|
|
|
| Geochemical characteristics and Cr metallogenic potential evaluation of the middle section of the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin |
CHEN Xi1( ), AN Zhao2( ), AN Zhao2( ), ZHANG Wen-Quan2, XU Yun-Fu3, MA Ying4, SHI Lian-Chang2, TAO Zhi-Hua5 ), ZHANG Wen-Quan2, XU Yun-Fu3, MA Ying4, SHI Lian-Chang2, TAO Zhi-Hua5 |
1. No.1 Bureau of China Metallurgical Geology Bureau, Sanhe 065201, China
2. Qinghai Provincial Geological Survey Bureau, Xining 810100, China
3. Qinghai Geological Survey Institute, Xining 810100, China
4. The Fifth Geological Exploration Institute of Qinghai Province, Xining 810100, China
5. The Second Bureau of Qinghai Nonferrous Metals Geological Exploration, Xining 810100, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract This study extracted 59238 pieces of original data on different scales (1:50000 stream sediment surveys and 1:25000 geochemical surveys) of the middle section of the northern margin of the Qaidam Basin. Based on these data, this study conducted the superposition analysis of mathematical index statistics and multivariate statistics, aiming to discover the element association relationship and determine the major metallogenic elements in the region and provide basic support for subsequent mineral work. According to the statistics, the mathematical indexes of Au, W, and Cr in the study area show great metallogenic potential. Combined with the multivariate statistical analysis and existent metallogenic facts, the authors of this study believed that the study area has the great potential for the prospecting of chromium deposits associated with ultramafic rocks besides tectonic altered rock-type and hydrothermal gold deposits. Owing to the relatively high overall background value of local chromium (Cr) element, the traditional method using X+2σ (129×10-6) or the cumulative frequency 85% (142.9×10-6) used to delineate the anomaly threshold cannot meet the requirement for delineating local anomalies in the study area. Therefore, this study improved the anomaly threshold using the 1/4 concentration grading value (234×10-6). As a result, many anomalies exhibiting significant zonal distribution in the concentration center were delineated, and most weak anomalies were eliminated. Based on the geological, geophysical, and geochemical results, this study inferred zones favorable for the further exploration of chromium deposits and determined four favorable metallogenic zones and five prospecting areas.
|
|
Received: 26 September 2021
Published: 27 April 2023
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
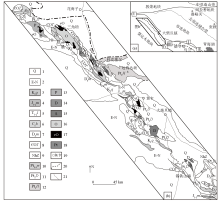
Regional tectonic unit in the northern margin of Qaidam Basin (a) and geological map of the region(b)
1—Quaternary sediments; 2—Paleogene-Neogene; 3—lower Cretaceous Quanyagou formation; 4—lower-middle Jurassic Dameigou formation; 5—lower-middle Triassic Longwuhe formation; 6—lower Carboniferous Huaitoutala formation; 7—upper Devonian Maoniushan formation; 8—Cambrian-Ordovician Tanjianshan group; 9—Nanhua period Quanji group; 10—middle Proterozoic Wandonggou group;11—Paleoproterozoic Dakendaban group; 12—Paleoproterozoic Hualong group; 13—the Permian rock mass; 14—the Devonian rock mass; 15—the Silurian rock mass; 16—the Ordovician rock mass; 17—the Ordovician gabbro; 18—the Paleoproterozoic ringspot granite; 19—place names; 20—road;21—stratigraphic boundary;Ⅰ—the southern margin of Lajiishan-middle Qilian fault; Ⅱ—Zongwulong-Qinghainanshan fault;Ⅲ—Wulan-Yuka fault; Ⅳ—the fault of the north Chaidamu basin; Ⅴ—Altun strike-slip fault
|

| 参数 | Ag | As | Au | Co | Cr | Cu | Mo | Ni | Pb | Sb | W | Zn | | 青海省丰度[18] | 70.00 | 16.89 | 1.38 | 10.05 | 53.13 | 20.24 | 0.70 | 24.09 | 24.03 | 0.92 | 1.67 | 59.85 | | 柴北缘丰度[18] | 69.00 | 6.04 | 1.45 | 10.93 | 72.34 | 24.89 | 0.60 | 25.98 | 25.00 | 0.34 | 1.34 | 55.80 | | 最大值 | 10100 | 1668 | 11300 | 222 | 27567 | 1358 | 95 | 16212 | 6457 | 382 | 735 | 10283 | | 丰度X1 | 49.77 | 7.23 | 1.92 | 15.59 | 113.20 | 30.75 | 0.85 | 40.80 | 21.37 | 0.38 | 1.89 | 61.33 | | 标准差S1 | 70.40 | 16.45 | 54.00 | 11.00 | 438.50 | 27.00 | 1.32 | 107.10 | 41.40 | 1.69 | 9.14 | 71.33 | | 变异系数CV1 | 1.41 | 2.28 | 28.13 | 0.71 | 3.87 | 0.88 | 1.55 | 2.63 | 1.94 | 4.45 | 4.84 | 1.16 | | 背景值X2 | 45.42 | 4.11 | 0.88 | 14.45 | 55.90 | 26.50 | 0.60 | 24.90 | 18.71 | 0.26 | 0.98 | 58.43 | | 标准差S2 | 11.88 | 2.47 | 0.45 | 8.50 | 34.60 | 17.00 | 0.32 | 16.40 | 6.87 | 0.14 | 0.52 | 23.42 | | 变异系数CV2 | 0.26 | 0.60 | 0.51 | 0.59 | 0.62 | 0.64 | 0.53 | 0.66 | 0.37 | 0.54 | 0.53 | 0.40 | | 剔除数Nh | 2423 | 7449 | 6481 | 1728 | 6303 | 3175 | 5650 | 5600 | 2136 | 6195 | 6262 | 1027 | | 剔除比率R | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.05 | 0.10 | 0.09 | 0.04 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.02 | | 浓集系数N1 | 0.71 | 0.43 | 1.39 | 1.55 | 2.13 | 1.52 | 1.21 | 1.69 | 0.89 | 0.41 | 1.13 | 1.02 | | 浓集系数N2 | 0.72 | 1.20 | 1.32 | 1.43 | 1.56 | 1.24 | 1.42 | 1.57 | 0.85 | 1.12 | 1.41 | 1.10 | | 叠加强度D | 6.49 | 11.72 | 261.8 | 1.40 | 25.66 | 1.84 | 5.84 | 10.70 | 6.88 | 17.64 | 33.90 | 3.20 |
|
Statistical table for superposition analysis of mathematical indexes of original data
|
|
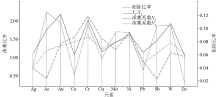
Fitting curves of concentration coefficient,abundance and rejection ratio
|
|
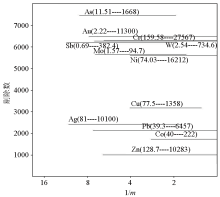
The diagram of rich quantile
|
|
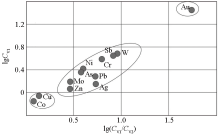
Fitting graph of variation coefficients
|
|
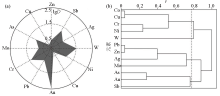
Superposed intensity(a) and cluster tree(b)
|

| 元素 | F1 | F2 | F3 | F4 | F5 | F6 | | Ag | 0.573 | 0.004 | 0.471 | -0.049 | 0.000 | -0.062 | | As | 0.155 | -0.018 | 0.793 | 0.144 | 0.151 | 0.156 | | Au | -0.060 | 0.027 | 0.868 | -0.038 | -0.054 | -0.014 | | Co | 0.025 | 0.573 | 0.004 | 0.726 | -0.006 | -0.012 | | Cr | 0.010 | 0.853 | -0.001 | 0.032 | -0.003 | 0.004 | | Cu | 0.068 | 0.027 | 0.037 | 0.927 | 0.016 | -0.001 | | Mo | 0.113 | -0.160 | 0.179 | 0.344 | 0.497 | 0.098 | | Ni | 0.005 | 0.846 | 0.012 | 0.085 | 0.002 | 0.007 | | Pb | 0.901 | -0.010 | 0.021 | -0.064 | 0.059 | 0.036 | | Sb | 0.075 | 0.011 | 0.087 | 0.002 | 0.011 | 0.981 | | W | -0.009 | 0.088 | -0.033 | -0.104 | 0.897 | -0.040 | | Zn | 0.829 | 0.032 | -0.025 | 0.243 | 0.012 | 0.102 | | 特征值 | 2.468 | 2.036 | 1.379 | 1.181 | 1.025 | 0.951 | | 方差贡献率/% | 20.563 | 16.964 | 11.495 | 9.843 | 8.539 | 7.923 | | 累积方差贡献率/% | 20.563 | 37.528 | 49.023 | 58.866 | 67.405 | 75.328 |
|
Principal components of rotation factor analysis
|
|
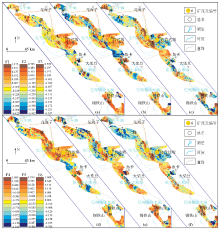
Factor measurement charts
a—F1 factor (Pb-Zn-Ag) score chart;b—F2 factor (Cr-Ni) score chart;c—F3 factor (Au-As) score chart;d—F4 factor (Ca-Co) score chart;e—F5 factor (W-Mo) score chart;f—F6 factor (Sb) score chart;1—the Saishitengshan copper depsosit; 2—the Yeluotuoquan gold-cobalt deposit; 3—the Hongliugou gold deposit; 4—the Qinglonggou gold deposit; 5—the Longbaigou gold deposit; 6—the Tanjianshan gold deposit; 7—the Xijinggou gold deposit; 8—the Luofengpo chromitite deposit; 9—the Shuangkoushan Pt-Ag-Zn deposit; 10—the Xitieshan Pt-Zn deposit
|
|
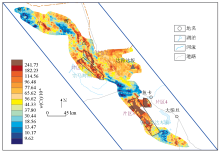
Geochemical map of chromium
|
|
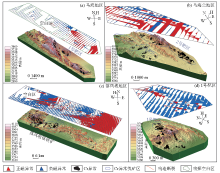
3D topography and geophysical section plan of abnormal area
|

| 地区 | 靶区 | 地质特征 | 化探特征 | 物探特征 | 已发现的矿化点 | 成矿评价 | | 马海 | 1号 | 大面积分布的滩间山岩群与牦牛山组呈断层接触,强蚀变橄辉岩、辉长岩大面积发育,发育多组北西向断裂构造 | 圈定2处Cr为主的异常,伴生有Ni、Au等,峰值达803×10-6,均具3级浓度分带,规模大,规律性强,重砂异常显示有铬铁矿重晶石的出现 | 极值在-344~554nT之间,化极延伸不强 | 暂未发现 | 具蛇纹石化、褐铁矿化的强蚀变橄辉岩的出现是引起物化探异常的主要原因,是铬镍成矿的有利地段 | | 马海北 | 1号 | 大面积分布的滩间山岩群与牦牛山组呈断层接触,发育多组NW—SE向断裂构造,第四系覆盖较厚,偶见辉绿玢岩脉发育,第四系覆盖较厚 | 圈定7处Cr为主的异常,伴生有Ni、Au等,异常峰值在(2000~5455)×10-6之间,3级浓度分带,规模大,沿NE向次级断裂展布 | 极值达2000nT,化极上延
1000m仍有异
常反应 | 暂未发现 | 物化探异常峰值高、规模大,整体随构造方向呈现明显的规律性,地表偶见的超基性岩株出露,推断深部可能存在一条NW向的基性—超基性岩韵律层,是寻找深部超基性岩型铬铁矿的有利地段 | | 2号 | 基性辉长岩大面积侵入于万洞沟群千枚岩段中,发育一条长约9.3km、宽约100~200m的超基性蛇纹石化橄榄岩,韵律明显,NW向构造为主,NE向次级断裂次之 | 圈定6处Cr为主的异常,伴生有Ni、Au、As、Hg、Ag、W、Pb等,峰值在(2000~3441)×10-6之间,3级浓度分带,规模大 | 极值-138~
1549nT之间,强度高,梯度陡,化极上延1000m仍有反映 | 2处石棉矿化点,1处铬铁矿化点 | 断裂构造发育,热液活动强烈,成矿物质来源丰富,是寻找超基性岩型铬铁矿的有利地段 | | 落凤坡 | 1号 | 辉长岩、辉橄岩大面积侵入于达肯达坂岩群中,NW向断裂发育,NE向次之 | 圈定2处Cr为主的异常,伴生有Cu、Co、Ni、Pb、W、Bi等,峰值达8591×10-6,3级浓度分带,规模大 | 2处物探磁异常显示-2179~1104nT,化极上延800m仍有反映 | 1处铬铁矿点 | 蛇纹石化的辉长岩、辉橄岩反应的规模强度均较高的物化探异常,显示了该区是寻找超基性岩型铬矿的有利地段 | | 黑石山 | 1号 | 侵入到滩间山岩群之中的辉长岩大面积发育,西侧与达肯大坂岩群呈断层接触,接触带上见有超镁铁质岩呈不连续的脉状产出,多见玄武岩包体和蛇纹石化辉石橄榄岩包体 | 圈定的9处Cr异常伴生有W、Mo、Bi、Hg、Au等异常,异常峰值达1729×10-6,具三级浓度分带,规模大 | 幅值在-2179~1104nT之间,正磁异常 | 金、铜、铬铁、石棉等矿(化)点5处 | 成矿物质较为丰富,区域构造作用对成矿形成了促进到破坏再到促进的循环模式,不仅热液型元素成矿潜力较大,铬镍等基性—超基性元素成矿也较为有利 |
|
Division of prospecting target areas of chromium element in the study area
|
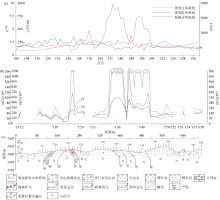
|
1:5 000 geophysical (a),geochemical (b) and geological (c) profile of Mahaibei No.1 target area
|
| [1] |
陈炳蔚, 王彦斌, 左国朝. 青藏高原北部地体划分及其构造演化[J]. 地球物理学报, 1995, 38(S2):98-113.
|
| [1] |
Chen B W, Wang Y B, Zuo G C. Terrain subdivision of the northern Qinghai-Xizang(Tibet) plateau and its tectonic evolution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 1995, 38(S2):98-113.
|
| [2] |
殷鸿福, 张克信. 中央造山带的演化及其特点[J]. 地球科学, 1998, 23(5):438-442.
|
| [2] |
Yin H F, Zhang K X. Evolution and characteristics of the Central Orogenic Belt[J]. Earth Science, 1998, 23(5):438-442.
|
| [3] |
于凤池, 马国良, 魏刚锋, 等. 青海滩间山金矿床地质特征和控矿因素分析[J]. 矿床地质, 1998, 17(1):47-56.
|
| [3] |
Yu F C, Ma G L, Wei G F, et al. Geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of the Tanjianshan gold deposit,Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1998, 17(1):47-56.
|
| [4] |
姜芷筠, 赵呈祥, 李碧乐, 等. 柴北缘滩间山金矿田细晶沟花岗斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄与Hf同位素特征及其与金矿化的关系[J]. 黄金, 2020, 439(5):7-14.
|
| [4] |
Jiang Z Y, Zhao C X, Li B L, et al. U-Pb age,Hf isotope of zircons from granite porphyry in Xijinggou,Tanjianshan Gold Field,Northern margin of Qaidam Basin,and their relations to the gold mineralization[J]. Gold, 2020, 439(5):7-14.
|
| [5] |
杨佰慧. 青海金龙沟金矿矿床地质特征及矿床成因研究[D]. 吉林: 吉林大学, 2019.
|
| [5] |
Yang B H. Geological characteristics and genesis of Jinlonggou gold deposit in Qinghai[D]. Jilin: Jilin University, 2019.
|
| [6] |
呼格吉勒, 马国栋, 邓元良, 等. 滩间山地区青龙沟金矿床成矿条件及模式[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(3):155-160.
|
| [6] |
Hu G J L, Ma G D, Deng Y L, et al. Metallogenic conditions and modes of the Qinglonggou gold deposit in Tanjianshan area,Qinghai[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(3):155-160.
|
| [7] |
冯志兴, 陈正乐, 李正明, 等. 柴北缘锡铁山铅锌矿床控矿构造特征及找矿预测[J]. 地质力学学报, 2020, 26(3):329-344.
|
| [7] |
Feng Z X, Chen Z L, Li Z M, et al. Characteristics of ore-controlling structures and oreprospecting of the Xitieshan lead-zinc deposit,Northern edge of the Qaidam basin,NW China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2020, 26(3):329-344.
|
| [8] |
李明喜, 张文秦. 青藏高原水系沉积物地球化学衰减模式与区域地球化学勘查对策[J]. 青海地质, 1996(1):53-72.
|
| [8] |
Li M X, Zhang W Q. The discuss of the geochemical attenuation pattern and regional exploration countermeasure in stream sediments on Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geological of Qinghai, 1996(1): 53-72.
|
| [9] |
王富春, 王贵仁. 1:2.5万水系沉积物测量在柴达木周边地区金矿找矿工作中的应用及其效果[J]. 青海地质, 2001(S1):36-40.
|
| [9] |
Wang F C, Wang G R. Application of 1:25000 stream sediment survey to gold-prospecting around Qaidum Basin and its effect[J]. Geological of Qinghai, 2001(S1):36-40.
|
| [10] |
李革委. 青海省格尔木红土沟—红石山一带元素地球化学特征及化探找矿效果[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.
|
| [10] |
Li G W. Element geochemical characteristics and geochemical prospecting effect of Hongtugou-Hongshishan area in Golmud,Qinghai Province[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2015.
|
| [11] |
王晓云, 马忠贤, 李文君, 等. 青海省沟里地区金矿地质特征及控矿因素分析[J]. 中国锰业, 2017, 35(6):45-48,54.
|
| [11] |
Wang X Y, Ma Z X, Li W J, et al. An analysis on geological characteristics and ore-controlling factors of gold deposits in Goulis region of Qinghai Province[J]. China’s Manganese Industry, 2017, 35(6):45-48,54.
|
| [12] |
赵娟, 许光, 杨宝荣, 等. 青海东昆仑地区1:2.5万地球化学测量方法技术及应用成果[J]. 西北地质, 2018, 51(1):209-217.
|
| [12] |
Zhao J, Xu G, Yang B R, et al. Technique and application result of 1:25000 geochemical survey in East Kunlun,Qinghai Province[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2018, 51(1):209-217.
|
| [13] |
袁海彪, 陈健, 祁永爱. 1:2.5万地球化学测量在青海省都兰县尕之麻—约尔根地区找矿中的应用[J]. 世界有色金属, 2018, 514(22):42-42.
|
| [13] |
Yuan H B, Chen J, Qi Y A. Application of 1:25000 geochemical survey to prospecting in Gazhima-Yorgenarea,Dulan County,Qinghai Province[J]. World Nonferrous Metals County, 2018, 514(22):42-42.
|
| [14] |
陈健. 1:2.5万地球化学测量在青海马里木吾卡地区找矿中的应用[J]. 黄金, 2019, 40(4):14-18.
|
| [14] |
Chen J. Application of 1:25000 geochemical survey to ore prospecting in Malimuwuka area of Qinghai[J]. Gold, 2019, 40(4):14-18.
|
| [15] |
杨鸿鹏, 赵志逸, 韩杰, 等. 沟系土壤地球化学测量在东昆仑Au元素低背景区的应用及成效——以格尔木市深沟地区1:2.5万沟系土壤地球化学测量为例[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(2):291-301.
|
| [15] |
Yang H P, Zhao Z Y, Han J, et al. Application and effect of soil geochemical survey in the Au low background of East Kunlun elemants: A case study of soil geochemistry in Shengou area of Geermu City[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(2):291-301.
|
| [16] |
安朝, 杨敏, 陈熙, 等. 东昆仑东段都兰地区地球化学特征及其成矿意义——基于大比例尺微沟系(土壤)测量工作[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 494(6):56-67.
|
| [16] |
An Z, Yang M, Chen X, et al. Geochemical characteristics and metallogenic significance of the Dulan area in the Eastern section of the East Kunlun Mountains derived from large-scale micro channel system(soil) measurement[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 494(6):56-67.
|
| [17] |
陈宣华, 邵兆刚, 熊小松, 等. 祁连造山带断裂构造体系、深部结构与构造演化[J]. 中国地质, 2019, 46(5):995-1020.
|
| [17] |
Chen X H, Shao Z G, Xiong X S, et al. Fault system,deep structure and tectonic evolution of the Qilian Orogenic Belt,Northwest China[J]. Geology in China, 2019, 46(5): 995-1020.
|
| [18] |
青海省矿产资源潜力评价[R]. 青海省地质矿产勘查开发局, 2017.
|
| [18] |
Evaluation of Mineral Resources Potential in Qinghai Province[R]. Qinghai Provincial Bureau of Geology and Mineral Exploration and Development, 2017.
|
| [19] |
肖霞, 倪师军, 冯德新, 等. 水系沉积物测量在西藏夏日多地区找矿中的应用[J]. 有色金属工程, 2016, 6(1):71-76.
|
| [19] |
Xiao X, Ni S J, Feng D X, et al. Application of stream sediment survey in Xiariduo area of Tibet[J]. Nonferrous Metals Engineering, 2016, 6(1):71-76.
|
| [20] |
翁望飞, 王德恩, 王邦民, 等. 安徽省祁门—黟县地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 物探与化探, 2020, 44(1):1-12.
|
| [20] |
Weng W F, Wang D E, Wang B M, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments and prospecting direction in Qinmen-Yixian area of Anhui Province[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2020, 44(1): 1-12.
|
| [21] |
臧金生, 王东晓, 赵瑞强. 化探异常定量评价[J]. 物探与化探, 2014, 38(6):1114-1118.
|
| [21] |
Zang J S, Wang D X, Zhao R Q. Quantitative evaluation of geochemical anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 38(6): 1114-1118.
|
| [22] |
刘文辉. 应用浓幅分位值对确定区域成矿元素的探讨[J]. 甘肃科技, 2009, 25(1):41-44.
|
| [22] |
Liu W H. Discuss on determining regional metallogenic elements by using concentration quantile value[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2009, 25(1):41-44.
|
| [23] |
陈健. 浓幅分位确定成矿元素的应用探究[J]. 新疆大学学报, 2019, 36(2):192-197.
|
| [23] |
Chen J. Application of concentrated grading to determine the ore-forming elements[J]. Journal of Xinjiang University, 2019, 36(2): 192-197.
|
| [24] |
李武俊, 唐开金. 区域化探异常研究方法探讨[J]. 陕西地质, 1991, 9(1):57-67.
|
| [24] |
Li W J, Tang K J. A discussion on the research methods of regional anomalies in geochemical exploration[J]. Geology of Shaanxi, 1991, 9(1):57-67.
|
| [25] |
崔晓亮, 刘婷婷, 王文恒, 等. 东昆仑布青山地区水系沉积物测量地球化学特征及找矿方向[J]. 物探与化探, 2011, 35(5):573-578.
|
| [25] |
Cui X L, Liu T T, Wang W H, et al. Geochemical characteristics and ore search prospects of Buqingshan area in Qinghai Province based on stream sediment survey[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2011, 35(5):573-578.
|
| [26] |
何旺, 罗先熔, 高文, 等. 青海省都兰县五龙沟—高地地区水系沉积物地球化学特征及找矿远景[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(5):1017-1023.
|
| [26] |
He W, Luo X R, Gao W, et al. Geochemical characteristics of stream sediments in the Wulonggou-Gaodi area,Dulan County,Qinghai Province and their exploration prospective[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2019, 38(5):1017-1023.
|
| [27] |
郑明贵, 袁雪梅. 基于灰色神经网络的中国2020—2030年铬矿需求预测[J]. 资源开发与市场, 2018, 34(6):747-752.
|
| [27] |
Zheng M G, Yuan X M. Demand forecasting of China’s chrome ore from 2020 to 2030 based on grey neural network[J]. Resource Development and Market, 2018, 34(6):747-752.
|
| [1] |
XIANG Zhu-Bao, ZHANG Da-Zhou, ZHU De-Bing, LI Ming-Zhi, XIONG Zhang-Qiang. Exploring the Rayleigh wave propagation characteristics in different aggregate concrete models[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1226-1235. |
| [2] |
REN Rui, ZHANG Zhi-Min, WANG Hui, CHEN Ji-Ping, QIAO Xin-Xing, LIANG Dong-Li. Exploring selenium enrichment criteria for soils in the Guanzhong area, Shaanxi Province: A case study of wheat[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1354-1360. |
|
|
|
|

