|
|
|
| The distribution and influencing factors of zinc in the fluvo-aquic soil and the lime concretion black soil in northern Anhui Province |
LI Peng-Fei( ), GUAN Hou-Chun, WANG Xiang, Chen Yan-Bin, WANG Yao, WU Heng, SHI Chun-Hong ), GUAN Hou-Chun, WANG Xiang, Chen Yan-Bin, WANG Yao, WU Heng, SHI Chun-Hong |
| Geological Survey of Anhui Province, Hefei 230001, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract The 1∶250 000 multi-target geochemical survey shows that there is a large area of zinc-rich fluvo-aquic soil in northern Anhui Province, and the study on the distribution law, bioavailability, and influencing factors of zinc in the soil is of great significance to the development of zinc-rich agricultural industries. This study investigated the distribution characteristics, occurrence forms, bioavailability, and influencing factors of zinc in the topsoil at a depth of 0~20 cm and the section soil of 0~200 cm depth of both the fluvo-aquic soil and the lime concretion black soil in northern Anhui Province. The results are as follows: The fluvo-aquic soil has abundant total zinc and moderate available zinc, while the lime concretion black soil lacks the total zinc in general and is rich in available zinc. The total zinc in the fluvo-aquic soil is significantly positively correlated with manganese, organic matter, and phosphorus. The available zinc in both the fluvo-aquic soil and the lime concretion black soil is positively correlated with the available phosphorus and negatively correlated with pH. The zinc in the soil at the depth of 0~200 cm mainly occurs as residuals for both the fluvo-aquic soil and the sand concretion black soil. The total content of the water-soluble and ion-exchangeable zinc that is easily absorbed by plants in the plough layer of the fluvo-aquic soil area accounts for 0.29% of the total zinc content, and the content of iron-manganese oxide bound zinc accounts for 23.62% of the total zinc content. The total zinc is obviously enriched in the soil at a depth of 0~85 cm, which is significantly restricted by the phosphorus and manganese contents in the soil. The total content of the water-soluble and ion-exchangeable zinc in the plough layer of the lime concretion black soil area accounts for 0.41% of the total zinc content, and the total zinc content in the soil at a depth of 0~200 cm slightly changes. This study indicates that the fluvo-aquic soil in the study area has rich total zinc and moderate available zinc and that the available zinc content is mainly restricted by the pH of soil. Therefore, applying conditioners to reduce the pH of soil is an effective way to enhance the bioavailability of zinc in the total-zinc-rich fluvo-aquic soil.
|
|
Received: 09 October 2021
Published: 03 January 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
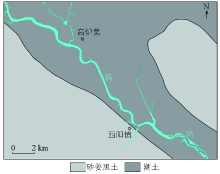
|
Soil types of the study area
|
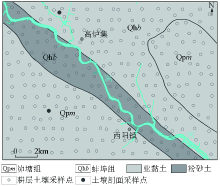
|
The soil sampling sites of the study area
|

| 地层 | 岩性 | 成土母质 | 土壤类型 | 地貌 | 指标 | 最小值 | 最大值 | 算术平均值 | 中位数 | 标准离差 | 变异系数 | 蚌
埠
组
(Qhb) | 亚
黏
土 | 黄
泛
冲
积
物 | 潮
土 | 泛
滥
坡
平
地
(N=89) | 全Zn | 65.1 | 105.3 | 82.5 | 81.7 | 9.26 | 0.11 | | 有效Zn | 0.300 | 5.630 | 0.853 | 0.700 | 0.74 | 0.87 | | 全Mn | 572.9 | 942.7 | 787.6 | 789.2 | 93.23 | 0.12 | | 全P | 708.0 | 1530.0 | 973.9 | 973.0 | 160.25 | 0.16 | | 有效P | 9.20 | 85.08 | 17.97 | 16.37 | 10.18 | 0.57 | | TFe2O3 | 4.760 | 6.200 | 5.610 | 5.790 | 0.44 | 0.08 | | 硅铝率 | 3.76 | 4.89 | 4.20 | 4.09 | 0.32 | 0.08 | | 有机质 | 0.790 | 1.440 | 1.138 | 1.160 | 0.17 | 0.15 | | pH值 | 8.02 | 8.31 | | 8.16 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 粉
砂
土 | 黄
泛
冲
积
物 | 潮
土 | 泛
滥
微
高
地
(N=52) | 全Zn | 55.5 | 101.7 | 78.9 | 80.1 | 12.44 | 0.16 | | 有效Zn | 0.250 | 6.850 | 1.096 | 0.800 | 1.18 | 1.08 | | 全Mn | 510.6 | 973.5 | 758.8 | 775.8 | 127.18 | 0.17 | | 全P | 615.0 | 1591.0 | 1017.3 | 1049.0 | 217.39 | 0.21 | | 有效P | 5.18 | 76.24 | 22.39 | 19.36 | 14.27 | 0.64 | | TFe2O3 | 4.730 | 5.980 | 5.111 | 4.980 | 0.36 | 0.07 | | 硅铝率 | 3.93 | 4.98 | 4.59 | 4.68 | 0.32 | 0.07 | | 有机质 | 0.490 | 1.480 | 1.096 | 1.135 | 0.25 | 0.22 | | pH值 | 7.04 | 8.45 | | 8.12 | 0.27 | 0.03 | 峁
塘
组
(Qpm) | 亚
黏
土 | 黄土性古河湖相沉积物 | 砂
姜
黑
土 | 河
间
平
地
(N=126) | 全Zn | 46.9 | 97.6 | 59.3 | 56.5 | 9.49 | 0.16 | | 有效Zn | 0.300 | 6.460 | 2.460 | 2.580 | 1.45 | 0.59 | | 全Mn | 359.2 | 938.3 | 611.3 | 601.4 | 102.97 | 0.17 | | 全P | 384.0 | 1242.0 | 683.5 | 652.0 | 181.66 | 0.27 | | 有效P | 5.39 | 207.40 | 55.79 | 47.44 | 39.10 | 0.70 | | TFe2O3 | 4.110 | 5.360 | 4.628 | 4.580 | 0.28 | 0.06 | | 硅铝率 | 4.34 | 5.70 | 5.05 | 5.06 | 0.30 | 0.06 | | 有机质 | 0.490 | 1.640 | 1.002 | 1.000 | 0.26 | 0.26 | | pH值 | 4.90 | 8.22 | | 6.41 | 1.05 | 0.16 |
|
Statistical results of characteristic parameters of soil zinc content in the study area
|
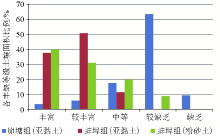
|
Percentage of soil area rich in total zinc and deficient in total zinc
|
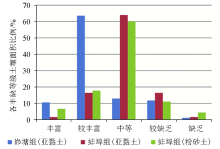
|
Percentage of soil area rich in effective zinc and deficient in total zinc
|
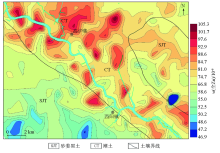
|
Spatial distribution characteristics of total zinc in surface soils in the study area
|
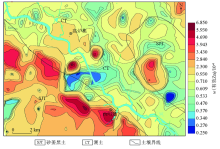
|
Spatial distribution characteristics of available zinc in surface soils in the study area
|

| 指标 | 全P | 有效P | 全Mn | 有效Mn | 全Zn | 有效Zn | TFe2O3 | 硅铝率 | 有机质 | pH值 | | 全P | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | 有效P | 0.251* | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | 全Mn | 0.479** | -0.153 | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | 有效Mn | 0.210** | -0.094 | 0.849** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | 全Zn | 0.793** | -0.133 | 0.659** | 0.380** | 1.000 | | | | | | | 有效Zn | -0.019 | 0.642** | -0.170 | -0.030 | -0.203 | 1.000 | | | | | | TFe2O3 | 0.595** | -0.008 | 0.287** | 0.055 | 0.562** | -0.099 | 1.000 | | | | | 硅铝率 | -0.534** | 0.013 | -0.265* | -0.022 | -0.505** | 0.153 | -0.974** | 1.000 | | | | 有机质 | 0.598** | 0.453** | 0.342** | 0.166 | 0.483** | 0.353** | 0.288** | -0.225** | 1.000 | | | pH值 | 0.367** | -0.622** | 0.328** | 0.092 | 0.525** | -0.607** | 0.480** | -0.474** | -0.115 | 1.000 |
|
The correlation coefficient between zinc content and the main physical and chemical indexes in surface soil(lime concretion black soil)of Maotang Formation
|

| 指标 | 全P | 有效P | 全Mn | 有效Mn | 全Zn | 有效Zn | TFe2O3 | 硅铝率 | 有机质 | pH值 | | 全P | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | | 有效P | 0.282** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | | 全Mn | 0.264** | -0.205* | 1.000 | | | | | | | | | 有效Mn | 0.025 | -0.202* | 0.786** | 1.000 | | | | | | | | 全Zn | 0.395** | -0.076 | 0.888** | 0.659** | 1.000 | | | | | | | 有效Zn | 0.143 | 0.630** | -0.124 | -0.109 | 0.080 | 1.000 | | | | | | TFe2O3 | -0.155 | -0.200* | 0.358** | 0.327** | 0.333* | -0.230* | 1.000 | | | | | 硅铝率 | 0.101 | 0.205* | -0.380** | -0.337** | -0.360** | 0.259** | -0.983** | 1.000 | | | | 有机质 | 0.395** | 0.195* | 0.379** | 0.219* | 0.438** | 0.174 | 0.133 | -0.147 | 1.000 | | | pH值 | 0.043 | -0.634** | 0.162 | 0.124 | 0.175 | -0.518** | 0.211* | -0.250** | -0.240* | 1.000 |
|
The correlation coefficient between zinc content and the main physical and chemical indexes in surface soil(fluvo-aquic soil)of Bengbu formation
|

采样
深度/cm | 岩性 | 全Zn | 类别 | 各形态Zn含量及其比例 | | 水溶态 | 离子
交换态 | 碳酸盐
结合态 | 腐殖酸
结合态 | 铁锰氧化物
结合态 | 强有机
结合态 | 残渣态 | | 0~20 | 粉质黏土 |
116.7 | 含量/10-6 | 0.07 | 0.27 | 9.73 | 10.64 | 27.57 | 7.90 | 60.56 | | 比例/% | 0.06 | 0.23 | 8.34 | 9.11 | 23.62 | 6.77 | 51.88 | | 20~40 | 黏土 |
91.5 | 含量/10-6 | 0.06 | 0.13 | 6.99 | 5.05 | 16.29 | 7.16 | 55.78 | | 比例/% | 0.06 | 0.15 | 7.64 | 5.52 | 17.81 | 7.83 | 60.99 | | 40~60 | 黏土 |
89.9 | 含量/10-6 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 4.27 | 3.39 | 8.89 | 5.19 | 68.01 | | 比例/% | 0.06 | 0.12 | 4.75 | 3.77 | 9.89 | 5.77 | 75.65 | | 60~85 | 黏土 |
74.7 | 含量/10-6 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 1.85 | 1.91 | 7.06 | 4.63 | 59.03 | | 比例/% | 0.02 | 0.21 | 2.48 | 2.56 | 9.45 | 6.21 | 79.07 | | 85~100 | 粉质黏土 |
45.9 | 含量/10-6 | 0.01 | 0.15 | 1.24 | 1.87 | 4.48 | 3.62 | 34.51 | | 比例/% | 0.03 | 0.33 | 2.70 | 4.08 | 9.76 | 7.89 | 75.22 | | 100~120 | 黏土 |
41.7 | 含量/10-6 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 1.13 | 1.82 | 3.73 | 3.31 | 31.49 | | 比例/% | 0.00 | 0.46 | 2.71 | 4.38 | 8.95 | 7.93 | 75.57 | | 120~140 | 黏土 |
61.6 | 含量/10-6 | 0.00 | 0.21 | 0.83 | 1.44 | 3.81 | 3.83 | 51.44 | | 比例/% | 0.00 | 0.34 | 1.35 | 2.34 | 6.19 | 6.21 | 83.56 | | 140~170 | 黏土 |
60.7 | 含量/10-6 | 0.01 | 0.23 | 0.65 | 1.48 | 4.84 | 3.96 | 49.54 | | 比例/% | 0.02 | 0.37 | 1.08 | 2.44 | 7.98 | 6.52 | 81.60 | | 170~200 | 黏土 |
61.0 | 含量/10-6 | 0.00 | 0.22 | 0.91 | 1.37 | 4.29 | 3.43 | 50.79 | | 比例/% | 0.00 | 0.35 | 1.50 | 2.25 | 7.04 | 5.62 | 83.24 |
|
The zinc content of each form and its proportion in total zinc in each layer of fluvo-aquic soil
|

采样
深度/cm | 岩性 | 全Zn | 类别 | 各形态Zn含量及比例 | | 水溶态 | 离子
交换态 | 碳酸盐
结合态 | 腐殖酸
结合态 | 铁锰氧化物
结合态 | 强有机
结合态 | 残渣态 | | 0~20 | 粉质黏土 |
54.0 | 含量/10-6 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 1.22 | 1.83 | 4.78 | 6.30 | 39.69 | | 比例/% | 0.15 | 0.26 | 2.25 | 3.39 | 8.84 | 11.66 | 73.45 | | 20~40 | 黏土 |
52.2 | 含量/10-6 | 0.02 | 0.16 | 1.29 | 1.52 | 4.66 | 5.22 | 39.36 | | 比例/% | 0.04 | 0.31 | 2.46 | 2.92 | 8.92 | 9.99 | 75.37 | | 40~60 | 黏土 |
53.0 | 含量/10-6 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 1.10 | 1.19 | 4.38 | 5.57 | 40.51 | | 比例/% | 0.01 | 0.45 | 2.07 | 2.24 | 8.26 | 10.51 | 76.46 | | 60~80 | 黏土 |
51.0 | 含量/10-6 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.97 | 1.10 | 3.94 | 5.50 | 39.19 | | 比例/% | 0.02 | 0.61 | 1.91 | 2.16 | 7.72 | 10.78 | 76.80 | | 80~100 | 黏土 |
58.4 | 含量/10-6 | 0.04 | 0.44 | 0.60 | 1.24 | 5.54 | 5.62 | 44.91 | | 比例/% | 0.07 | 0.76 | 1.03 | 2.12 | 9.49 | 9.63 | 76.90 | | 100~120 | 黏土 |
59.5 | 含量/10-6 | 0.06 | 0.54 | 1.34 | 1.00 | 7.49 | 5.00 | 44.05 | | 比例/% | 0.10 | 0.91 | 2.25 | 1.69 | 12.59 | 8.41 | 74.05 | | 120~160 | 粉质黏土 |
54.9 | 含量/10-6 | 0.02 | 0.61 | 0.84 | 1.30 | 5.76 | 5.10 | 41.27 | | 比例/% | 0.04 | 1.10 | 1.53 | 2.36 | 10.50 | 9.29 | 75.19 | | 160~200 | 粉质黏土 |
57.5 | 含量/10-6 | 0.01 | 0.28 | 0.96 | 1.29 | 6.22 | 5.71 | 43.07 | | 比例/% | 0.01 | 0.48 | 1.66 | 2.24 | 10.81 | 9.93 | 74.87 |
|
The zinc content of each form and its proportion in total zinc in each layer of lime concretion black soil
|
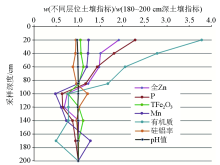
|
Vertical distribution of zinc and other elements in fluvo-aquic soil area
|
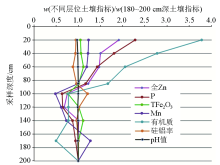
|
Vertical distribution of zinc and other elements in lime concretion black soil area
|
| [1] |
谢薇, 杨耀栋, 侯佳渝, 等. 天津市蓟州区富硒土壤成因与土壤硒来源研究[J]. 物探与化探, 2019, 43(6): 1373-1381.

|
| [1] |
Xie W, Yang Y D, Hou J Y, et al. Studies on causes and influential factors of selenium-enriched soils in Jizhou district of Tianjin[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 43(6): 1373-1381.

|
| [2] |
吴价. 江西瑞金土壤硒、锌元素地球化学特征及土地资源区划[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019.
|
| [2] |
Wu J. Selenium,zinc element geochemical characteristics and land resource zoning in Ruijin soil,Jiangxi[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2019.
|
| [3] |
廖启林, 崔晓丹, 黄顺生, 等. 江苏富硒土壤元素地球化学特征及主要来源[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [3] |
Liao Q L, Cui X D, Huang S S, et al. Elemental geochemistry of Selenium-enriched soil and its main origin in Jiangsu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6):1813-1825.
|
| [4] |
李朋飞, 刘超, 陶春军, 等. 再生铅工业园周边土壤重金属分布特征及来源解析[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(4):663-671.
|
| [4] |
Li P F, Liu C, Tao C J, et al. Spatial distribution and source analysis of heavy metal pollution in soils around recycled lead industrial park[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(4):663-671.
|
| [5] |
周墨, 唐志敏, 张明, 等. 赣州市水稻及根系土中硒的含量特征与富硒土壤界限值[J]. 地质通报, 2021, 40(4):604-609.
|
| [5] |
Zhou M, Tang Z M, Zhang M, et al. Selenium contents of rice and rhizosphere soil and threshold value of selenium-rich soil in Ganzhou of Jiangxi Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2021, 40( 4) : 604-609.
|
| [6] |
吴兴盛. 福建省武平县富硒土壤特征及成因分析[J]. 物探与化探, 2021, 45(3),778-784.

|
| [6] |
Wu X S. Characteristics and genesis of selenium-rich soil in Wuping area,Fujian Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2021, 45(3),778-784.

|
| [7] |
刘琦, 王张民, 潘斐, 等. 大田条件下水稻锌营养强化方法探究及效果评估[J]. 土壤, 2019, 51(1):32-38.
|
| [7] |
Liu Q, Wang Z M, Pan F, et al. Effect evaluation on method of zinc biofortification for rice in paddy field[J]. Soils, 2019, 51(1):32-38.
|
| [8] |
佘旭, 王朝辉, 马小龙, 等. 黄土高原旱地冬小麦籽粒锌含量差异与主要土壤理化性状的关系[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(22):4338-4349.
|
| [8] |
She X, Wang Z H, Ma X L, et al. Variation of winter wheat grain zinc concentration and its relation to major soil characteristics in drylands of the loess plateau[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(22):4338-4349.
|
| [9] |
Bouis H E, Eozenou P, Rahman A. Food prices,household income,and resource allocation: Socioeconomic perspectives on their effects on dietary quality and nutritional status[J]. Food and Nutrition Bulletin, 2011, 32(s1): S14-S23.

|
| [10] |
Ma G S, Jin Y, Li Y P, et al. Iron and zinc deficiencies in China: What is a feasible and cost-effective strategy ?[J]. Public Health Nutrition, 2008, 11(6): 632-638.

|
| [11] |
Bouis H E, Saltzman A. Improving nutrition through biofortification: A review of evidence from Harvest Plus,2003 through 2016[J]. Global Food Security, 2017, 12:49-58.

|
| [12] |
管后春. 1∶5万楚店集、高炉集、江集和望町集幅覆盖区综合地质调查报告[R]. 安徽省地质调查院, 2021.
|
| [12] |
Guan H C. A report of 1∶50000 comprehensive geological survey in the area covered by the Wanchudianji,Gaofuji,Jiangji and Wangdingji maps of Anhui[R]. Geological survey institute of Anhui province, 2021.
|
| [13] |
佘旭. 旱地田块间小麦籽粒锌含量差异的原因分析[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林大学, 2017.
|
| [13] |
She X. Reasons for wheat grain zinc difference among fileds in dryland areas[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2017.
|
| [14] |
丁婷婷. 土壤各形态锌对DTPA-Zn的贡献量及土壤供锌能力的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林大学, 2016.
|
| [14] |
Ding T T. Contribution of zinc fractions to DTPA-Zn and zinc supply capacity[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2016.
|
| [15] |
魏世强, 陈事荣, 刘陈. 四川主要土壤锌形态和含量的研究[J]. 西南农业大学学报, 1990, 12(6): 600-603.
|
| [15] |
Wei S Q, Chen S R, Liu C. The study on the zinc morphology and contents of purpie soils in Sichuan[J]. Journal of Southwest Agriculture University, 1990, 12(6): 600-603.
|
| [16] |
黄婷苗, 王朝辉, 黄倩楠, 等. 黄淮麦区小麦籽粒锌含量差异原因与调控[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 58(6):1496-1506.
|
| [16] |
Huang T M, Wang Z H, Huang Q N, et al. Causes and regulation of variation of zinc concentration in wheat grains produced in Huanghuai wheat production region of China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 58(6):1496-1506.
|
| [17] |
陆欣春. 潜在缺锌土壤上土施锌肥对冬小麦锌营养品质及土壤锌形态转化的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林大学, 2012.
|
| [17] |
Lu X C. Effect of zinc fertilization to soil on zinc nutritional quality of winter wheat and zinc fractions and transformation in potentiallty Zn-deficient soil[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2012.
|
| [18] |
张伟. 供磷水平对小麦玉米锌吸收、累积的影响及其作用机制[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017.
|
| [18] |
Zhang W. The mechanisms of zinc uptake and accumulation in wheat and maize as affected by phosphorus levels[D] .Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017.
|
| [19] |
陈富荣, 李朋飞, 杜国强, 等. 安徽淮北—亳州地区多目标地球化学调查报告[R]. 安徽省地质调查院, 2017.
|
| [19] |
Chen F R, Li P F, Du G Q, et al. A report on the results of multi-target geochemical surveys in the Huaibei-Bozhou area of Anhui[R]. Geological survey institute of Anhui province, 2017.
|
| [20] |
魏复盛, 陈静生, 吴燕玉, 等. 中国土壤环境背景值研究[J]. 环境科学, 1991, 12(4):12-20.
|
| [20] |
Wei F S, Chen J S, Wu Y Y, et al. Research on soil environmental background value in China[J]. Environmental Science, 1991, 12(4):12-20.

|
| [21] |
赵建, 师华定, 吴啸, 等. 遵义市土壤锌空间分布特征研究[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2019, 36(3):298-303.
|
| [21] |
Zhao J, Shi H D, Wu X, et al. Study on spatial distribution of zinc in soils in Zunyi City,China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2019, 36(3): 298-303.
|
| [22] |
刘智杰, 黄丽, 李峰, 等. 长期施肥对土壤颗粒粘粒矿物组成及其演变特征的影响[J]. 矿物学报, 2018, 39(5):563-571.
|
| [22] |
Liu Z J, Huang L, Li F, et al. Effect of long-term fertilization on the composition and evolution of clay minerals in soil particles[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2018, 39(5):563-571.
|
| [23] |
高弼模, 吴建明, 高贤彪. 土壤中锌的吸附固定及影响因子[J]. 山东农业大学学报, 1987, 18(2):25-32.
|
| [23] |
Gao B M, Wu J M, Gao X B. Absorptive fixation and effective factors of Zinc in soil[J]. Journal of Shandong Agricultural University, 1987, 18(2):25-32.
|
| [24] |
张会民, 吕家珑, 徐明岗, 等. 土壤性质对锌吸附影响的研究进展[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2006, 34(5):114-118.
|
| [24] |
Zhang H M, Lu J L, Xu M G, et al. Research progress on the influence of soil properties on zinc adsorption[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University:Natural Science Edition, 2006, 34(5):114-118.
|
| [25] |
陆文龙, 潘洁, 薛家骅. 土壤锌吸附动力学[J]. 华北农学报, 1996, 11(1):81-86.
|
| [25] |
Lu W L, Pan J, Xue J H. A study on the kinetics of soil zinc adsorption[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 1996, 11(1):81-86.
|
| [26] |
姚敏. 长江三角洲地区主要类型土壤对锌的吸附—解吸特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京工业大学, 2005.
|
| [26] |
Yao M. Study on charaeters of zinc adsorption-desorption of the principal types soil at Yangtze River Delta[D]. Nangjing: Nanjing Tech University, 2005.
|
| [27] |
李朋飞, 杜国强, 刘超, 等. 安徽淮北平原农田土壤酸碱度特征及酸化趋势研究[J]. 华东地质, 2019, 40(3):234-240.
|
| [27] |
Li P F, Du G Q, Liu C, et al. Study on soil acidity and basicity characteristics and acidification trend of farmland in Huaibei plain of Anhui Province[J]. East China Geology, 2019, 40(3):234-240.
|
| [28] |
刘合满, 张兴昌, 苏少华, 等. 黄土高原主要土壤锌有效性及其影响因素[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 27(3):898-902.
|
| [28] |
Liu H M, Zhang X C, Su S H, et al. Available zinc content and related properties of main soil in the loess plateau[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 27(3):898-902.
|
| [29] |
蒋廷惠, 胡霭堂, 秦怀英. 土壤中锌的形态分布及其影响因素[J]. 土壤学报, 1993, 30(3):260-265.
|
| [29] |
Jiang T H, Hu A T, Qin H Y. Distribution of zinc fractions in soils in relation to soil properties[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1993, 30(3):260-265.
|
| [30] |
蔡奎, 张蒨, 吴云霞, 等. 河北平原农田土壤重金属形态分布特征及控制因素研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2017, 12(2):155-168.
|
| [30] |
Cai K, Zhang Q, Wu Y X, et al. Speciation distribution and its influencing factors of Cd,Cr,Pb,As,Hg in farmland soil from Heibei Plain,China[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2017, 12(2):155-168.
|
| [31] |
杨红飞, 甄泉, 严密, 等. 砂姜黑土中重金属Cu、Cd、Zn形态分布与土壤酶活性研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2007, 38(1):111-115.
|
| [31] |
Yang H F, Zhen Q, Yan M, et al. Study on the form distribution of heavy metals Cu,Cd,Zn in Shajiang black soil and soil enzyme activities[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2007, 38(1):111-115.
|
| [1] |
HUANG Ping-An, WANG Xia-Qing, TANG Xiang-Ling, WANG Yu-Tang, LI Wei, LUO Zeng, Lyu Fei-Ya. Research progress in the influencing factors and correction methods of XRF-CS[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(3): 726-738. |
| [2] |
LI Mu-Si, CHEN Li-Rong, XIE Fei, GU Lan-Ding, WU Xiao-Dong, MA Fen, YIN Zhao-Feng. Comparison of deep learning algorithms for geochemical anomaly identification[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(1): 179-189. |
|
|
|
|

