Application of portable X-ray fluorescence analyzer with Si-PIN detector in analysis of marine polymetallic nodule crusts[J]. Rock and mineral testing, 2002,01.
|
| [10] |
葛良全, 赖万昌, 林延畅 . 现场X射线荧光检测技术研究[J]. 四川地质学报, 2006,26(2):117-120.
|
| [10] |
Ge L Q, Lai W C, Lin Y C . On-site X-ray fluorescence detection technology[J]. Sichuan Journal of Geology, 2006,26(2):117-120.
|
| [11] |
刘松 . 道坨超大型锰矿床外围找矿潜力探讨——以大路锰矿为例[J]. 中国锰业, 2017,35(5):30-32.
|
| [11] |
Liu S . Discussion on the prospecting potential in the periphery of daotuo super large manganese deposit—Taking Dalu manganese mine as an example[J]. Manganese Industry of China, 2017,35(·):30-32.
|
| [12] |
糜从斌, 刘松 . 松桃大路锰矿进展性突破工作思路的探讨[J]. 世界有色金属, 2016(22):137-139.
|
| [12] |
Mi C B , Liu S.Discussion on the working thought of progressive breakthrough in Songtao Dalu manganese mine[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2016(22):137-139.
|
| [13] |
DZ/T0200-2002 铁、锰、铬矿地质勘查规范[S]. 中华人民共和国地质行业勘查标准.
|
| [13] |
DZ/T0200-2002 Specification for geological exploration of iron, manganese and chromium deposits[S]. Geological Industry Exploration Standard of the People’s Republic of China.
|
| [14] |
De X M, Jin Y, Xiao Q C , et al. The application of portable X-ray fluorescence instrument to the polymetallic ore district[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2013.
|
| [15] |
刘松 . 地质填图+X荧光快速测量在三什江金矿靶区预测中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018(11):232-234.
|
| [15] |
Liu S . Application of geological mapping+X-ray fluorescence rapid survey in target area prediction of Sanshijiang gold mine[J]. World Nonferrous Metals, 2018 ( 11):232-234.
|
| [1] |
WANG Bin, LUO Yan-Jun, MENG Guang-Lu, ZHANG Jing, ZHANG Hai-Di, CHEN Bo, HE Zi-Xin. Potential assessment of gold, copper, lead, zinc, tungsten, and tin deposits in Kyrgyzstan based on 1∶1 000 000 scale geochemical data[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 58-69. |
| [2] |
ZHAO Ze-Lin, LI Jun-Jian, ZHANG Tong, NI Zhen-Ping, PENG Yi, SONG Li-Jun. Geological characteristics and prospecting direction of rare earth element deposits in North China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2022, 46(1): 46-57. |
|
|
|
|
