|
|
|
| Pollution analysis and assessment of sediments in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River |
YANG Chan1( ), WU Juan-Juan1, CHE Xu-Xi1, YUE Si-Yu1,2, LIU Zhi-Feng1,2, SONG Feng-Min1,2( ), WU Juan-Juan1, CHE Xu-Xi1, YUE Si-Yu1,2, LIU Zhi-Feng1,2, SONG Feng-Min1,2( ) ) |
1. School of Chemical and Environmental Science, Shaanxi University of Technology,Hanzhong 723001, China
2. Key Laboratory of Qinba Biological Resources and Ecological Environment (Cultivation),Hanzhong 723001, China |
|
|
|
|
Abstract To ascertain the pollution characteristics and source of sediments in the upper reaches of the Hanjiang River, this study collected sediment samples at 17 sampling sites in the study area. Based on these samples, this study determined the concentrations of organochlorine compounds (α-666;β-666;γ-666;δ-666;4,4'-DDE;4,4'-DDD;2,4'-DDT; and 4,4'-DDT) and heavy metals (V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Cd, and Pb) in the sediments. Then, it assessed the heavy metal pollution using the geoaccumulation and potential ecological risk indices. Furthermore, through redundancy analysis and multivariate statistical analysis, this study explored the sources of heavy metals and the relationships between the physicochemical properties of the sediments and heavy metals concentrations. The results indicate that: (1) The organochlorine compounds in the sediments at all sampling sites show low concentrations, without affecting the ecological environment. However, attention should be paid to the pollution caused by organochlorine compounds; (2) All the heavy metals from the sampling sites show non-pollution or mild pollution, except for Cd, which caused slightly strong pollution; (3) As revealed by the analysis of potential ecological risks, heavy metals generally show extremely high potential risks. Cd, which causes the most serious environmental pollution at the sampling sites, serves as the main factor influencing the environmental and ecological risks in the study area; (4) The redundancy analysis shows that there is no significant relationship between the physicochemical properties of sediments and the concentrations of heavy metals in the study area; (5) As revealed by the multivariate statistical analysis, Cd and Pb may be related to the application of agricultural materials (e.g., chemical fertilizers and pesticides) and the discharge of waste gas, wastewater, and industrial residue, indicating anthropogenic sources; the concentrations of V, Cr, Mn, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn, and As are related to the natural weathering of rocks mainly and to industrial wastewater and agricultural activities partially, indicating dominant natural sources. The comprehensive study shows that the potential ecological hazards caused by heavy metals (dominated by Cd) in the sediments should be treated seriously.
|
|
Received: 29 August 2022
Published: 27 October 2023
|
|
|
|
Corresponding Authors:
SONG Feng-Min
E-mail: yc1487819481@163.com;sfm3297@163.com
|
|
|
|
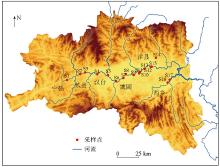
|
Distribution of sediment sampling sites in the upper reaches of Hanjiang River
|

| 地累积指数Igeo | Igeo< 0 | 0≤I geo< 1 | 1≤I geo< 2 | 2≤I geo< 3 | 3≤I geo< 4 | 4≤I geo< 5 | I geo≥5 | | 等级 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | | 污染程度 | 无污染 | 无—中污染 | 中度污染 | 中强污染 | 强污染 | 强—极强污染 | 极强污染 |
|
Contamination level of sediment by heavy metals classified based on Igeo
|

单金属潜在生态
风险指数(Ei) | 综合潜在生态风
险指数(R) | 潜在生态
风险等级 | | Ei < 30 | R< 80 | 轻度污染 | | 30≤Ei <60 | 80≤R < 160 | 中度污染 | | 60≤Ei<120 | 160≤R <240 | 偏重污染 | | 120≤Ei<240 | 240≤R < 320 | 重度污染 | | Ei≥240 | R≥320 | 极重污染 |
|
Classification standards of potential ecological risk assessment
|
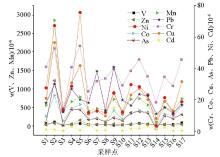
|
Distribution of heavy metal concentrations in soils
|

| 重金属 | 最大值/10-6 | 最小值/10-6 | 平均值/10-6 | 标准差/10-6 | 超标率/% | 变异系数/% | 陕西省土壤
重金属背景
值[15]/10-6 | | V | 108.21 | 18.88 | 46.49 | 23.08 | 5.88 | 49.65 | 76.40 | | Cr | 54.18 | 12.33 | 35.63 | 10.76 | 11.76 | 30.20 | 51.90 | | Mn | 2855.13 | 110.14 | 673.15 | 571.20 | 58.82 | 84.85 | 482.00 | | Co | 22.75 | 3.54 | 11.17 | 4.59 | 41.18 | 39.20 | 11.20 | | Ni | 75.67 | 3.38 | 24.78 | 18.66 | 17.65 | 75.30 | 28.60 | | Cu | 56.50 | 8.12 | 22.10 | 12.43 | 41.18 | 56.24 | 20.40 | | Zn | 156.98 | 13.06 | 48.93 | 30.31 | 11.76 | 61.95 | 68.00 | | As | 32.39 | 1.45 | 10.21 | 6.44 | 35.29 | 63.08 | 11.10 | | Cd | 14.85 | 0.16 | 2.22 | 3.36 | 100 | 151.35 | 0.10 | | Pb | 40.93 | 11.01 | 20.86 | 8.51 | 35.29 | 40.80 | 21.2 |
|
The statistics of results of heavy metals in surface sediments of the upper reaches of Hanjiang River(n=17)
|

| 样点 | pH | 总磷TP/
10-3 | 铵态氮NH3-N/
10-6 | | S1 | 7.24 | 0.28 | 2.38 | | S2 | 7.42 | 0.24 | 1.93 | | S3 | 7.50 | 0.25 | 2.10 | | S4 | 6.93 | 0.91 | 0.96 | | S5 | 7.66 | 0.25 | 2.16 | | S6 | 7.53 | 0.24 | 1.54 | | S7 | 7.39 | 0.25 | 2.89 | | S8 | 6.78 | 0.25 | 3.03 | | S9 | 7.60 | 0.90 | 1.51 | | S10 | 7.49 | 0.74 | 1.56 | | S11 | 7.35 | 1.44 | 2.24 | | S12 | 6.99 | 0.31 | 1.63 | | S13 | 7.85 | 0.59 | 0.82 | | S14 | 7.23 | 0.25 | 0.02 | | S15 | 7.22 | 0.67 | 1.11 | | S16 | 7.26 | 0.25 | 2.21 | | S17 | 7.35 | 0.29 | 1.73 | | 均值 | 7.34 | 0.48 | 1.75 |
|
Physical and chemical properties of sediments
|

| 元素 | 地累积指数(Igeo) | 不同污染等级样点个数 | | 最大值 | 最小值 | 均值 | 0级 | 1级 | 2级 | 3级 | 4级 | 5级 | 6级 | 7级 | | V | -0.08 | -2.60 | -1.45 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cr | -0.52 | -2.66 | -1.21 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Mn | 1.98 | -2.71 | -0.40 | 14 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Co | 0.44 | -2.25 | -0.72 | 15 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Ni | 0.82 | -3.67 | -1.14 | 15 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cu | 0.88 | -1.91 | -0.68 | 13 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Zn | 0.62 | -2.97 | -1.25 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | As | 0.96 | -3.52 | -0.96 | 16 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | | Cd | 6.63 | 0.09 | 2.94 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | | Pb | 0.36 | -1.53 | -0.72 | 15 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
|
The geo-accumulation index of heavy metals in surface sediment of the upper reaches of Hanjiang River
|

| 样点 | 单项潜在生态风险系数(Ei) | 综合潜在生态
危害指数(R) | | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | | S1 | 1.12 | 1.58 | 1.16 | 4.26 | 4.83 | 5.13 | 0.53 | 5.29 | 327 | 4.26 | 355.16 | | S2 | 2.83 | 2.03 | 5.92 | 10.16 | 11.77 | 13.85 | 1.06 | 29.18 | 264 | 7.06 | 347.85 | | S3 | 0.60 | 0.48 | 0.85 | 3.03 | 2.38 | 3.55 | 0.42 | 3.84 | 96 | 2.90 | 114.04 | | S4 | 1.13 | 1.57 | 1.36 | 6.52 | 5.01 | 7.55 | 0.79 | 12.52 | 894 | 6.33 | 936.78 | | S5 | 1.74 | 2.09 | 1.62 | 7.61 | 13.23 | 10.26 | 2.31 | 12.36 | 222 | 4.77 | 277.99 | | S6 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.84 | 3.36 | 2.07 | 2.65 | 0.44 | 6.85 | 1266 | 4.27 | 1288.35 | | S7 | 0.91 | 1.22 | 0.97 | 3.68 | 2.23 | 3.14 | 0.58 | 7.27 | 153 | 9.02 | 182.03 | | S8 | 0.95 | 1.29 | 0.87 | 2.67 | 2.08 | 2.37 | 0.55 | 5.60 | 204 | 3.12 | 223.52 | | S9 | 0.49 | 1.53 | 1.49 | 5.83 | 4.24 | 6.08 | 0.76 | 7.72 | 4455 | 9.65 | 4492.81 | | S10 | 0.78 | 1.12 | 0.82 | 3.38 | 2.11 | 2.64 | 0.43 | 6.21 | 126 | 4.68 | 148.16 | | S11 | 1.09 | 1.48 | 1.49 | 4.95 | 5.19 | 5.65 | 0.77 | 10.67 | 447 | 3.87 | 482.14 | | S12 | 1.86 | 1.75 | 1.52 | 5.83 | 4.95 | 6.70 | 0.92 | 11.31 | 591 | 5.55 | 631.39 | | S13 | 1.26 | 1.34 | 1.17 | 5.38 | 4.03 | 4.94 | 0.73 | 10.46 | 990 | 5.28 | 1024.59 | | S14 | 0.68 | 0.70 | 0.23 | 1.58 | 0.59 | 1.99 | 0.47 | 1.31 | 408 | 2.60 | 418.14 | | S15 | 0.99 | 1.33 | 1.04 | 4.84 | 3.73 | 4.64 | 0.67 | 8.86 | 741 | 3.54 | 770.66 | | S16 | 1.07 | 1.11 | 0.86 | 4.38 | 1.92 | 3.15 | 0.19 | 7.36 | 48 | 2.75 | 70.80 | | S17 | 2.29 | 1.75 | 1.52 | 7.27 | 3.27 | 7.76 | 0.62 | 9.59 | 108 | 3.99 | 146.06 | | 均值 | 1.22 | 1.37 | 1.40 | 4.98 | 4.33 | 5.42 | 0.72 | 9.20 | 667 | 4.92 | 700.62 |
|
Potential ecological risk coefficient of heavy metals in surface sediments in the upper reaches of Hanjiang River
|

| 元素 | V | Cr | Mn | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | As | Cd | Pb | | V | 1 | | | | | | | | | | | Cr | 0.748** | 1 | | | | | | | | | | Mn | 0.773** | 0.609** | 1 | | | | | | | | | Co | 0.829** | 0.854** | 0.811** | 1 | | | | | | | | Ni | 0.669** | 0.793** | 0.717** | 0.824** | 1 | | | | | | | Cu | 0.828** | 0.831** | 0.849** | 0.964** | 0.900** | 1 | | | | | | Zn | 0.455 | 0.693** | 0.352 | 0.605* | 0.875** | 0.686** | 1 | | | | | As | 0.810** | 0.705** | 0.950** | 0.888** | 0.770** | 0.885** | 0.458 | 1 | | | | Cd | -0.321 | 0.080 | -0.015 | 0.096 | -0.028 | 0.032 | 0.019 | -0.042 | 1 | | | Pb | 0.105 | 0.409 | 0.375 | 0.423 | 0.281 | 0.368 | 0.229 | 0.389 | 0.581* | 1 |
|
Pearson correlation coefficient between heavy metal content and physical and chemical properties of sediments
|

| 成分 | 初始特征值 | 提取载荷平方和 | | 总计 | 方差/% | 累积/% | 总计 | 方差/% | 累积/% | | 1 | 6.484 | 64.841 | 64.841 | 6.484 | 64.841 | 64.841 | | 2 | 1.635 | 16.347 | 81.188 | 1.635 | 16.347 | 81.188 | | 3 | 0.939 | 9.390 | 90.578 | | | | | 4 | 0.357 | 3.569 | 94.147 | | | | | 5 | 0.334 | 3.339 | 97.486 | | | | | 6 | 0.105 | 1.051 | 98.536 | | | | | 7 | 0.077 | 0.773 | 99.310 | | | | | 8 | 0.051 | 0.512 | 99.822 | | | | | 9 | 0.013 | 0.126 | 99.948 | | | | | 10 | 0.005 | 0.052 | 100.000 | | | |
|
Principal component analysis of heavy metals in sediments
|

| 重金属 | 成分 | | 主成分1 | 主成分2 | | V | 0.848 | -0.378 | | Cr | 0.881 | 0.071 | | Mn | 0.864 | -0.041 | | Co | 0.962 | 0.052 | | Ni | 0.912 | -0.055 | | Cu | 0.980 | -0.016 | | Zn | 0.706 | 0.013 | | As | 0.919 | -0.054 | | Cd | 0.019 | 0.930 | | Pb | 0.424 | 0.782 |
|
Initial factor load matrix of heavy metals in sediments
|
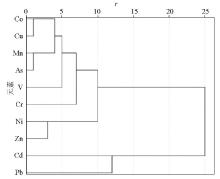
|
Tree diagram of systematic cluster analysis of heavy metals
|
| [1] |
宋力, 黄民生. 底泥中持久性有毒物质研究现状与展望[J]. 华东师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 37(1):73-86.
|
| [1] |
Song L, Huang M S. Research status and prospect of persistent toxic substances in sediment[J]. Journal of East China Normal University:Natural Science, 2011, 37(1):73-86.
|
| [2] |
开晓莉. 清水河重金属与有机氯农药的环境行为及健康风险研究[D]. 银川: 宁夏大学, 2021.
|
| [2] |
Kai X L. Study on environmental behavior and health risk of heavy metals and organochlorine pesticides in Qing-shui River[D]. Yinchuan: Ningxia University, 2021.
|
| [3] |
于霞, 安艳玲, 吴起鑫. 赤水河流域表层沉积物重金属的污染特征及生态风险评价[J]. 环境科学学报, 2015, 35 (5):1400-1407.
|
| [3] |
Yu X, An Y L, Wu Q X. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Chishui River Basin[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2015, 35 (5):1400-1407.
|
| [4] |
王国光, 刘巧灵, 冯丽娟, 等. 黄海、东海及其邻近海域沉积物中的典型持久性有机污染物[J]. 中国科学:化学, 2017, 47 (11):1284-1297.
|
| [4] |
Wang G G, Liu Q L, Feng L J, et al. Typical persistent organic pollutants in sediments of the Yellow Sea,the East China Sea and their adjacent sea areas[J]. Chinese Science:Chemistry, 2017, 47 (11):1284-1297.
|
| [5] |
Pitacco V, Mistri M, Ferrari C R, et al. Heavy metals OCPs,PAHs, and PCDD/Fs contamination in surface sediments of a coastal lagoon(Valli di Comacchio,NW Adriatic,Italy):Long term trend (2002-2013) and effect on benthic community[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2018, 135 (OCT.):1221-1229.

|
| [6] |
Duarte-Restrepo E, Noguera-Oviedo K, Butryn D. et al. Spatial distribution of pesticides,organochlorine compounds,PBDEs,and metals in surface marine sediments from Cartagena Bay,Colombia[J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28:14632-14653.
|
| [7] |
El-Alfy M A, Hasballah A F, Abd El-Hamid H T. et al. Toxicity assessment of heavy metals and organochlorine pesticides in freshwater and marine environments,Rosetta area,Egypt using multiple approaches[J]. Sustain Environ. Res.2019, 29:19.
|
| [8] |
Kronvang B, Laubel A, Larsen S E, et al. Pesticides and heavy metals in Danish streambed sediment[J]. Hydrobiologia, 2003, 494 (1-3):93-101.

|
| [9] |
张桂斋. 两类持久性有机污染物和重金属在南四湖食物链中的分布和生物积累[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2014.
|
| [9] |
Zhang G Z. Distribution and bioaccumulation of two kinds of persistent organic pollutants and heavy metals in the food chain of Nansi Lake[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2014.
|
| [10] |
卫亚宁. 柘林湾养殖底泥中毒性污染物的生态风险及生物毒性评价[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2017.
|
| [10] |
Wei Y N. Ecological risk and biological toxicity assessment of toxic pollutants from aquaculture sediment in Zhelin Bay[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2017.
|
| [11] |
曹源, 仇雁翎, 杨晓红, 等. 南太湖区域表层沉积物中有机氯化合物及重金属污染现状[J]. 湖泊科学, 2011, 23 (4):561-567.
|
| [11] |
Cao Y, Qiu Y L, Yang X H, et al. Pollution status of organochlorine compounds and heavy metals in surface sediments of South Taihu Lake area[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2011, 23 (4):561-567.

|
| [12] |
水利部长江水利委员会. 2016年长江流域及西南诸河水资源公报[M]. 武汉: 长江出版社, 2017.
|
| [12] |
Changjiang Water Resources Commission of the Ministry of Water Resources. 2016 Yangtze River Basin and southwest rivers resources bulletin[M]. Wuhan: Changjiang Publishing House,2017.
|
| [13] |
周琴, 曹夏飞. 汉江流域水利现代化建设问题探讨[J]. 人民长江, 2013, 44 (24):79-83.
|
| [13] |
Zhou Q, Cao X F. Discussion on water conservancy modernization construction in Hanjiang River Basin[J]. People's Changjiang, 2013, 44 (24):79-83.
|
| [14] |
李欢娟, 李会霞, 史兴民. 西安市主要湖泊表层沉积物重金属污染及生态风险评估[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33 (2):122-126.
|
| [14] |
Li H J, Li H X, Shi X M, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals and ecological risk assessment for the surface sediments of the lakes in Xi'an[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(2):122-126.
|
| [15] |
魏复盛. 中国土壤元素背景值(第2版)[M]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990:247-251.
|
| [15] |
Wei F S. Background values of soil elements in China (2nd Edition)[M]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 1990:247-251.
|
| [16] |
Hakanson L. An econological risk index for aquatic pollution control:A sedimentological approach[J]. Water Research, 1980, 14 (8):975-1001.

|
| [17] |
张玉玺, 孙继朝, 向小平, 等. 阳宗海表层沉积物中的重金属生态风险评估[J]. 水资源保护, 2012, 28 (5):19-24.
|
| [17] |
Zhang Y X, Sun J Z, Xiang X P, et al. Ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in surface sediments of Yangzonghai sea[J]. Water Resources Protection, 2012, 28 (5):19-24.
|
| [18] |
李向阳, 吴疆, 刘洪强. 鄂东南5种森林土壤重金属含量及污染评价[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报, 2019, 39 (10):102-108.
|
| [18] |
Li X Y, Wu J, Liu H Q. Content and pollution assessment of heavy metals in five forest soils in Southeastern Hubei[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2019, 39 (10):102-108.
|
| [19] |
马建华, 韩昌序, 姜玉玲. 潜在生态风险指数法应用中的一些问题[J]. 地理研究, 2020, 39 (6):1233-1241.
|
| [19] |
Ma J H, Han C X, Jiang Y L. Some problems in the application of potential ecological risk index[J]. Geographical Research, 2020, 39 (6):1233-1241.
|
| [20] |
Wang S H, Wang W W, Chen J Y, et al. Geochemical baselineestablishment and pollution source determination of heavy metalsin lake sediments:A case study in Lihu Lake,China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 657:978-986.

|
| [21] |
Pan L, Ma J, Hu Y, et al. Assessment of levels,potential ecological risk,an human health risk of heavy metals in the soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province,China[J]. Environment Science & Pollution Research, 2016, 23 (19):1-11.
|
| [22] |
Karim Z, Qureshi B A, Mumtaz M. Geochemical baseline determination and pollution assessment of heavy metals in urban soils of Kara-chi,Pakistan[J]. Ecological Indicate, 2015, 48:358-364.
|
| [23] |
冯乾伟, 王兵, 马先杰, 等. 黔西北典型铅锌矿区土壤重金属污染特征及其来源分析[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2020, 39 (4):863-870.
|
| [23] |
Feng Q W, Wang B, Ma X J, et al. Pollution characteristics and source analysis of heavy metals in soils of typical lead-zinc mining areas in Northwest Guizhou[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy,Petrology and Geochemistry, 2020, 39 (4):863-870.
|
| [24] |
宋凤敏, 岳晓丽, 刘智峰, 等. 汉江上游水体表层沉积物重金属污染特征评价[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2020, 39(7):1576-1584.
|
| [24] |
Song F M, Yue X L, Liu Z F, et al. Evaluation on heavy metal pollution characteristics of surface sediments in the upper reaches of Hanjiang River[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 2020, 39(7):1576-1584.
|
| [25] |
彭清辉, 罗琳, 张嘉超, 等. 涟水及其支流沉积物重金属污染特征及风险评价[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2021, 44 (S2):316-324.
|
| [25] |
Peng Q H, Luo L, Zhang J C, et al. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Lianshui and its tributaries[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2021, 44 (S2):316-324.

|
| [26] |
周旭, 吕建树. 山东省广饶县土壤重金属来源、分布及生态风险[J]. 地理研究, 2019, 38(2):414-426.
|
| [26] |
Zhou X, Lyu J S. Source, distribution and ecological risk of heavy metals in soil of Guangrao County,Shandong Province[J]. Geographical Research, 2019, 38(2):414-426.
|
| [27] |
余贵芬, 蒋新, 孙磊, 等. 有机物质对土壤镉有效性的影响研究综述[J]. 生态学, 2002, 22(5):682-688.
|
| [27] |
Yu G F, Jiang X, Sun L, et al. A review for effect of organic substances on the availability of cadmium in soils[J]. Acta EcologicaSinica, 2002, 22(5):682-688.
|
| [1] |
WAN Tai-Ping, ZHANG Li, LIU Han-Liang. Regional geochemical characteristics and metallogenic prospect area prediction of strategic mineral antimony in the Eerguna block, Heilongjiang Province, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1179-1188. |
| [2] |
FAN Hai-Yin, SONG Rui-Rui, YU Lin-Song, TENG Yong-Bo, WAN Fang, ZHANG Xiu-Wen, LI Sheng-Yu, ZHAO Chuang. Heavy metal pollution and health risk assessment of groundwater in a typical chemical industry park in northwestern Shandong, China[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 2023, 47(5): 1326-1335. |
|
|
|
|

