|
|
|
| Research on soil sampling density and environmental quality of Huaibei plain covered area: A case study of 1∶50 000 Gaoluji Sheet |
TAO Chun-Jun( ), SHI Chun-Hong, ZHANG Xiao-Rong, GUAN Hou-Chun, JIA Shi-Jun ), SHI Chun-Hong, ZHANG Xiao-Rong, GUAN Hou-Chun, JIA Shi-Jun |
| Geological Survey Institute of Anhui Province,Hefei 230001,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract 1∶50 000 Gaoluji Sheet was chosen as the research object in this study. The soil elements at two sampling densities of 6 points/km 2 and 4 points/km 2 are similar in geochemical parameter characteristics and spatial distribution. The sampling density of 4 points/km 2 in the map can meet the requirements of 1∶50,000 land quality survey and evaluation work. Based on the comparative analysis of the geochemical characteristics of soil elements under different sampling densities, the authors hold that the minimum sampling density (4 points/km 2) can be used when 1∶50,000 land quality survey is conducted in a relatively continuous farming area in the Huaibei plain coverage area. The soil environmental quality evaluation results show that the quality of the soil environment in this area is excellent. The priority is given to protecting the soil, and the safe use type soil is only in scattered distribution. The main impact indicator is Cd. The results can provide a scientific basis for the implementation of green pollution-free industries in this area.
|
|
Received: 01 April 2020
Published: 01 March 2021
|
|
|
|
|
|
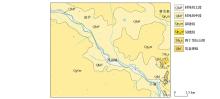
|
General geological map of research area
|

| 指标 | 分析方法 | 要求检出限 | 配套方法检出限 | 测定范围 | | As | AFS | 1 | 0.2 | 0.2~500 | | B | ES | 1 | 0.8 | 0.8~200 | | Cd | ICP-MS | 0.03 | 0.02 | 0.02~4.0 | | S | XRF | 30 | 20 | 20~2000 | | Co | XRF | 1 | 1 | 1~100 | | Cr | XRF | 5 | 3 | 3~3500 | | Cu | XRF | 1 | 0.8 | 0.8~2000 | | F | ISE | 100 | 50 | 50~5000 | | Hg | AFS | 0.0005 | 0.0005 | 0.0005~10 | | Ge | AFS | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.05~100 | | Mn | XRF | 10 | 5 | 5~2500 | | Mo | POL | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2~100 | | N | VOL | 20 | 15 | 15~5000 | | Ni | XRF | 2 | 2 | 2~2000 | | P | XRF | 10 | 8 | 8~4500 | | Pb | XRF | 2 | 2 | 2~2000 | | Se | AFS | 0.01 | 0.008 | 0.008~100 | | V | XRF | 5 | 2 | 2~10000 | | Zn | XRF | 4 | 2 | 2~3000 | | K2O | XRF | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05~7 | | Corg | VOL | 0.1 | 0.05 | 0.05~10 | | pH | ISE | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1~14.0 |
|
Detection limit of soil sample element analysis method
|

| 土壤分类 | 执行标准 | 色阶 | 分 级 含 义 | | 优先保护类 | 低于筛选值 |  | 农用地土壤污染风险低,一般情况下可忽略 | | 安全利用类 | 筛选-管控值 |  | 可能存在食用农产品不符合质量安全标准等土壤污染风险,原则上应当采取农业调控、替代种植等安全利用措施 | | 严格管控类 | 高于管控值 |  | 食用农产品不符合质量安全标准,土壤污染风险高,且难以通过安全利用措施降低该风险,原则上应当采取禁止种植食用农产品、退耕还林等严格管控措施 |
|
Soil environmental quality grading standard
|

| 指标 | 采样密度6个点/km2 | 采样密度4个点/km2 | 背景值
比值 | | 背景值 | 标准
离差 | 变异
系数 | 样点
个数 | 分布
形态 | 背景值 | 标准
离差 | 变异
系数 | 样点
个数 | 分布
形态 | | As | 12.1 | 3.15 | 0.26 | 2737 | 偏态 | 12.1 | 3.18 | 0.26 | 1963 | 对数正态 | 1.00 | | B | 56 | 5.02 | 0.09 | 2741 | 正态 | 56 | 5.09 | 0.09 | 1963 | 正态 | 1.00 | | Cd | 0.186 | 0.058 | 0.31 | 2693 | 正态 | 0.184 | 0.058 | 0.31 | 1925 | 正态 | 1.01 | | Co | 14.5 | 1.72 | 0.12 | 2740 | 偏态 | 14.4 | 1.72 | 0.12 | 1962 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | Cr | 74.2 | 8.80 | 0.12 | 2741 | 偏态 | 74.0 | 8.79 | 0.12 | 1963 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | Cu | 29.2 | 4.19 | 0.14 | 2740 | 偏态 | 29.1 | 4.21 | 0.14 | 1962 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | F | 573 | 102 | 0.18 | 2740 | 偏态 | 571 | 101 | 0.18 | 1962 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | Hg | 0.034 | 0.010 | 0.28 | 2539 | 偏态 | 0.034 | 0.010 | 0.29 | 1820 | 偏态 | 0.99 | | Mn | 688 | 137 | 0.20 | 2741 | 对数正态 | 689 | 134 | 0.19 | 1951 | 对数正态 | 1.00 | | Mo | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 2709 | 偏态 | 0.50 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 1939 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | N | 1.28 | 0.24 | 0.19 | 2741 | 正态 | 1.28 | 0.25 | 0.19 | 1963 | 正态 | 1.00 | | Ni | 32.4 | 5.49 | 0.17 | 2741 | 偏态 | 32.3 | 5.49 | 0.17 | 1963 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | P | 0.83 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 2718 | 偏态 | 0.83 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 1944 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | Pb | 26.6 | 2.67 | 0.10 | 2729 | 正态 | 26.6 | 2.70 | 0.10 | 1951 | 正态 | 1.00 | | S | 207 | 35 | 0.17 | 2741 | 对数正态 | 207 | 35 | 0.17 | 1963 | 对数正态 | 1.00 | | Se | 0.21 | 0.035 | 0.17 | 2715 | 正态 | 0.21 | 0.036 | 0.17 | 1946 | 正态 | 1.00 | | V | 90.6 | 12.60 | 0.14 | 2740 | 偏态 | 90.2 | 12.62 | 0.14 | 1962 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | Zn | 69.5 | 14.4 | 0.21 | 2738 | 偏态 | 69.3 | 14.4 | 0.21 | 1960 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | K2O | 2.27 | 0.32 | 0.14 | 2741 | 偏态 | 2.26 | 0.33 | 0.14 | 1963 | 偏态 | 1.00 | | Corg | 2.00 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 2719 | 正态 | 2.00 | 0.43 | 0.22 | 1948 | 正态 | 1.00 | | pH | 7.3 | 1.13 | 0.15 | 2741 | 偏态 | 7.3 | 1.13 | 0.16 | 1963 | 偏态 | 1.00 |
|
Statistical values of elemental geochemical parameters in two sampling densities
|
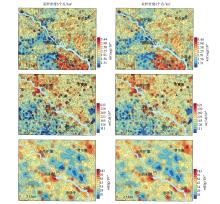
|
Geochemical maps of soil Corg, Cd and Hg in two sampling densities
|
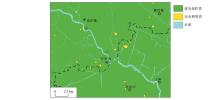
|
Comprehensive classification of soil environmental quality
|
| [1] |
Heim A, Wehrli L, Eugster W, et al. Effects of sampling design on the probability to detect soil carbon stock changes at the SwisCarboEurope site Lägeren[J]. Geoderma, 2009,149(3):347-354.

|
| [2] |
Vašát R, Heuvelink G B M, Borüvka L. Sampling design optimization for multivariate soil mapping[J]. Geoderma, 2010,155(3/4):147-153.

|
| [3] |
谷庆宝, 张倩, 卢军, 等. 我国土壤污染防治的重点与难点[J]. 环境保护, 2018,46(1):14-18.
|
| [3] |
Gu Q B, Zhang Q, Lu J, et al. Priority areas and difficulties of soil pollution control in China[J]. Environmental Protection, 2018,46(1):14-18.
|
| [4] |
武春林, 王瑞廷, 丁坤, 等. 中国土壤质量地球化学调查与评价的研究现状和进展[J]. 西北地质, 2018,51(3):240-252.
|
| [4] |
Wu C L, Wang R T, Ding K, et al. Geochemical survey and evaluation on soil quality in china: Research status and advances[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018,51(3):240-252.
|
| [5] |
Tang X J, Shen C F, Shi D Z, et al. Heavy metal and persistent organic compound contamination insoil from Wenling:An emerging e-waste recycling city in Taizhou area,China[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010,173(1/2/3):653-660.

|
| [6] |
李小平, 徐长林, 刘献宇, 等. 宝鸡城市土壤重金属生物活性与环境风险[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015,35(4):1241-1249.

|
| [6] |
Li X P, Xu C L, Liu X Y, et al. Bioactivity and environment risk of heavy metals in urban soil from Baoji City,P.R.China[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015,35(4):1241-1249.

|
| [7] |
王玉军, 吴同亮, 周东美, 等. 农田土壤重金属污染评价研究进展[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2017,36(12):2365-2378.
|
| [7] |
Wang Y J, Wu T L, Zhou D M, et al. Advances in soil heavy metal pollution evaluation based on bibliometrics analysis[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2017,36(12):2365-2378.
|
| [8] |
Zhao F J, Ma Y B, Zhu Y G, et al. Soil contamination in China:Current status and mitigation strategies[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015,49(2):750-759.

|
| [9] |
刘春早, 黄益宗, 雷鸣, 等. 湘江流域土壤重金属污染及生态环境风险评价[J]. 环境科学, 2012,33(1):260-265.
|
| [9] |
Liu C Z, Huang Y Z, Lei M, et al. Soil contamination and assessment of heavy metals of Xiangjiang River basin[J]. Environmental Science, 2012,33(1):260-265.
|
| [10] |
Hu Y N, Wang D X, Wei L J, et al. Bioaccumulation of heavy metals in plant leaves from Yan’an city of the loess plateau,China[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2014,110:82-88.

|
| [11] |
王爽, 李荣华, 张增强, 等. 陕西潼关农田土壤及重金属污染及潜在风险[J]. 中国环境科学, 2014,34(9):2313-2320.

|
| [11] |
Wang S, Li R H, Zhang Z Q, et al. Assessment of the heavy metal pollution and potential ecological hazardous in agricultural soils and crops of Tongguan, Shaanxi Province[J]. China Environmental Science, 2014,34(9):2313-2320.

|
| [12] |
生态环境部. GB15618—2018土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
|
| [12] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment. GB 15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018.
|
| [13] |
杨琳, 朱阿兴, 秦承志, 等. 一种基于样点代表性等级的土壤采样设计方法[J]. 土壤学报, 2011,48(5):938-946.
|
| [13] |
Yang L, Zhu A X, Qin C Z, et al. A soil sampling method based on representativeness grade of sampling points[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2011,48(5):938-946.
|
| [14] |
于伟宣, 赵明松, 王萌, 等. 采样数量与空间插值方法对土壤属性预测精度的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017,17(25):186-191.
|
| [14] |
Yu W X, Zhao M S, Wang M, et al. Effects of sampling sizes and spatial interpolation methods on prediction accuracy of soil properties[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017,17(25):186-191.
|
| [1] |
JIANG Bing, LIU Yang, WU Zhen, ZHANG De-Ming, SUN Zeng-Bing, MA Jian. Geochemical characteristics of fluorine in irrigation water and soils in the Gaomi area, Shandong Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1348-1353. |
| [2] |
NAN Zhe, WANG Lin-Shi, HOU Xu, ZHAI Zheng-Bo, WANG Yang, LIU Yang. Geological and geochemical characteristics and prospecting potential of rare element and rare earth element deposits in Saima alkaline complex[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 670-680. |
|
|
|
|

