|
|
|
| Cr and Ni geochemistry and some suggestions on soil pollution risk prevention control in the Zhelong-Gasa area, Yunnan Province |
WU Song1,2( ), CHEN Zheng1, LI Yuan-Bin1, HUANG Zhao1,2,3( ), CHEN Zheng1, LI Yuan-Bin1, HUANG Zhao1,2,3( ), ZHANG Lin1, XU Sheng-Chao1, WANG Kai-Gui1 ), ZHANG Lin1, XU Sheng-Chao1, WANG Kai-Gui1 |
1. Yunnan Institute of Geological Survey, Kunming 650216, China
2. Key of Laboratory of Sanjiang Metallogeny and Resourses Exploration and Utilization,MRN,Kunming 650051,China
3. College of Territory and Resources Engineering, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming 650093,China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract Based on the land quality geochemical survey data obtained in the Zhelong-Gasa area, Yunnan Province, the authors studied geochemical characteristics and main influencing factors of Cr and Ni in surface soil and analyzed Cr and Ni content characteristics of agricultural products. The results show that the content of Cr and Ni in the surface soil is mainly controlled by the geological background. The content of Cr and Ni in the soil developed in the Guangshan-Pingyakou rock mass (σ) of the study area is significantly higher than that in other strata. The medium values of Cr and Ni in different types of soils are quite different, and land use also affects the content of Cr and Ni in the soil. The Cr and Ni values of agricultural products such as corn, citrus, tea, sugarcane, bananas, and walnuts in the study area do not exceed the food safety standards. Only the values of 11 rice Cr samples exceed the Cr content standards set by national standards,accounting for 11.3% of the total rice samples. The overall evaluation of agricultural products in this area shows safety. The area of agricultural land such as paddy field, dry land, garden land and grassland in this area is 554.73 km2, of which, the area of safety area is 408.61 km2, accounting for 73.66%, the area of risk area is 112.96 km2, accounting for 20.36%, and the area of control area is 33.16 km2, accounting for 5.98%.For some areas with soil Cr and Ni pollution risk, measures are proposed such as soil and water conservation, fertilization adjustment, and water-dry rotation to prevent and control pollution risks.
|
|
Received: 15 January 2020
Published: 29 April 2021
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
HUANG Zhao
E-mail: 1719702709@qq.com;151230199@qq.com
|
|
|
|
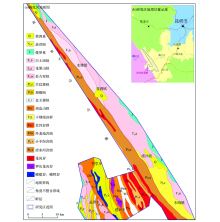
|
Geological map in study area
|

| 样品类型 | 分析元素 | 分析方法 | 检出限/10-6 | 标准 | 检测单位 | | 土壤和岩石 | Cr | ICP-MS | 0.82 | DZ/T 0295—2016 | 自然资源部昆明矿产资源监督检测中心 | | Ni | ICP-MS | 0.439 | DZ/T 0295—2016 | 自然资源部昆明矿产资源监督检测中心 | | 农产品 | Cr | ICP-MS | 0.05 | DZ/T 0253.1—2014 | 自然资源部昆明矿产资源监督检测中心 | | Ni | ICP-MS | 0.05 | DZ/T 0253.1—2014 | 自然资源部昆明矿产资源监督检测中心 |
|
Analytical methods,detection limits and analytical standards
|

| 类型 | 类别 | Cr含量/10-6 | Ni含量/10-6 | 原始数据信息
(剔除离散数据) | 样品数 | 9137 | 8975 | | 最大值 | 204 | 77.5 | | 最小值 | 4.8 | 0.15 | | 平均值(X1) | 95.5 | 31.9 | | 中位数(M1) | 94 | 30.9 | | 变异系数(Cv1) | 0.38 | 0.48 | | 中国土壤背景值(A)[12]/10-6 | 61 | 27 | | 峨山—元江多目标区域地球化学调查区平均值(B)[8] /10-6 | 114.4 | 48.1 | | 富集系数K1(X1/A) | 1.65 | 1.23 | | 富集系数K2(X1/B) | 1.00 | 1.14 |
|
Statistical parameters of chromium and nickel contents in top soil
|

| 地层 | 岩石 | 表层土壤 | | 样品数 | Cr平均值/
10-6 | Ni平均值/
10-6 | 样品数 | Cr平均值/
10-6 | Ni平均值/
10-6 | Cr次生
富集系数 | Ni次生
富集系数 | | 清水河岩组(Pt1q) | 110 | 52.7 | 22.3 | 2007 | 122.3 | 50.1 | 2.32 | 2.25 | | 三叠系花果山组(T3h) | 50 | 66.1 | 24.6 | 652 | 92.5 | 29.8 | 1.4 | 1.22 | | 三叠系白土田组(T3b) | 140 | 67.0 | 30.1 | 1998 | 87.1 | 29.8 | 1.3 | 0.99 | | 新近系茨营组(N2c) | 40 | 89.6 | 45.8 | 925 | 97.2 | 34.9 | 1.08 | 0.76 | | 侏罗纪德胜母岩体(Jγ) | 65 | 23.2 | 7.3 | 607 | 67.4 | 26.6 | 2.91 | 3.67 | | 三叠系干坝塘岩组(TG.) | 30 | 89.1 | 32.3 | 220 | 103.2 | 23.6 | 1.16 | 0.73 | | 外麦地岩组(Pzw) | 30 | 95.6 | 42.5 | 375 | 127.0 | 36.7 | 1.33 | 0.86 | | 泥盆系南边组(Dn) | 30 | 85.6 | 39.8 | 420 | 200.8 | 113.6 | 2.34 | 2.85 | | 二叠系羊八组(P2y) | 40 | 172.0 | 100.3 | 751 | 181.8 | 73.0 | 1.06 | 0.73 | | 三叠系歪古村组(T3w) | 30 | 62.4 | 29.1 | 399 | 89.0 | 31.9 | 1.43 | 1.09 | | 光山—和平丫口岩体(σ) | 30 | 1653.3 | 1750 | 185 | 1093.4 | 787.9 | 0.66 | 0.45 | | 三叠纪纸厂岩体(Tξγ) | 20 | 34.0 | 33.7 | 71 | 90.1 | 34.0 | 2.65 | 1.01 | | 大红山群(Pt1dh) | 30 | 73.3 | 32.6 | 281 | 106.9 | 42.5 | 1.46 | 1.3 | | 外麦地岩组(Pzc) | 30 | 117.8 | 38.5 | 54 | 128.3 | 30.2 | 1.09 | 0.78 | | 样本总数 | 675 | | | 8945 | | | | |
|
Chromium and nickel average in rocks and top soils as well as secondary enrichment factor of top soil vs rock
|
Fig.1)
">
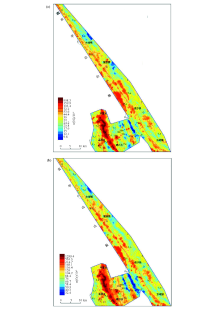
|
Geochemical distribution of nickel(a) and chromium(b) in the surface soil of the study area(the legend is the same as Fig.1)
|
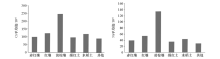
|
The average concentration of chromium and nickel in different soil types
|
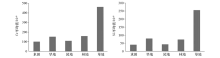
|
The mean values of chromium and nickel contents in different land use
|
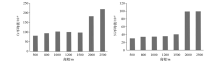
|
The mean values maps of chromium and nickelelemental contents in soil of different elevation
|

土地
利用现状 | 酸碱度(pH) | 样品数 | Cr平均值/10-6 | 污染风险筛选值/10-6 | 超标样数 | 超标率/% | | 水田 | pH≤5.5 | 1033 | 90 | 250 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 1084 | 101.3 | 250 | 0 | 0 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 355 | 121.2 | 300 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 96 | 119.5 | 350 | 0 | 0 | | 旱地 | pH≤5.5 | 1337 | 129.5 | 150 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 301 | 258 | 150 | 84 | 27.9 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 74 | 131.5 | 200 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 9 | 106 | 250 | 0 | 0 | | 园地 | pH≤5.5 | 1450 | 108.9 | 150 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 1345 | 109.8 | 150 | 0 | 0 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 721 | 109.3 | 200 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<PH | 264 | 110.9 | 250 | 0 | 0 | | 林地 | pH≤5.5 | 1165 | 144.1 | 150 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 212 | 284.1 | 150 | 27 | 12.7 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 66 | 89.6 | 200 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 40 | 85 | 250 | 0 | 0 | | 草地 | pH≤5.5 | 165 | 286.8 | 150 | 66 | 40 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 26 | 1647.4 | 150 | 15 | 57.7 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 5 | 391.7 | 200 | 2 | 40 |
|
The risk assessment of chromium pollution of different land use types
|

土地利用
现状 | 酸碱度 | 样品数 | Ni平均值/10-6 | 污染风险筛选值/10-6 | 超标样数 | 超标率/% | | 水田 | pH≤5.5 | 1033 | 32.2 | 60 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 1084 | 39.7 | 70 | 0 | 0 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 355 | 52.1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 96 | 56.8 | 190 | 0 | 0 | | 旱地 | pH≤5.5 | 1337 | 55.5 | 60 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 301 | 183.9 | 70 | 90 | 29.9 | | 6.5<pH≤6.5 | 74 | 76.9 | 100 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 9 | 54.2 | 190 | 0 | 0 | | 园地 | pH≤5.5 | 1450 | 39.7 | 60 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 1345 | 43.8 | 70 | 0 | 0 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 721 | 42.1 | 100 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 264 | 46.6 | 190 | 0 | 0 | | 林地 | pH≤5.5 | 1165 | 52.1 | 60 | 0 | 0 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 212 | 202.8 | 70 | 31 | 14.6 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 66 | 38.3 | 100 | 0 | 0 | | 7.5<pH | 40 | 33.2 | 190 | 0 | 0 | | 草地 | pH≤5.5 | 165 | 104.9 | 60 | 38 | 23 | | 5.5<pH≤6.5 | 26 | 1247 | 70 | 16 | 61.5 | | 6.5<pH≤7.5 | 5 | 312.5 | 100 | 2 | 40 |
|
The risk assessment of nickele pollution of different land use types in the survey area
|

| 作物 | 类型 | Cr含量/10-6 | Ni含量/10-6 | 样本数
(N) | 评价 | 参考标准 | | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | 最小值 | 平均值 | 最大值 | | 粮食类 | 玉米 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.26 | 0.06 | 0.31 | 2.08 | 71 | 未超标 | 国标 | | 水稻 | 0.13 | 0.99 | 5.09 | 0.11 | 0.61 | 1.84 | 97 | 11件超标 | 国标 | | 经济类 | 柑橘 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 39 | 未超标 | 国标 | | 茶叶 | 0.26 | 1.22 | 1.22 | 3.23 | 8.05 | 24.67 | 42 | 未超标 | 国标 | | 甘蔗 | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.39 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.30 | 36 | 未超标 | 国标 | | 香蕉 | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.14 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.39 | 36 | 未超标 | 国标 | | 核桃 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 0.85 | 0.60 | 5.48 | 20.48 | 71 | 未超标 | 国标 |
|
The chromium and nickele content of main agricultural products in survey area
|
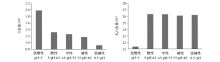
|
The mean values maps of nitrogen and potassium oxide elemental contents in different soil acidity
|
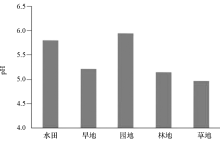
|
The mean values of soil acidity in different land use
|
| [1] |
唐豆豆, 袁旭音, 汪宜敏, 等. 地质高背景农田土壤中水稻对重金属的富集特征及风险预测[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018,37(1):18-26.
|
| [1] |
Tang D D, Yuan X Y, Wang Y M, et al. Enrichment characteristics and risk prediction of heavy metals for rice grains growing in paddy soils with a high geological[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018,37(1):18-26.
|
| [2] |
唐将, 王世杰, 付绍红, 等. 三峡库区土壤环境质量评价[J]. 土壤学报, 2008,45(4):601-607.
|
| [2] |
Tang J, Wang S J, Fu S H, et al. Evaluation of so environment quality in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2008,45(4):601-607.
|
| [3] |
刘意章, 肖唐付, 熊艳, 等. 西南镉地质背景区农田土壤与农作物的重金属富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2019,40(6):2877-2833.
|
| [3] |
Liu Y Z, Xiao T F, Xiong Y, et al. Accumulation of heavy metals in agricultural soils and crops from an area with a high geochemical background of cadmium, southwestern China[J]. Environmental Science, 2019,40(6):2877-2833.
|
| [4] |
陈慧茹, 董亚玲, 王琦, 等. 重金属污染土壤中Cd、Cr、Pb元素向水稻的迁移累积研究[J]. 中国农学通报, 2015,31(12):236-241.
|
| [4] |
Chen H R, Dong Y L, Wang Q, et al. Distribution and transportation of Cd,Cr,Pb in rice with contamination in soil[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2015,31(12):236-241.
|
| [5] |
Shanker A K, Venkateswarlu B. Chromium: Environmental pollution, health effects and mode of action[J]. Encyclopedia of Environmental Health, 2011: 650-659.
|
| [6] |
于洋, 宋波, 陈同斌, 等. 西江流域土壤镍含量特征及风险评估[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2018,40(6):698-709.
|
| [6] |
Yu Y, Song B, Chen T B, et al. Content characteristic and assessment of Ni in soils of Xijiang River basin[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2018,40(6):698-709.
|
| [7] |
He G H, Gao L C. Studies Cu, Pb, Zn and Cr inhumed ant acid rain[J]. Chemical Letter, 1994,5(1):93-94.

|
| [8] |
云南省地质调查院. 峨山—元江地区1∶25万多目标区域地球化学调查报告[R]. 2010.
|
| [8] |
Geological Survey Institute of Yunnan Province. The multi-purpose geochemical survey report of 1∶250,000 in Eshan-Yuanjiang area [R]. 2010.
|
| [9] |
中国地质调查局. DZ/T 0295—2016 土地质量地球化学评价规范[S]. 2016.
|
| [9] |
China Geological Survey. DZ/T 0295—2016 Standard for geochemical evalution of land quality[S]. 2016.
|
| [10] |
武松, 潘发明. SPSS统计分析大全[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2014.
|
| [10] |
Wu S, Pan F M. SPSS statistical analysis encyclopedia [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2014.
|
| [11] |
鄢明才, 迟清华, 顾铁新, 等. 中国东部地壳元素丰度与岩石平均化学组成研究[J]. 物探与化探, 1997,21(6):451-459.

|
| [11] |
Yan M C, Chi Q H, Gu T X, et al. Chemical composition of continental crust and rocks in Eastern China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1997,21(6):451-459.

|
| [12] |
迟清华, 鄢明才. 应用地球化学元素风度数据手册[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2007.
|
| [12] |
Chi Q H, Yan M C. Handbook of applied geochemical element wind data [M]. Beijing: Geological Press, 2007.
|
| [13] |
GB15618—2018 土壤环境质量农用地土壤污染风险管控标准(试行)[S]. 2018.
|
| [13] |
GB15618—2018 Soil environmental quality risk control standard for soil contamination of agricultural land[S]. 2018.
|
| [14] |
中华人民共和国国家食品药品监督管理局. GB2762—2017 食品安全国家标准,食品中污染物限量[S]. 2017.
|
| [14] |
State Food and Drug Administration of the People's Republic of China. GB 2762—2017 National food safety standard limit of contaminants in foods[S]. 2017.
|
| [15] |
马宏宏, 彭敏, 刘飞, 等. 广西典型碳酸盐岩区农田土壤—作物系统重金属生物有效性及迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2020,41(1):449-459.
|
| [15] |
Ma H H, Peng M, Liu F, et al. Bioavailability,Translocation, and accumulation characteristic of Heavy metals in soil-crop system from a typical carbonate rocks area in Guangxi, China[J]. Environmental Science, 2020,41(1):449-459.
|
| [16] |
余涛, 杨忠芳, 钟坚, 等. 土壤中重金属元素 Pb、Cd 地球化学行为影响因素研究[J]. 地学前缘, 2008,15(5):67-73.
|
| [16] |
Yu T, Yang Z F, Zhong J, et al. Factors affecting the geochemical behavior of heavy metal elements Pb and Cd in soil[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008,15(5):67-73.
|
| [17] |
张钊熔, 段星星, 夏明哲, 等. 白银东大沟水体和底泥中重金属污染评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(3):649-657.
|
| [17] |
Zhang Z R, Duan X X, Xia M Z, et al. Contamination situation and evalution of heavy mental polution in water and sediments of Dongdagou area, Baiyin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(3):649-657.
|
| [18] |
陈怀满, 朱永官, 董元华, 等. 环境土壤学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010.
|
| [18] |
Cheng H M, Zhu Y G, Dong Y H, et al. Environmental soil science[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2010.
|
| [19] |
周亚龙, 郭志娟, 王成文, 等. 云南省镇雄县土壤中金属污染及潜在生态风险评估[J]. 物探与化探, 2019,43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [19] |
Zhou Y L, Guo Z J, Wang C W. Assessment of heavy metal pollution and potential ecological risks of soils in Zhenxiong Country, Yunnan Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019,43(6):1358-1366.
|
| [1] |
WAN Tai-Ping, ZHANG Li, LIU Han-Liang. Regional geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospect area prediction of strategic mineral antimony in the Eerguna block, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1179-1188. |
| [2] |
YUAN Yu-Ting, LIU Xue-Min, WANG Xue-Qiu, TAN Qin-Ping. Sulfur-lead isotopes based tracing of the metal element anomalies identified in the total metal measurement of surface fine-grained soils: A case study of the Shuiyindong Carlin-type concealed gold deposit[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(4): 1083-1097. |
|
|
|
|

